Teeth are an essential part of our daily lives. They help us chew food, speak clearly, and give us a bright smile. However, when our teeth take longer than usual to grow, it can be a cause for concern. Delayed tooth growth is a common issue that affects both children and adults, and it can be caused by a variety of factors.
Understanding tooth development is key to understanding why teeth may take longer to grow. Teeth develop in stages, and any disruption during these stages can lead to delayed tooth growth. Factors such as genetics, nutrition, and oral hygiene can all play a role in tooth development. Additionally, age can also affect tooth growth, with some teeth taking longer to emerge as we get older.
If you’re wondering why your teeth are taking longer to grow, it’s essential to seek medical attention to determine the underlying cause. In some cases, delayed tooth growth may be a sign of a more serious condition. However, in most cases, it’s a natural part of the tooth development process. In this article, we’ll explore the factors affecting tooth growth, the role of age in tooth development, and when to seek medical attention.
Key Takeaways
- Tooth development occurs in stages and can be disrupted by various factors such as genetics, nutrition, and oral hygiene.
- Age can also play a role in tooth growth, with some teeth taking longer to emerge as we get older.
- It’s important to seek medical attention if you’re concerned about delayed tooth growth, as it may be a sign of a more serious condition.
Understanding Tooth Development
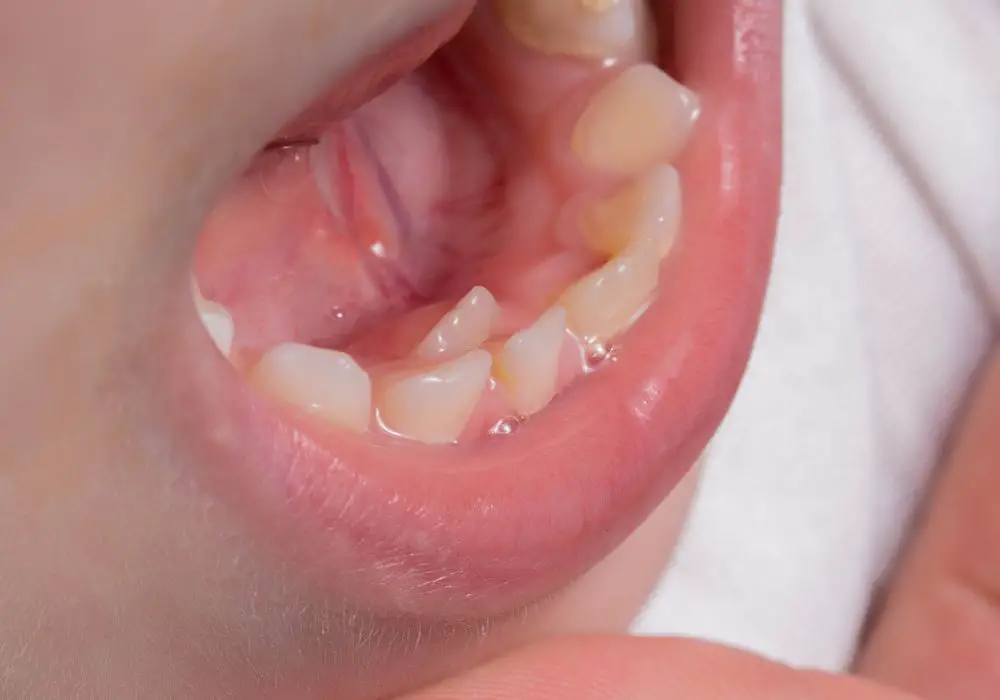
Tooth development is a complex process that begins before birth and continues throughout childhood and adolescence. Understanding the stages of tooth eruption can help you better understand why your teeth may be taking longer to grow.
The Stages of Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption occurs in several stages, which can vary from person to person. The following are the typical stages of tooth eruption:
- Primary Teeth: Primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, usually begin to erupt around six months of age. The first teeth to erupt are usually the lower central incisors, followed by the upper central incisors.
- Permanent Teeth: Permanent teeth begin to erupt around age six, starting with the first molars and lower central incisors. By age 21, all 32 permanent teeth should be present.
- Wisdom Teeth: Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, usually begin to erupt between ages 17 and 25. However, not everyone develops wisdom teeth, and some people may only develop one or two.
It’s important to note that the timing of tooth eruption can vary widely from person to person. Some people may experience delayed tooth eruption, while others may have teeth erupt earlier than expected.
Factors that can affect tooth eruption include genetics, nutrition, and overall health. If you are concerned about the timing of your tooth eruption, it’s important to speak with your dentist or orthodontist for an evaluation.
By understanding the stages of tooth eruption and the factors that can affect it, you can better understand why your teeth may be taking longer to grow. With proper dental care and regular check-ups, you can ensure that your teeth develop properly and stay healthy for years to come.
Factors Affecting Tooth Growth
Genetic Factors
Genetics play a significant role in determining when and how teeth grow. Some children may experience delayed tooth eruption due to genetic factors. In some cases, children may have inherited genes that cause their teeth to develop at a slower rate. For example, a child may have inherited a gene that causes their teeth to grow in later than usual. Alternatively, a child may have inherited a gene that causes their teeth to grow in abnormally.
Nutritional Factors
Nutrition is also an important factor in tooth growth. Children who do not receive adequate nutrition may experience delayed tooth eruption or abnormal tooth development. Nutritional deficiencies, such as a lack of calcium or vitamin D, can affect tooth growth and development.
Health Conditions
Certain health conditions can also affect tooth growth. For example, children with hypothyroidism may experience delayed tooth eruption. Other health conditions, such as cleft lip and palate, can also affect tooth development. Additionally, children who have undergone radiation therapy to the head or neck may experience delayed tooth eruption or abnormal tooth development.
It is important to note that while genetic factors, nutritional factors, and health conditions can affect tooth growth, most children will have their teeth develop normally. If you have concerns about your child’s tooth development, it is best to consult with a dentist or pediatrician.
The Role of Age in Tooth Growth

Tooth growth is a complex process that is influenced by various factors, including genetics, nutrition, and overall health. Age is also an important factor that affects tooth growth. In this section, we will explore the role of age in tooth growth and the changes that occur in our teeth as we age.
Baby Teeth
Baby teeth, also known as primary teeth, begin to form in the fetus around the sixth week of pregnancy. They usually start to emerge through the gums between six months and one year of age. By the age of three, most children have a full set of 20 baby teeth.
Permanent Teeth
Permanent teeth, also known as secondary teeth, begin to form in the jawbone during childhood. The first permanent teeth, the molars, usually erupt around the age of six. By the age of 12 or 13, most children have all their permanent teeth except for the wisdom teeth, which may not emerge until the late teens or early twenties.
Tooth Growth and Age
Tooth growth is a gradual process that occurs over many years. The rate of tooth growth varies depending on the individual and their age. During childhood, teeth grow and develop at a faster rate than during adulthood. As we age, the rate of tooth growth slows down, and our teeth become more susceptible to wear and tear.
Changes in Tooth Structure
As we age, our teeth undergo various changes in structure that can affect their appearance and function. The enamel, the hard outer layer of the tooth, can become thinner and more prone to cracking and chipping. The dentin, the softer layer beneath the enamel, can become darker and more yellow in color. The pulp, the soft tissue inside the tooth, can also become smaller and less sensitive.
In conclusion, age plays a significant role in tooth growth and development. Understanding the changes that occur in our teeth as we age can help us take better care of our oral health and maintain a healthy, beautiful smile for years to come.
When to Seek Medical Attention

If you or your child are experiencing delayed tooth eruption or absence of teeth, it is important to seek medical attention. Here are some reasons to consider:
Delayed Tooth Eruption
Delayed tooth eruption is when a tooth takes longer than usual to emerge from the gums. This can be a sign of an underlying medical condition, such as hypothyroidism or Down syndrome. If you or your child experiences delayed tooth eruption, you should consult a dentist or doctor.
Absence of Teeth
Absence of teeth, or tooth agenesis, is when a person is missing one or more teeth that never developed. This can be a genetic condition or a result of an underlying medical condition, such as cleft palate. If you or your child has missing teeth, you should consult a dentist or doctor.
In some cases, a dental implant or bridge may be recommended to replace missing teeth. Your dentist or doctor can help you determine the best course of action for your individual situation.
Remember, it is important to seek medical attention if you or your child are experiencing delayed tooth eruption or absence of teeth. Early intervention can help prevent further complications and ensure proper dental health.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take for teeth to grow back after tooth extraction?
The time it takes for teeth to grow back after tooth extraction varies from person to person. Generally, it takes about 6 to 8 weeks for the gum tissue to heal. Once the gum tissue has healed, it can take several months for the new tooth to grow back.
How long does it take for a tooth to grow back for a 6 year old?
For a 6 year old, it can take about 6 years for all of their permanent teeth to grow in. However, the timing varies from child to child.
7 year old two front teeth not coming
It is not uncommon for the two front teeth to take longer to grow in than the other teeth. However, if the teeth have not grown in after a certain amount of time, it is best to consult with a dentist.
When should I worry about permanent teeth not coming in?
If a permanent tooth has not grown in by the age of 13, it is best to consult with a dentist. Additionally, if there are any concerns about the growth and development of teeth, it is best to consult with a dentist.
How long does it take for a canine tooth to grow back?
It can take several months for a canine tooth to grow back after it has been lost or extracted. The timing varies from person to person.
Teeth not coming out for 7 year old
It is not uncommon for teeth to take longer to grow in for some children. However, if there are any concerns about the growth and development of teeth, it is best to consult with a dentist.