Are you curious about the teeth of African elephants? These majestic creatures have a unique set of teeth that are well-suited to their herbivorous diet. In fact, elephants have some of the most interesting teeth in the animal kingdom.
African elephants have a total of 26 teeth, which include 12 molars, 12 premolars, and two tusks. The molars and premolars are used for grinding and chewing tough plant material, while the tusks are used for a variety of purposes, such as digging for water, stripping bark from trees, and even defending against predators. Interestingly, some elephants are born without tusks due to a genetic mutation.
Understanding the teeth of African elephants is important for their conservation. By studying the wear and tear on their teeth, researchers can estimate the age of individual elephants and track the health of populations. Additionally, the ivory from elephant tusks has unfortunately led to poaching, which has had devastating effects on elephant populations. It’s important to continue learning about these incredible animals and finding ways to protect them.
Overview of African Elephant Teeth
African elephants are known for their large size and long, curved tusks. But what about their teeth? Elephants have a unique set of teeth that are adapted to their herbivorous diet and long lifespan. Here’s what you need to know about African elephant teeth:
- African elephants have 26 teeth in total, with 12 molars and 12 premolars in the back of their mouth, and two large tusks in the front.
- The molars and premolars are used for grinding and chewing tough vegetation, while the tusks are used for defense, digging, and manipulating objects.
- Elephant teeth are constantly growing and being worn down throughout their lifetime, with new teeth replacing old ones as they wear out.
- Unlike humans, who have teeth that grow from the top and bottom of the mouth, elephant teeth grow from the back and move forward.
The structure and shape of elephant teeth are adapted to the types of vegetation that they eat. African elephants have sloping teeth with a diamond-shaped profile, which is suited for grinding tough grasses, trees, shrubs, and bark. The enamel on their teeth is also thicker than that of other herbivores, which helps to protect their teeth from wear and tear.
In addition to their molars and tusks, African elephants also have a set of incisors at the front of their mouth, which are used for grasping and tearing vegetation. These incisors are not visible from the outside of the elephant’s mouth, but they are important for their feeding habits.
Overall, African elephant teeth are a fascinating adaptation to their herbivorous lifestyle and long lifespan. Understanding the structure and function of their teeth can help us to better appreciate these magnificent animals and the unique challenges they face in the wild.
Tusk Teeth of African Elephants
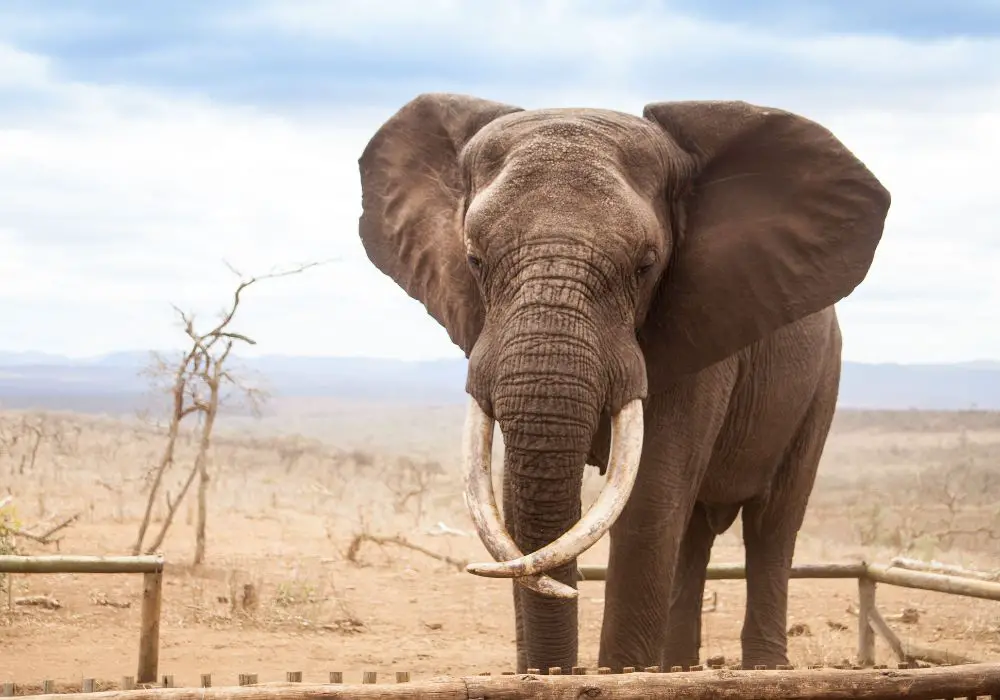

African elephants are known for their impressive tusks, which are modified incisors that grow continuously throughout their lives. These tusks are a defining feature of the African elephant and can grow up to 3 meters in length and weigh up to 100 kilograms.
The tusks of African elephants are composed of dentin, a hard, dense, bony tissue, and enamel, the hardest substance in the body. The inner portion of the tusk is called the pulp cavity, which contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue.
African elephants use their tusks for a variety of purposes, including foraging for food, digging for water, and defending themselves against predators. They also use their tusks for social interactions, such as greeting and communicating with other elephants.
Unfortunately, elephants are often targeted by poachers for their ivory tusks, which has led to a significant decline in their population. As a result, conservation efforts have been put in place to protect these majestic animals and preserve their habitat.
In summary, the tusks of African elephants are modified incisors made of dentin and enamel that grow continuously throughout their lives. They are used for a variety of purposes and are a defining feature of these magnificent animals.
Molar Teeth of African Elephants
African elephants have a unique set of teeth that are shaped differently than any other animal. They have a total of 26 teeth, including 12 molars. The molar teeth of African elephants are diamond-shaped with ridges that are adapted to their diet of grasses, trees, shrubs, and bark.
The molars of African elephants are different from those of Asian elephants. African elephants have sloping teeth, which is why they are called “loxodont.” The sloping teeth help African elephants to grind down tough vegetation. The molars of Asian elephants, on the other hand, have a compressed diamond-shaped lamella profile.
The molars of African elephants are also unique because they are replaced six times throughout their lifetime. The first set of molars emerges when the elephant is about two years old, and the last set emerges when the elephant is about 30 years old. The molars are replaced because they wear down from the constant grinding of tough vegetation.
In addition to their unique shape, the molars of African elephants are also incredibly large. They can weigh up to 5 pounds each and are about the size of a brick. The molars are also covered in a thick layer of enamel, which helps to protect them from wear and tear.
Overall, the molar teeth of African elephants are perfectly adapted to their diet and lifestyle. They are strong, durable, and designed to grind down tough vegetation.
Development and Growth of Elephant Teeth
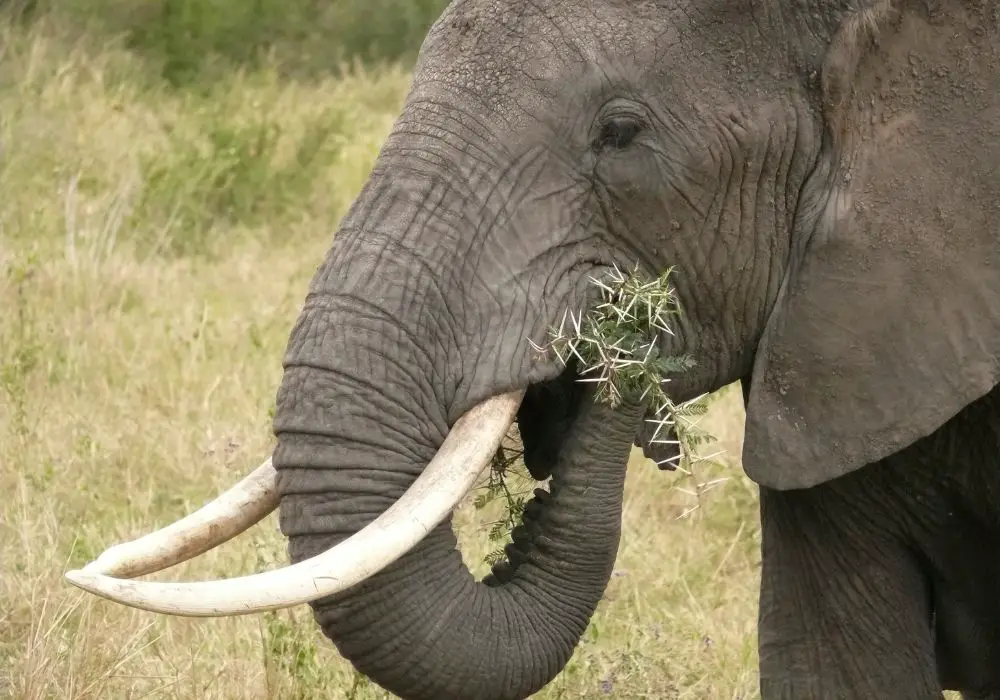

Elephant dentition is unique and fascinating. Unlike most animals, where teeth are produced from the top and bottom of the mouth, elephant teeth are developed from the back and push forward.
African elephants have 26 teeth in total, 12 in the upper jaw and 14 in the lower jaw. They have six sets of molars in their lifetime, with each set weighing around 5 kg and measuring up to 30 cm in length. As a tooth wears out through relentless grinding, another pushes forward to replace it.
Elephant teeth continue to grow throughout their lives, and the tusks are the most prominent teeth. Tusks are modified elongated incisors made of ivory, and they have the same three components as human teeth. Tusks are enormous, and they are way bigger than what is visible to the human eye, as one-third of them are embedded deep into the elephant’s head.
The growth rate of elephant teeth is impressive. It is estimated that an African elephant’s first set of molars erupt at around six months of age, and by the age of two, all six sets of molars will have come through. By the age of 15, an elephant’s molars will have worn down to the point where they are useless for grinding food, and the elephant will eventually die of starvation.
In conclusion, the development and growth of elephant teeth is a unique and fascinating process. The continuous growth of teeth throughout their lives is essential for their survival, and it is an important aspect of their biology that sets them apart from other animals.
Function and Use of Teeth in African Elephants
African elephants have unique teeth that are adapted to their specific diet and lifestyle. Their teeth are important tools that allow them to efficiently gather and process their food. Here is a breakdown of the different types of teeth that African elephants have and their functions:
Incisors
African elephants have four incisors, two on the top and two on the bottom. These incisors are elongated and form the tusks that are so iconic to elephants. The tusks are used for a variety of purposes, including defense, digging for food and water, and stripping bark from trees. The tusks are also used for social interactions, such as sparring with other elephants during mating season.
Cheek Teeth
African elephants have 24 cheek teeth, 12 on the top and 12 on the bottom. These teeth are used for grinding and chewing food. Unlike other herbivores, African elephants chew their food with a forward and backward motion rather than a sideways motion. This unique chewing motion allows them to efficiently break down tough vegetation, such as tree bark and roots.
Tooth Replacement
African elephants have a unique system for replacing their teeth. As their teeth wear down from constant use, new teeth grow in from the back of their mouths and push the old teeth forward. Eventually, the old teeth fall out and are replaced by the new teeth. This process continues throughout their lifetime, allowing them to maintain their ability to efficiently gather and process their food.
In summary, African elephants have unique teeth that are adapted to their specific diet and lifestyle. Their tusks are important tools for defense, digging, and social interactions, while their cheek teeth are used for grinding and chewing food. Their tooth replacement system allows them to maintain their ability to gather and process food throughout their lifetime.
Health and Care of African Elephant Teeth

As an elephant ages, its teeth will wear down and eventually fall out. This can lead to a variety of health problems, including malnutrition, weight loss, and even death. It is important to take good care of an African elephant’s teeth to ensure they remain healthy and strong.
Here are some tips for maintaining the health of an African elephant’s teeth:
- Regular check-ups: Elephants should have their teeth checked regularly by a veterinarian to ensure they are healthy and properly aligned.
- Proper diet: Elephants need a diet that is high in fiber to help keep their teeth healthy. This can include hay, grass, and other vegetation.
- Dental care: Elephants may require dental care, such as filing or extraction, if their teeth become damaged or infected.
- Enrichment activities: Providing enrichment activities, such as toys or puzzle feeders, can help keep an elephant’s teeth healthy by encouraging them to chew and grind their food.
- Water: Elephants need access to clean water to help keep their teeth healthy and prevent dehydration.
By taking good care of an African elephant’s teeth, you can help ensure they remain healthy and strong throughout their life.
Impact of Diet on African Elephant Teeth
African elephants have unique teeth that are adapted to their herbivorous diet. Their teeth are constantly growing and being worn down due to their diet of tough vegetation. The diet of elephants has a significant impact on the structure and function of their teeth.
The cheek teeth of elephants are known as molars and premolars. These teeth are used to grind and crush the tough vegetation that elephants consume. African elephants have four molars and up to six premolars on each side of their mouth. Their molars can weigh up to 5 kg each and measure up to 30 cm in length.
The shape and size of elephant teeth are adapted to their diet. Elephants that consume a diet of softer vegetation have flatter molars, while elephants that consume a diet of tougher vegetation have more ridged molars. The ridges on their molars help to break down the tough vegetation.
Elephants also have a unique chewing motion that helps them to break down vegetation. Unlike other herbivores that chew in a sideways motion, elephants chew their food with a forward and backward motion. This motion helps them to break down the tough vegetation and extract as many nutrients as possible.
In conclusion, the diet of African elephants has a significant impact on the structure and function of their teeth. Their teeth are adapted to their herbivorous diet and are constantly growing and being worn down due to their consumption of tough vegetation. The shape and size of elephant teeth are adapted to their diet, with elephants that consume a diet of tougher vegetation having more ridged molars.
African Elephant Teeth and Age Estimation
African elephants have a unique dental formula, which is I 1/0 C 0/0 PM 3/3 M 3/3. This means that they have a total of 24 teeth, including 12 molars and 6 incisors in each jaw. The tusks, which are elongated incisors, are also present in both males and females.
The teeth of African elephants are constantly growing and being replaced throughout their lives. This process of tooth replacement can be used to estimate the age of an elephant. However, identifying the age of an elephant based on their teeth can be challenging, as the size, shape, and position of each tooth change throughout their life.
Several methods have been developed to estimate the age of African elephants based on their teeth. One such method involves measuring the thickness of the mandible and the width of the ascending ramus. Another method involves studying the progression of molars throughout an elephant’s life.
It is important to accurately estimate the age of African elephants, as it can help with conservation efforts and management of elephant populations. The escalation of poaching in recent years has further emphasized the importance of accurately determining the age of elephant carcasses found in the wild.
Overall, the teeth of African elephants play a crucial role in age estimation and management of elephant populations. Understanding the unique dental formula and tooth replacement process of African elephants can aid in their conservation and protection.
Threats to African Elephant Teeth

African elephants have unique teeth that are essential for their survival. Unfortunately, these teeth are under threat from various factors. Here are some of the threats to African elephant teeth:
Poaching for Ivory
African elephants have two long, curved teeth, called tusks, which are made of ivory. The tusks are used for defense, digging, and foraging. However, ivory is highly valued in many cultures, and there is a high demand for it in the illegal wildlife trade. This has led to a significant decline in the African elephant population over the years. Poachers often kill elephants for their tusks, leaving them with missing or broken teeth that can affect their ability to forage and survive.
Habitat Loss and Fragmentation
African elephants require large areas of land to roam and forage. However, human activities such as logging, mining, and agriculture have led to habitat loss and fragmentation, making it difficult for elephants to find enough food and water. Elephants often resort to eating bark and roots, which can damage their teeth and lead to dental problems.
Climate Change
Climate change is affecting the availability and quality of food and water sources for African elephants. Droughts and floods can cause vegetation to die, reducing the amount of food available for elephants. This can lead to malnutrition, which can affect the health of their teeth and overall well-being.
Human-Elephant Conflict
As human populations expand, they encroach on elephant habitats, leading to conflicts between humans and elephants. Elephants may raid crops and destroy property, leading to retaliation from humans. This can lead to injuries and deaths of elephants, including damage to their teeth.
In conclusion, the threats to African elephant teeth are many and varied. It is essential to protect these magnificent animals and their habitats to ensure their survival.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of teeth that African elephants have?
African elephants have two types of teeth: molars and tusks. They have 24 molars and 2 tusks. The tusks are modified upper incisors that grow continuously throughout their life.
What is the purpose of African elephant teeth?
African elephant teeth are used for grinding and chewing their food. They eat a lot of vegetation, so their molars are designed to crush and grind tough plant material. Their tusks are used for various purposes, including digging for water, stripping bark, and as weapons for defense.
How many teeth do African elephants have?
African elephants have a total of 26 teeth. They have 12 molars and 12 premolars, which are located towards the back of their mouth. They also have two tusks, which are located in their upper jaw.
Do African elephants have molars?
Yes, African elephants have molars. In fact, they have 24 molars and 12 premolars. Their molars are flat and wide, and they are designed to grind and crush tough plant material.
What is the lifespan of African elephant teeth?
African elephant teeth can last for up to 10 years. However, their tusks can last for much longer, up to 70 years. As they age, their teeth wear down and eventually fall out, which can make it difficult for them to eat and survive in the wild.
How do African elephants use their teeth in the wild?
African elephants use their teeth for a variety of purposes in the wild. They use their tusks for digging for water, stripping bark, and as weapons for defense. Their molars are used for grinding and chewing tough plant material, which makes up the majority of their diet.