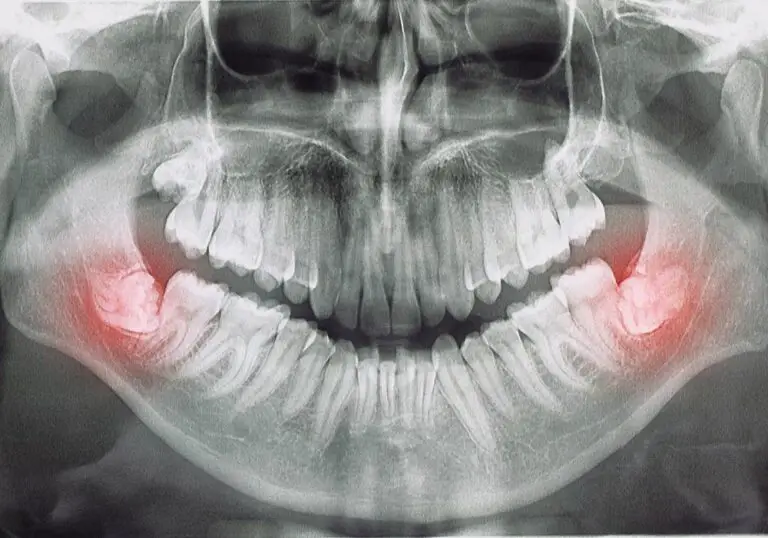
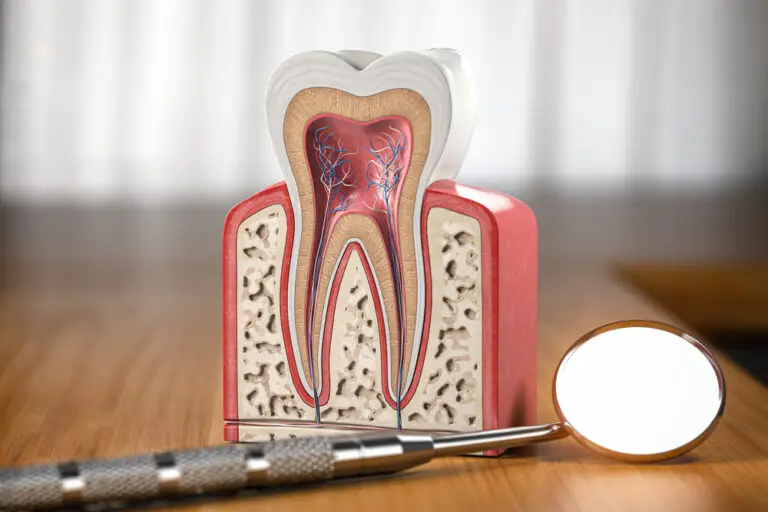
Are teeth considered bones or tissue? This is a common question that many people ask. The answer is that teeth are not bones, but they are made up of different types of tissue. Teeth are actually a unique part of the body that have their own distinct composition.
Teeth are made up of four different types of tissue: dentin, enamel, cementum, and pulp. The pulp is the innermost part of a tooth and contains blood vessels and nerves. Enamel is the hard outer layer made of minerals like calcium phosphate, and it is actually harder than bones. Although teeth resemble bones, they are quite different. Bones can regenerate, but teeth cannot.
It’s important to understand the difference between teeth and bones because they have different functions in the body. Bones provide support and structure, while teeth are used for biting, chewing, and grinding food. Knowing the composition of teeth can also help you take better care of them. By brushing and flossing regularly, you can help keep your teeth healthy and strong.
Teeth: Bone or Tissue?
If you’re wondering whether teeth are considered bones or tissues, you’re not alone. While they share some similarities, teeth are actually quite different from bones and tissues. In this section, we’ll explore what teeth are made of and why they’re not considered bones or tissues.
Understanding Teeth
Teeth are complex structures that play a critical role in our ability to eat, speak, and smile. They’re made up of four main components: enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp. Enamel is the hard, outer layer of the tooth that protects it from damage. Dentin is the layer beneath the enamel and is softer than enamel but still quite hard. Cementum is a layer that covers the root of the tooth and helps anchor it in the jawbone. Finally, the pulp is the soft tissue at the center of the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels.
Defining Bone
Bone is a type of connective tissue that provides support and protection for the body. It’s made up of cells, collagen fibers, and minerals like calcium and phosphorus. Bones are constantly being broken down and rebuilt throughout our lives, which is why they’re able to adapt to changes in our bodies.
Defining Tissue
Tissue is a broad term that refers to any group of cells that work together to perform a specific function. There are four main types of tissue in the body: epithelial, connective, muscle, and nervous. Each type of tissue has a unique structure and function, and they all work together to keep our bodies functioning properly.
In summary, while teeth do contain some of the same minerals as bones, they are not considered bones or tissues. Teeth are a unique type of structure that serve a specific purpose in the body, and they require their own category. Understanding the differences between teeth, bones, and tissues can help you better appreciate the complexity and diversity of the human body.
Composition of Teeth
When it comes to the question of whether teeth are bones or not, the answer is no. Teeth are not bones, but they are considered to be a type of hard tissue. Teeth are composed of four different types of tissue: enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp.
Enamel
Enamel is the hard, outermost layer of the tooth. It is the hardest substance in the human body and is made up of mostly calcium phosphate. Enamel is translucent and ranges in color from white to light yellow. It is responsible for protecting the inner layers of the tooth from damage caused by chewing, biting, and grinding.
Dentin
Dentin is the softer, yellowish layer of tissue that lies underneath the enamel. It is made up of tiny tubes called dentinal tubules that run from the pulp to the enamel. Dentin is responsible for providing support to the enamel and protecting the pulp from damage.
Pulp
The pulp is the innermost layer of the tooth. It contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. The pulp is surrounded by dentin, which is covered by the enamel. The pulp is responsible for providing nutrients and oxygen to the tooth and for transmitting sensory information such as pressure, temperature, and pain.
In conclusion, teeth are not bones but are a type of hard tissue made up of enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp. Understanding the composition of teeth is important for maintaining good oral health and preventing dental problems.
Composition of Bones
Bones are complex structures that are made up of different components. Understanding the composition of bones can help you better understand how they function and why they are important for your overall health.
Cortical Bone
Cortical bone, also known as compact bone, is the hard outer layer of bone. It is dense and strong, and it provides support and protection for the body. Cortical bone is made up of tightly packed layers of bone cells called osteons. These osteons are arranged in a circular pattern around a central canal that contains blood vessels and nerves.
Cortical bone is made up of about 80% mineralized bone matrix, which is a combination of calcium and phosphate. The remaining 20% is made up of collagen, water, and other proteins. This combination of minerals and collagen gives cortical bone its strength and flexibility.
Cancellous Bone
Cancellous bone, also known as spongy bone, is the softer, more porous inner layer of bone. It is less dense than cortical bone, but it is still strong and resilient. Cancellous bone is made up of a network of tiny, interconnected trabeculae, which are like small beams or struts that provide support and help distribute weight.
Cancellous bone is made up of about 20% mineralized bone matrix, which is a combination of calcium and phosphate. The remaining 80% is made up of collagen, water, and other proteins. This combination of minerals and collagen gives cancellous bone its strength and flexibility.
In summary, bones are complex structures that are made up of different components, including cortical bone and cancellous bone. Understanding the composition of bones can help you better understand how they function and why they are important for your overall health.
Differences Between Teeth and Bones
When it comes to teeth and bones, there are some similarities, but there are also some key differences. In this section, we will explore two of the major differences between teeth and bones.
Regeneration Capabilities
One of the main differences between teeth and bones is their ability to regenerate. Bones have the ability to repair themselves when they are damaged. For example, if you break a bone, it will heal itself over time. This is because bones have living cells that can create new bone tissue.
Teeth, on the other hand, do not have the ability to regenerate. If you damage a tooth, it will not heal itself. This is because teeth do not have living cells. Once a tooth is damaged, it will remain damaged unless it is repaired by a dentist.
Structural Differences
Another major difference between teeth and bones is their structure. While both teeth and bones are hard and white, they are made up of different materials. Bones are made up of living cells, collagen, and calcium phosphate. Teeth, on the other hand, are made up of enamel, dentin, and pulp.
Enamel is the hard, white outer layer of the tooth. It is the hardest substance in the human body and protects the tooth from damage. Dentin is the layer beneath the enamel and is made up of living cells. It is not as hard as enamel, but it is still very strong. The pulp is the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains blood vessels and nerves.
In summary, while teeth and bones may look similar, they are actually quite different. Bones have the ability to regenerate and are made up of living cells, collagen, and calcium phosphate. Teeth, on the other hand, cannot regenerate and are made up of enamel, dentin, and pulp.
Similarities Between Teeth and Bones
Teeth and bones share some similarities in terms of their material composition, function, and structure.
Material Composition
Both teeth and bones are composed of calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals, which give them their hardness and strength. The enamel, which is the outermost layer of teeth, is the hardest substance in the body, even harder than bone. Similarly, bones are made up of a hard outer layer called the cortex and a spongy inner layer called the trabecular bone. Both teeth and bones also contain collagen, a protein that provides flexibility and support.
Function and Structure
Teeth and bones have different functions, but they share some similarities in their structure. Bones provide support for the body and protect internal organs, while teeth are used for biting and chewing food. Both teeth and bones are living tissues that are constantly being remodeled and repaired throughout life. They both have a blood and nerve supply that keeps them healthy and functioning properly.
In terms of structure, both teeth and bones have a similar layered structure. The enamel, which is the outermost layer of teeth, is similar in composition to the cortex of bones. The dentin, which is the layer beneath the enamel, is similar to the trabecular bone. Both teeth and bones also have a central cavity that contains soft tissue, such as nerves and blood vessels.
Overall, while teeth and bones have different functions, they share some similarities in their material composition and structure. Understanding these similarities can help us appreciate the complexity and importance of these vital parts of our body.
Scientific Viewpoints
When it comes to the question of whether teeth are bones or tissues, there are different scientific viewpoints. Here are some of them:
- Teeth are not bones, but they are hard tissues. Teeth are composed of different layers, including enamel, dentin, cementum, and pulp. Enamel is the hardest substance in the body and covers the crown of the tooth. Dentin is a hard tissue that lies beneath the enamel and makes up most of the tooth. Cementum is a hard tissue that covers the root of the tooth. Pulp is the soft tissue that contains nerves and blood vessels. While teeth share some similarities with bones, such as being hard and containing calcium, they are not bones because they do not contain collagen, which is the main protein in bones.
- Teeth are specialized bones. Some scientists argue that teeth are specialized bones because they develop from the same type of tissue as bones, called mesenchyme. They also contain many of the same minerals as bones, such as calcium and phosphorus. However, they differ from bones in their structure and function. Bones are designed to provide support, protect organs, and produce blood cells, while teeth are mainly used for biting, chewing, and grinding food.
- Teeth are unique structures that cannot be classified as either bones or tissues. Some scientists believe that teeth are unique structures that cannot be classified as either bones or tissues. They argue that teeth have a complex structure that is different from both bones and tissues. For example, teeth have a hard outer layer (enamel) that is not found in any other tissue, and they have a pulp chamber that contains nerves and blood vessels. Teeth also have a unique shape and arrangement that allows them to perform specific functions.
In summary, the scientific viewpoints on whether teeth are bones or tissues are varied. While some scientists consider teeth to be hard tissues that are distinct from bones, others argue that teeth are specialized bones or unique structures that cannot be classified as either bones or tissues.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are teeth made of?
Teeth are made up of different layers. The outer layer is called enamel, which is the hardest substance in the human body. The next layer is called dentin, which is a softer, porous material. The innermost layer is called the pulp, which contains nerves and blood vessels.
What are teeth classified as?
Teeth are classified as hard, mineralized structures that are used for biting and chewing food. They are also considered part of the skeletal system.
Why are teeth not bones?
Although teeth are classified as part of the skeletal system, they are not considered bones. This is because bones are made up of living tissue that can repair and grow, while teeth cannot. Additionally, bones have a marrow cavity, while teeth do not.
What are teeth if not bones?
Teeth are considered to be a type of connective tissue. They are made up of specialized cells and proteins that give them their unique properties.
Are teeth counted in the 206 bones?
No, teeth are not counted in the 206 bones of the human body. This is because teeth are not considered bones, but rather a separate type of structure.
What is human teeth made of?
Human teeth are primarily made up of calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals. They also contain proteins and other organic substances that give them their unique properties.