Wisdom teeth, also known as the third molars, represent the final component of the full set of 32 adult teeth within an individual’s oral cavity. Typically emerging between the ages of 17 and 21, these additional molars serve functions related to chewing and grinding food like the other molars.
According to Sierra Dental, a dentist in Calgary, not everyone experiences the development of wisdom teeth, and those who do may only develop less than four of these teeth. While the growth of wisdom teeth is often unproblematic, there exists the potential for complications when the tooth lacks sufficient space to grow upright in the jaw, leading to a condition known as impacted wisdom teeth.
Identification of Impacted Wisdom Teeth
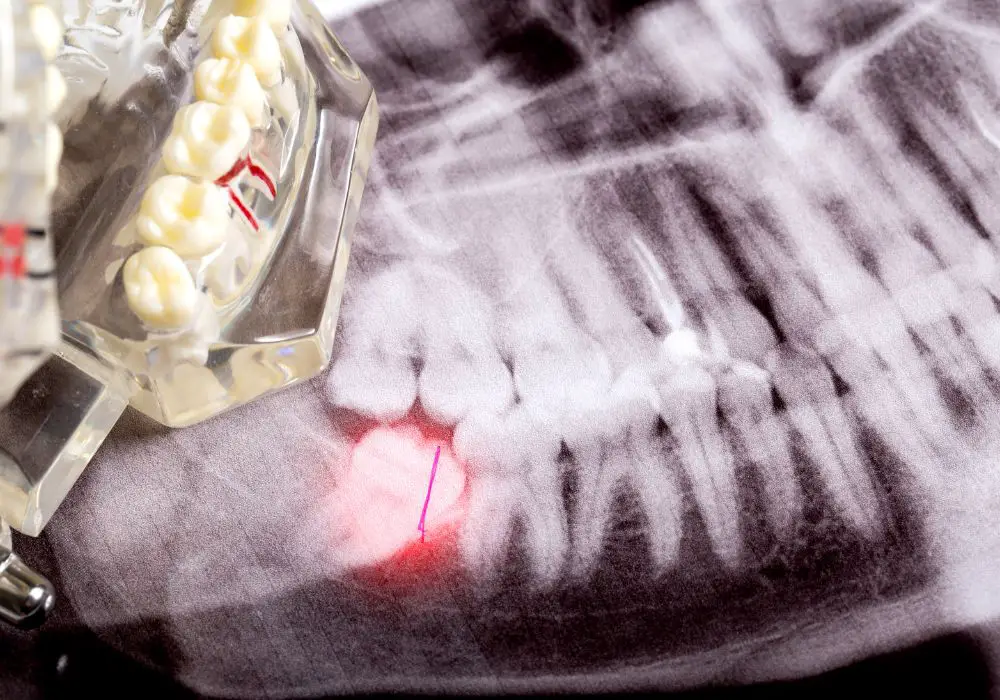
An impacted wisdom tooth is one that encounters restrictions preventing proper growth through the gum. This restriction may result in the tooth failing to erupt upright or remaining within the jaw, causing pain and other various dental complications.
Manifestation of impacted wisdom teeth can take two forms: partial emergence from the gum line, displaying only a portion of the molar crown, or complete submersion beneath the gum tissue. Despite the presentation, both scenarios share similar symptoms, contributing to diverse complications.
Signs and Symptoms of Impacted Wisdom Teeth
Although impacted wisdom teeth may not exhibit immediate signs, they are susceptible to infections, dental damage, and a range of complications if left unattended. Observable symptoms include:
- Reddish and swollen gums
- Gum pain
- Bad breath
- Tooth decay
- Bleeding gums
- Limitation in mouth opening
In addition to these symptoms, individuals with impacted wisdom teeth may experience an unpleasant taste and bad breath, primarily attributable to suboptimal oral hygiene. The implications of impacted wisdom teeth can significantly impact oral health. It is crucial to promptly identify and address this condition to prevent further deterioration. How, then, can you identify this condition quickly before it deteriorates?
- Growth Angulation Abnormalities
The growth angle of wisdom teeth is a key factor in determining impaction. In an ideal scenario, wisdom teeth emerge upright behind the second molar and align perfectly with other teeth; however, challenges may arise due to limited space in a small jaw. Dentists assess the angle at which these teeth grow, identifying mesial and distal impactions, horizontal angulation, and vertical growth anomalies.
A wisdom tooth could develop toward the second molar or to the back of the mouth. These are referred to as mesial and distal impaction, respectively. It’s also possible for the tooth to be angled horizontally, applying pressure against the second molar. The vertical growth anomalies occur when the wisdom tooth seems to develop like a normal tooth but remains lodged inside the gum. If a wisdom tooth shows any of these features, it is impacted.
- Dental Damage
Impacted wisdom teeth can cause significant damage to other teeth. Whichever angle a wisdom tooth grows, it applies considerable pressure on the second molar and its roots, which, in most cases, makes the teeth shift. As you would expect, this action has an adverse effect on other teeth and can only be addressed by realigning the shifted teeth.
- Pain in the Jaw
Jaw pain is a prevalent symptom of most oral conditions, and an impacted wisdom tooth is no different. As the wisdom teeth continue to apply pressure on the second molar and potentially cause a shift, this unnatural movement can cause tenderness in the jaw.
At this point, it’s normal to start feeling severe pains and swelling, making it extremely difficult to perform basic actions, including chewing, opening the jaw, and, sometimes, breathing. Impacted wisdom teeth on the upper jaw can also result in sinus complications.
- Cysts Formation
Cysts are small tissue pockets filled with fluid, pus, or other substances. These are primarily a result of duct blockages, inflammatory problems, or infections, to mention a few.
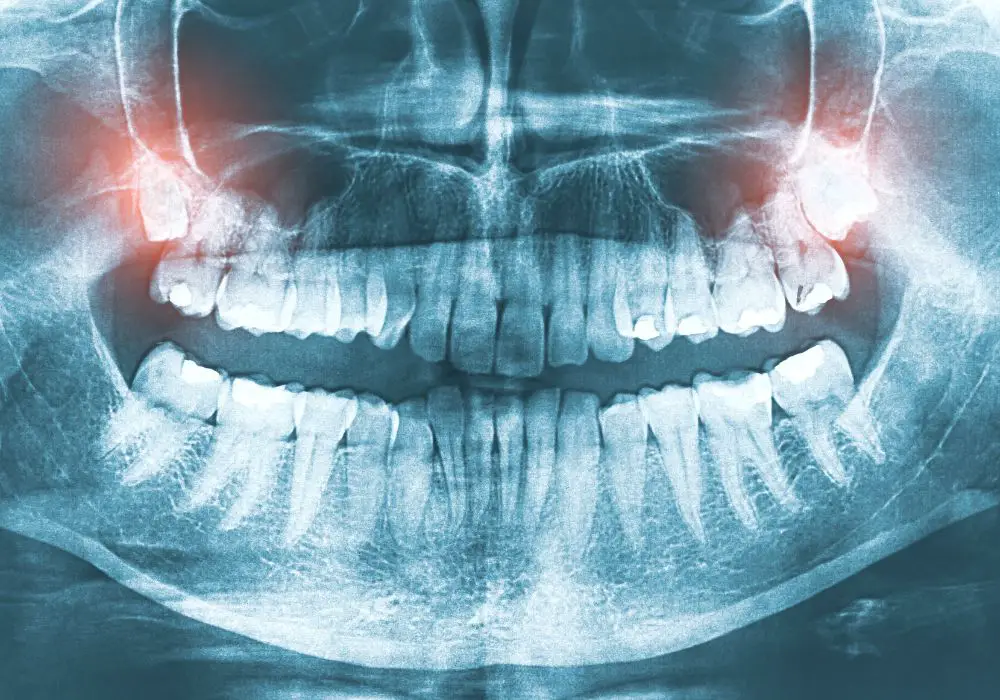
Impacted wisdom teeth can result in a dentigerous cyst, which develops when fluid gathers between the tooth’s crown and the enamel’s outer layer. In this case, the wisdom tooth is covered entirely by bone or soft tissue, which dentists recommend removing. It is also possible, albeit rare, for a noncancerous tumor to develop.
- Tooth Decay
Unlike other complications, only the impacted wisdom tooth is susceptible to decay because it is more difficult to clean. Typically, the location of molars makes them harder to clean and more vulnerable to abscesses, cavities, and other oral hygiene problems. Wisdom teeth also follow suit, with more potential to trap food particles and germs easily between themselves and the gum.
- Gum Disease
Gum diseases and infections are a result of tooth decay. As a result of the challenges associated with cleaning wisdom teeth, pericoronitis has also become a prevalent symptom of impaction.
Pericoronitis is a severe inflammatory condition that is characterized by swollen and infected soft tissues around the crown of a partially grown tooth. The inflammation results from the activities of microorganisms trapped beneath the gum flap.
Management and Prevention
Addressing symptoms and complications associated with impacted wisdom teeth involves various remedies prescribed by dentists. Over-the-counter pain relievers, antibacterial mouthwash, or a saltwater mixture can alleviate soreness, infection, and inflammation.
While it is impossible to prevent the impaction of wisdom teeth, adopting healthy habits, including bi-annual oral checkups and improved dental hygiene, can help identify and address issues early.
Extraction Considerations
When impacted wisdom teeth have the potential to cause disease, extraction becomes a recognized management option. The American Association of Oral and Maxillofacial Surgeons (AAOMS) recommends regular oral screenings for monitoring wisdom teeth and identifying complications proactively, especially in asymptomatic cases.
Regular screenings provide valuable insights into characteristics such as growth angle and pressure exerted on adjacent teeth, facilitating informed decisions regarding extraction when necessary.