Have you ever wondered what keeps your teeth alive? Teeth are often seen as hard, lifeless objects, but in reality, they are complex structures that require a combination of hard and soft tissues to thrive. The innermost layer of a tooth, known as the dental pulp, is what keeps the tooth alive.
The dental pulp contains nerves, blood vessels, specialized cells, and connective tissues that provide nutrients for the tooth. This rich source of nerves and blood vessels keeps the tooth healthy and functional. When these blood vessels and nerves die, the tooth dies as well.
There are many ways in which the dental pulp can become injured, including trauma, decay, and infection. It’s important to take care of your teeth and seek dental care if you experience any pain or discomfort, as this could be a sign of a dead tooth. Understanding what keeps your teeth alive is key to maintaining good oral health and preventing tooth loss.
The Anatomy of a Tooth
When it comes to understanding what keeps a tooth alive, it’s important to start with the basic anatomy of a tooth. There are three main parts of a tooth: enamel, dentin, and pulp.
Enamel
Enamel is the hard, outer layer of a tooth. It is the hardest substance in the human body, even stronger than bone. Enamel is made up of minerals, primarily calcium phosphate. It protects the tooth from wear and tear, as well as from acids and bacteria that can cause decay.
Dentin
Dentin is the layer of tooth structure that lies beneath the enamel. It is softer than enamel but still quite hard. Dentin is made up of tiny tubes called dentinal tubules that contain nerve endings. When the enamel is worn away or damaged, the dentin can become exposed, causing sensitivity and pain.
Pulp
The pulp is the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains blood vessels, nerves, and connective tissue. It is located in the center of the tooth, beneath the dentin. The pulp is responsible for supplying the tooth with nutrients and oxygen, as well as for transmitting sensory information to the brain. If the pulp becomes infected or inflamed, it can cause severe pain and may require a root canal procedure to remove it.
Understanding the anatomy of a tooth is crucial for maintaining good oral health. By taking care of your enamel, dentin, and pulp, you can help keep your teeth healthy and strong for a lifetime.
Blood Supply and Nerves
To keep your teeth alive, they need a constant supply of blood and a network of nerves that provide sensation. The blood vessels and nerves that supply the teeth are dependent on the blood vessels and nerves that supply the upper and lower jaws. As the maxilla is part of the midface and the mandible part of the lower face, respectively, they have separate neurovasculature.
Blood Vessels
The blood supply to the teeth comes from the branches of the external carotid artery, which is a major blood vessel in the head and neck. The external carotid artery gives off several branches that supply blood to the maxilla and mandible. These branches include the:
- Maxillary artery: supplies blood to the upper teeth and surrounding tissues.
- Mandibular artery: supplies blood to the lower teeth and surrounding tissues.
The veins that drain blood from the teeth and surrounding tissues drain into the internal and external jugular veins.
Nerves
The nerves that supply the teeth come from the branches of six cranial nerves, namely:
- Trigeminal nerve: supplies sensation to the upper and lower teeth and surrounding tissues.
- Facial nerve: supplies sensation to the teeth and tissues in the front part of the mouth.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve: supplies sensation to the back part of the mouth.
- Vagus nerve: supplies sensation to the back part of the mouth and throat.
- Hypoglossal nerve: supplies sensation to the tongue.
These nerves enter the teeth through small openings in the roots called apical foramina. The nerves provide the teeth with sensation, allowing you to feel hot and cold temperatures, pressure, and pain.
In summary, the blood vessels and nerves that supply the teeth are essential for keeping them alive and healthy. The blood vessels bring oxygen and nutrients to the teeth, while the nerves provide sensation. If you experience any problems with your teeth, such as pain or sensitivity, it is important to see a dentist or dental professional to determine the cause and receive appropriate treatment.
The Role of Saliva

Saliva is an essential part of maintaining a healthy mouth and keeping your teeth alive. It is a clear liquid that is produced by the salivary glands in your mouth. Saliva has a range of functions that are vital to your oral health, including:
- Lubricating the mouth and moistening food to make it easier to swallow
- Neutralizing acids produced by bacteria in the mouth that can cause tooth decay
- Providing minerals, such as calcium and phosphate, that help to remineralize and strengthen tooth enamel
- Fighting germs in the mouth and preventing bad breath
- Helping to maintain the pH balance in the mouth
One of the most important functions of saliva is its ability to neutralize acids in the mouth. When you eat foods that contain sugar, bacteria in your mouth produce acid as they break down the sugar. This acid can erode tooth enamel and lead to cavities. Saliva helps to neutralize this acid by washing it away and providing minerals that can help to repair and strengthen the enamel.
Saliva also plays a role in protecting your teeth from bacteria and other harmful substances in the mouth. It contains antibodies and enzymes that can help to fight off germs and prevent infections. Additionally, saliva helps to maintain the pH balance in the mouth, which is important for preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
Overall, saliva is a crucial component of maintaining good oral health and keeping your teeth alive. By keeping your mouth moist, neutralizing acids, and fighting germs, saliva helps to prevent tooth decay and gum disease. So, make sure to keep your mouth hydrated by drinking plenty of water and maintaining good oral hygiene practices to keep your saliva flowing and your teeth healthy.
Nutrition and Tooth Health
Maintaining a balanced and nutritious diet is essential for keeping your teeth healthy and strong. Your teeth require a variety of nutrients to remain healthy and function properly. In this section, we will discuss the importance of calcium, vitamins, and minerals for maintaining the health of your teeth.
Importance of Calcium
Calcium is a vital mineral that is essential for building and maintaining strong teeth and bones. Your teeth are made up of a combination of calcium and phosphate, which form a hard mineral called hydroxyapatite. Consuming foods that are rich in calcium, such as dairy products, leafy greens, and almonds, can help to strengthen your teeth and prevent tooth decay.
Vitamins and Minerals
In addition to calcium, your teeth require a variety of vitamins and minerals to remain healthy. Vitamins A, C, and D are particularly important for maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Vitamin A helps to maintain the mucous membranes in your mouth and promotes the healing of gum tissue. Vitamin C is essential for the production of collagen, which is a protein that helps to strengthen your teeth and gums. Vitamin D helps your body to absorb calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for building strong teeth and bones.
Minerals such as phosphorus and magnesium are also important for maintaining the health of your teeth. Phosphorus works together with calcium to build strong teeth and bones, while magnesium helps to regulate the levels of calcium in your body.
To ensure that you are getting the necessary vitamins and minerals for maintaining the health of your teeth, it is important to consume a balanced and varied diet that includes a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and dairy products. Drinking plenty of water can also help to flush away food debris and prevent the buildup of plaque and bacteria in your mouth.
Preventive Care and Maintenance
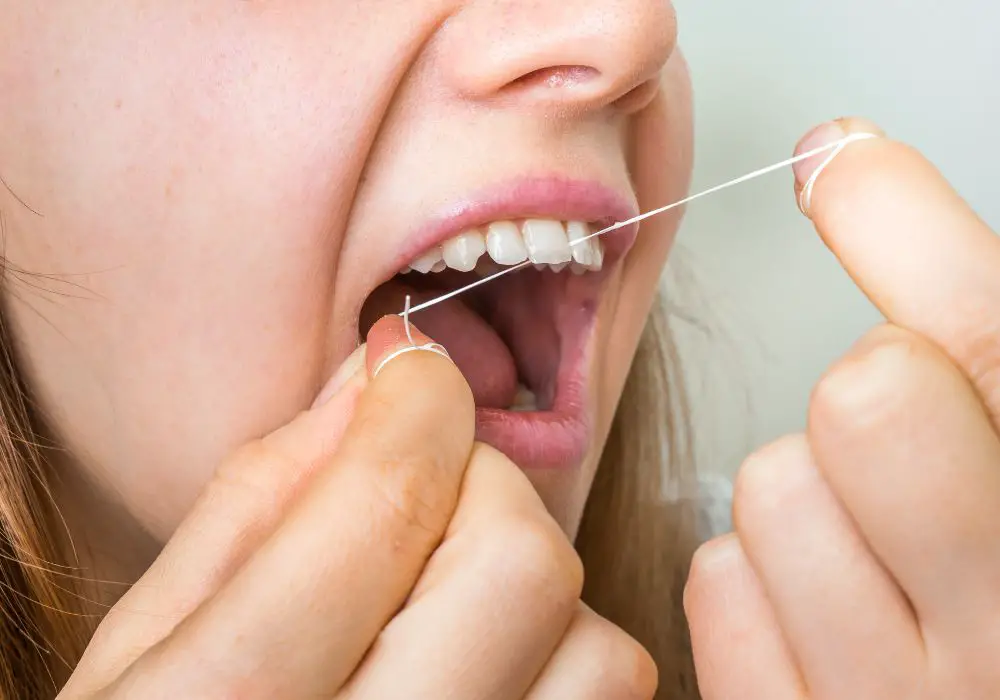
Taking good care of your teeth is essential to keep them alive and healthy. Preventive care and maintenance are crucial in preserving your natural teeth. Here are some tips to help you maintain good oral health:
Regular Brushing
Brushing your teeth twice a day is essential to remove plaque and bacteria that can cause tooth decay and gum disease. Use a fluoride toothpaste and a soft-bristled toothbrush to brush each tooth gently. Make sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. Brush your tongue and the roof of your mouth as well to remove bacteria and freshen your breath.
Flossing
Flossing helps to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth and along the gum line. It is recommended to floss at least once a day. Use about 18 inches of floss and wrap it around your fingers, gently sliding it between your teeth in a back-and-forth motion. Be gentle and avoid snapping the floss into your gums, which can cause bleeding.
Dental Check-ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential to maintain good oral health. Your dentist can detect any problems early on and provide treatment before they become more serious. It is recommended to visit your dentist every six months for a routine check-up and cleaning. During the check-up, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums, take X-rays if necessary, and clean your teeth to remove any plaque and tartar buildup.
In addition to these preventive care measures, there are other things you can do to maintain good oral health. These include:
- Eating a healthy diet that is rich in fruits and vegetables
- Limiting sugary and acidic foods and drinks
- Drinking plenty of water to help rinse away food particles and bacteria
- Using mouthwash to freshen your breath and kill bacteria
By following these preventive care tips, you can help keep your teeth healthy and alive for a lifetime.
Diseases That Can Affect Tooth Vitality
When it comes to maintaining the health of your teeth, it’s not just about brushing and flossing regularly. There are several diseases that can affect the vitality of your teeth, leading to potential tooth loss. In this section, we’ll discuss two common diseases that can affect tooth vitality: tooth decay and gum disease.
Tooth Decay
Tooth decay is a common dental problem caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth. Plaque is a sticky film of bacteria that forms on your teeth and can lead to the breakdown of tooth enamel. When tooth decay is left untreated, it can progress to the inner layers of the tooth, where it can cause an infection and lead to tooth loss.
To prevent tooth decay, it’s important to brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, floss daily, and visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. If you experience tooth pain or sensitivity, it’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible to prevent the decay from spreading.
Gum Disease
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and bone that support your teeth. It’s caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth and can lead to red, swollen, and bleeding gums, as well as tooth loss.
To prevent gum disease, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and using an antiseptic mouthwash. You should also visit your dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings. If you experience any symptoms of gum disease, such as bleeding gums or bad breath, it’s important to see your dentist as soon as possible to prevent the disease from progressing.
In conclusion, tooth decay and gum disease are two common diseases that can affect the vitality of your teeth. By practicing good oral hygiene and visiting your dentist regularly, you can help prevent these diseases and maintain the health of your teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the function of tooth pulp?
Tooth pulp is the soft tissue inside your tooth that contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. Its main function is to provide nourishment to your tooth and keep it alive. The pulp also helps to detect changes in temperature and pressure, which allows you to feel sensations in your teeth.
How can you treat an exposed tooth pulp?
An exposed tooth pulp can be a painful experience. It is important to see your dentist as soon as possible if you suspect that you have an exposed tooth pulp. Treatment may involve a root canal or a dental crown to protect the tooth and prevent further damage.
What are the signs of a dying tooth?
A dying tooth may have several signs, including discoloration, pain, sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, and bad breath. If you notice any of these signs, it is important to see your dentist immediately to determine the cause and receive treatment.
Is it possible to save a dying tooth?
In some cases, it is possible to save a dying tooth. Treatment may involve a root canal or dental crown to protect the tooth and prevent further damage. However, if the damage is too severe, the tooth may need to be extracted.
How long can a tooth stay alive?
A tooth can stay alive for many years if it is properly cared for. Regular dental check-ups, good oral hygiene, and a healthy diet can all help to keep your teeth healthy and alive for a long time.
How can you keep a broken tooth alive?
If you have a broken tooth, it is important to see your dentist as soon as possible. Treatment may involve a dental crown or filling to protect the tooth and prevent further damage. In some cases, a root canal may be necessary to save the tooth.