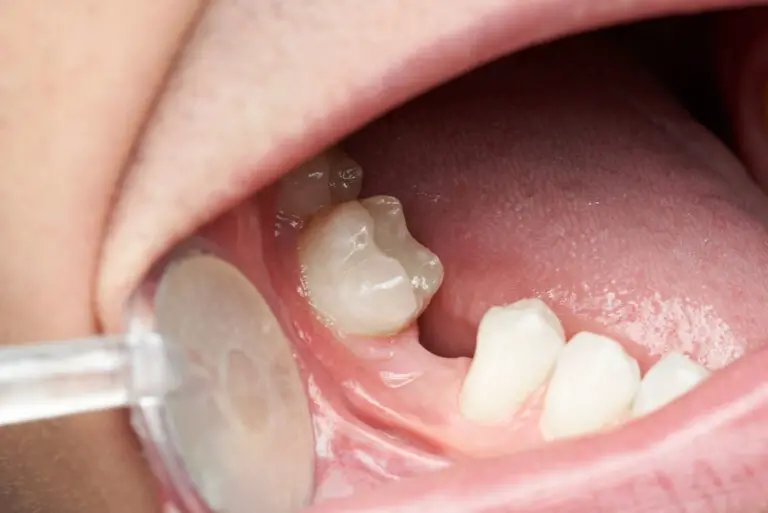
When do babies’ teeth start coming in?
Most babies get their first tooth between 6 and 10 months of age. However, teething times can vary widely among infants:
- Some babies are even born with teeth – these are called natal teeth. But it is rare, affecting only 1 in every 2,000 to 3,000 infants.
- On the other hand, some babies don’t get their first tooth until 12, 14 or even 16 months of age. Delayed teething is still considered normal for some.
- The average age range for the first tooth is between 6 to 10 months. Most full-term healthy babies get their first tooth during this timeframe.
- Premature babies may experience delayed teething, getting their first teeth later than 10 months.
Teething symptoms usually start 3-5 days before the tooth cuts through the gums. Some babies may have symptoms for weeks or months before the tooth comes through.
Most babies have their full set of 20 primary teeth by the time they are 3 years old. The primary teeth fall out as the permanent teeth come in between 6 to 12 years of age.
Can you see baby teeth in the gums?
Yes, you can often see signs of teeth under the gums before they emerge. Keep an eye out for these clues:
White spots
Look for localized whitish spots or bumps along the gums, especially along the bottom front gums. The whitish color comes from calcium deposits collecting under the gums where teeth are beginning to develop. These white bumps indicate teeth growing under the surface.
Blue or gray spots
In babies with darker skin tones, emerging teeth can cause bluish or grayish discoloration instead of white. Feel along the gumline – you may feel a hard ridge or lump beneath a dark spot.
Swollen gums
Gums may swell and become tender in areas where new teeth are erupting. Press gently and you may feel a hard mass under swollen gum tissue. This suggests an incoming tooth.
Protrusions
Subtle protrusions or raised whitish ridges along the gumline can indicate teeth pushing up from below. You may see hints of white along the protrusion as the tooth edges closer.
Lower central incisors first
Check the lower front gums early on, as the lower central incisors are typically the first teeth to come in. You’ll likely see signs here first.
Then upper central incisors
After the lower front teeth, uppers ones follow. Look for protrusions along the upper gumline near the lips. Swelling here indicates emerging central incisors.
What does teething look like on gums?

Teething gums go through noticeable changes. Here are the visual cues:
- Swollen gums – gums appear puffy and inflamed
- Increased saliva – gums look very wet, shiny
- Flushed gums – some babies get red or ruddy gums
- Raised whitish/bluish bumps – calcium deposits under erupting teeth
- White protrusions – erupting teeth edges poking through
- Uneven bumpy texture – lumps and ridges along gumline
- Redness around protrusions – inflammation where teeth are erupting
- Visible ridges – subtle outlines of teeth under gums
- Elevated blanched line – whitish line along baby’s gumline
- Increased blood flow – gums may appear deeper pink and filled with blood
How can you tell if teething gums are infected?
While swelling, discomfort and inflammation are normal during teething, sometimes it leads to infection requiring medical help. Signs of infected teething gums include:
- Severe crankiness and crying that lasts hours
- Refusing to nurse or take a bottle over several feeds
- Very swollen gum tissue that looks filled with pus
- Bright red gums or dark purple gums
- Gums that bleed excessively with minimal pressure
- Blisters, sores or ulceration on gums
- Pronounced bad breath
- High fever over 102°F (38.9°C)
- Small pimples around mouth and chin
- Dark spots or streaks on gums
- Rubbery or boggy feeling gums
- Loose teeth
- Green or yellow discharge from gums
- Swollen lymph nodes under jaw
These symptoms indicate bacterial or fungal infection of the gums that require prescription antibiotics or antifungal medication. Prompt pediatrician evaluation is needed.
Are lumps on gums always teeth coming in?
Not always. Bumps or lesions on the gums have other causes too:
- Epstein pearls – small cysts on newborn gums
- Thrush – white creamy patches from oral yeast infection
- Mucoceles – harmless cysts on gums
- Canker sores – painful ulcers
- Gemination – fused double tooth
- Natal teeth – teeth present at birth
- Herpes infection – sores or blisters from herpes
- Leukemia – abnormal gum growths
Any odd spots, unusual swelling or lesions on your baby’s gums should be examined. Tell the pediatrician about oral abnormalities at well-child visits. Proper diagnosis determines the appropriate treatment.
When should I call the pediatrician?

Contact your pediatrician promptly if teething is accompanied by:
- Fever over 101°F (38.3°C) that lasts over 24 hours
- Extreme irritability or lethargy
- Reduced eating or drinking over 1-2 days
- Signs of dehydration – reduced wet diapers, sunken eyes
- Gum blisters, sores, lesions
- Bleeding from gums unrelated to eruption
- Facial rash or hives
- Swelling or redness of lips, chin, cheeks
- Loose tooth or teeth
- Bad odor from mouth
These may indicate infection or other dental issues needing the pediatrician’s assessment. Prompt medical care can ease your baby’s symptoms and treat any serious underlying problem.
Conclusion
- Look for white/gray spots and swollen areas to detect emerging teeth.
- Visible ridges, protrusions show teeth moving up under gums.
- Red, purplish gums that bleed or have blisters need examination.
- Lumps could also be harmless cysts – have your pediatrician evaluate.
- Seek prompt medical care if teething is accompanied by facial rashes, gum blisters, or bite issues.
Frequently Asked Questions
How soon before teeth emerge can you see signs on the gums?
You may notice signs of teeth under the gums up to 2-3 months before they erupt through the surface. However, sometimes teeth can move down rapidly and emerge in just a few days. Each baby follows their own teething timeline.
Should I rub medication on my baby’s gums while teething?
Pediatricians often advise against rubbing numbing gels or medications directly onto swollen gums. These products can be harmful if ingested. Use a clean finger or wet gauze pad to gently massage the gums. Icing the gums can provide relief without medication. Consult your pediatrician first before applying anything.
What teeth typically come in after the lower front ones?
The lower central incisors are usually followed by the upper incisors, and then the first molars and canines on the upper and lower jaws. Next the second molars come in. But the eruption sequence can vary in some babies.
How can I differentiate teething pain from other problems?
Teething pain is usually localized to the gums, results in increased biting/chewing behaviors, and is temporary. Ear infections cause separate ear pain. Mouth injuries cause very localized pain. If the discomfort is widespread or causes decreased feeding, see your pediatrician.
Is slight gum bleeding normal with erupting teeth?
A small amount of blood when teeth first puncture through is common. But excessive bleeding or blood in saliva is abnormal and needs medical assessment. Gums should not bleed readily with light pressure. Consistent gum bleeding indicates infection.