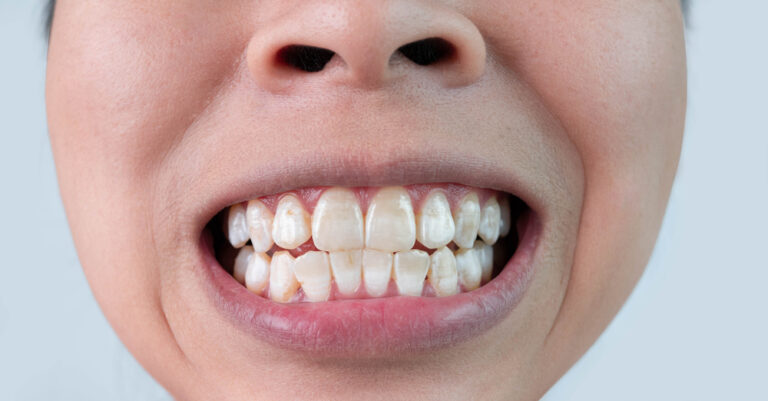
It’s very common for people to occasionally feel like their teeth are loose or wiggly, even when their teeth are perfectly healthy. There are a few potential reasons for this unsettling sensation. Understanding the causes can help put your mind at ease or determine when to seek dental care.
Changes in gum and bone tissue

The most common cause of teeth feeling loose is due to subtle changes in the gum tissue and bone structure surrounding and supporting the teeth.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums caused by a buildup of dental plaque. Symptoms include swollen, reddened gums that bleed easily when brushing or flossing. With gingivitis, plaque bacteria irritate the gum tissue, causing inflammation. The swollen gum tissue can make teeth feel loose and unstable.
Gingivitis is quite common, affecting 60% of adults globally. But it only causes mild looseness, and proper daily brushing and flossing can usually resolve gingivitis. Be sure to promptly treat gingivitis though, as prolonged inflammation can progress to more severe gum disease.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a serious gum infection affecting the gums and bone. When plaque is left to accumulate, toxins from the bacteria start breaking down gum tissue and bone structure. The gums pull away from the teeth, forming pockets that become infected. Bone loss occurs as bacteria spread and inflame the bone surrounding infected teeth.
At this stage, teeth can become loose, painful, and even fall out. Periodontitis also causes persistent bad breath. See a dentist immediately if you suspect periodontitis, as the condition can rapidly deteriorate without treatment.
Normal gum recession
As we age, it’s common for some gum recession to occur even with good oral hygiene. The gums slowly recede or pull away, exposing more of the tooth roots. This natural process leaves teeth feeling slightly looser since less gum tissue surrounds and holds the teeth in place.
Mild gum recession is usually not a major concern. But significant recessions can lead to root sensitivity, cavities, and increased loosening. See your dentist if you notice receding gums to evaluate the cause and treatment options, especially if tooth roots become fully exposed.
Other causes of loose teeth feeling
Aside from gum issues, other factors can also temporarily make teeth feel loose.
Medications
Certain prescription and over-the-counter medications reduce saliva flow, causing dry mouth. Saliva helps stabilize and cushion teeth, so inadequate saliva can make teeth feel loose in their sockets.
Common culprits include antihistamines, decongestants, blood pressure medications, antidepressants, diuretics, and muscle relaxants. Switching medications or dosage times may provide relief. Sugar-free gum or lozenges can also promote saliva flow if dry mouth is bothersome.
Teeth grinding and clenching
Habitually grinding or clenching your teeth puts intense pressure on them that can loosen teeth over time. These behaviors often worsen with stress. The excessive pressure wears down tooth enamel and can fracture teeth. It also overloads the ligaments securing teeth, allowing teeth to shift and feel loose.
See your dentist right away if you suspect teeth grinding. Custom-fitted nightguards are an effective treatment to protect teeth from grinding damage. Other therapies include bite guards, physical therapy, and stress reduction.
Recent dental work
It’s common for a tooth to feel slightly loose after having a filling, crown, or other restoration. The tooth may feel loose as it settles back into place after being worked on. Gentle chewing will allow it to stabilize within a few weeks. Avoid chewing excessively hard foods during this period.
But if it remains continuously loose for more than a month, see your dentist to adjust the restoration. The filling or crown may be too high and need replacing to properly fit your bite.
Ill-fitting dental restorations
Sometimes a crown, bridge, or filling may not fit properly. This prevents the restoration from providing a stable, tight fit. As you chew, the tooth can rock or twist slightly against the defective restoration. Over time, an ill-fitting crown or filling will need to be replaced or adjusted.
When to see a dentist

Schedule an appointment with your dentist promptly if you experience:
- Frequent or long-lasting loose teeth feeling
- Any signs of gum disease like painful, puffy, or bleeding gums
- Loose teeth that disrupt eating or speech
- Suspected grinding or clenching habits
- Pain, swelling, or pus discharge from a loose tooth
- Sudden trauma to the mouth loosening a tooth
The dentist can examine your mouth and diagnose the cause of the looseness. Depending on the condition, your dentist may provide treatment or refer you to a dental specialist. Some diagnostic tools include x-rays, pocket measurements, gum disease evaluation, bite assessment, and checking for cracked teeth.
Leaving loose, painful teeth unchecked could allow serious oral health problems to worsen. Seek prompt care to determine the cause and recommended treatment.
How dentists treat loose teeth
The treatment for loose teeth depends on the diagnosed cause. Your dentist may recommend:
Gum disease treatment
- Professional cleaning below the gumline
- Prescription antimicrobial mouth rinse
- Antibiotics for infection
- Oral hygiene instructions
Nightguard
- Custom-fitted acrylic mouthguard to prevent grinding damage
Replacing defective restorations
- Remove and replace loose crowns, fillings, or veneers
Bite adjustment
- Smoothing high spots on teeth to improve fit
Tooth extraction
- Removing loose teeth that cannot be saved
Bone grafts
- Grafting bone material to reinforce areas with significant bone loss
Splinting
- Connecting loose teeth together with bands or wires to provide stabilization
With appropriate treatment, the bothersome loose feeling generally goes away as the underlying problem is corrected. Practicing good daily oral hygiene and regular dental visits can protect your teeth.
When gum surgery is necessary
For moderate or advanced gum disease, additional procedures beyond a standard cleaning are often needed. Options include:
Flap surgery
- Lifting back the gums to access roots for deep cleaning and removal of diseased tissue
Bone grafts
- Transplanting bone to stimulate bone regeneration in areas of significant bone loss
Gum grafts
- Taking a small amount of gum tissue from the palate and attaching it to areas with receded gums
Guided tissue regeneration
- Placing a small piece of mesh-like material between the tooth and gum to allow bone and tissue re-growth
Soft tissue grafts
- Reinforcing thin gums with grafted tissue from elsewhere in the mouth
These surgeries aim to limit tooth loosening and bone loss caused by gum disease. Though intensive, they are often essential for saving severely loose teeth.
Home remedies for temporary relief

Seeing a dentist for an evaluation is important if you have ongoing loose teeth. But for temporary relief before your appointment, try these home remedies:
- Saltwater rinses – Swish warm salt water around the affected area to reduce inflammation and cleanse the area.
- Massage gums – Gently massage swollen gums with a clean finger to stimulate circulation.
- Over-the-counter pain medicine – Use as directed to relieve any discomfort from loose teeth. Avoid placing pills directly on gums.
- Soft foods – Stick to soft, cool foods that are gentle to chew.
- Bristle toothbrush – Switch to an ultra-soft bristle toothbrush and brush carefully along the gumline.
- Avoid chewing gum – Cut back on gum chewing to limit pressure on loose teeth.
- De-stress – Use relaxing techniques to avoid clenching and grinding habits that can worsen loose teeth.
While home remedies can temporarily help symptoms, be sure to still see a dentist to treat the underlying cause of loose teeth for the best outcome. Loose teeth that are left untreated have a high likelihood of worsening or falling out.
Prevention Tips
Practicing excellent oral hygiene and getting regular professional care are the best ways to prevent loose teeth and maintain your oral health:
- Brush properly twice a day – Position the toothbrush at a 45-degree angle to the gums and brush using short, gentle motions. Brush all inner, outer, and chewing surfaces.
- Floss daily – Use proper technique to remove plaque from between teeth where the toothbrush can’t reach.
- Use antimicrobial mouthwash – Rinse daily to reduce bacteria between cleanings.
- Watch sugary and acidic foods – Limit intake to avoid enamel erosion and plaque buildup.
- Have regular dental cleanings & exams – Get professional care every 6 months to catch problems early.
- Don’t smoke – Smoking worsens gum disease leading to increased tooth loss.
- Get restorations adjusted – Have loose-feeling fillings or crowns promptly adjusted.
- Use nightguards if grinding – Protect teeth from grinding damage at night.
- Treat gum disease – Follow all recommended gum disease treatment to stabilize loose teeth.
Let your dentist know right away if your teeth frequently feel loose. Treating loose teeth in the early stages prevents additional loosening and tooth loss down the road.
FAQ
What does it mean if a tooth is slightly loose but doesn’t hurt?
If a tooth is slightly mobile but not painful, it may be:
- Mild gum disease causing minor inflammation
- Normal gum recession from aging
- Recent dental work still settling
- Grinding habits placing excess pressure on teeth
Slight, painless looseness isn’t always a concern if it doesn’t worsen. Keep up good oral hygiene and mention it at your next dental visit for evaluation. The dentist can monitor for changes. Seek prompt care if looseness increases or becomes painful.
Why do my teeth hurt when they feel loose?
When loose teeth are also painful, it typically indicates:
- Advanced gum disease damaging the bone
- A dental abscess putting pressure on the root and nerve
- Cracked tooth syndrome
- Trauma causing injury to the root, ligaments, or bone
Don’t delay treatment for loose, painful teeth as they signal a significant problem requiring urgent dental care. The pain results from inflammation pressing on the tooth’s nerves.
Can loose teeth tighten back up on their own?
If teeth feel loose due to a temporary issue like recent dental work or medication use, they may tighten up once the condition resolves. With prompt gum disease treatment and avoiding grinding, mildly loose teeth have a chance to stabilize as the tissues heal.
But severely loose teeth with advanced gum disease or bone loss cannot tighten back up on their own. They require stabilization methods like splinting or gum surgery. Extraction is sometimes necessary for very loose teeth without enough bone remaining to save them.
Why do my teeth feel most loose in the morning?
You’re most likely to notice loose teeth in the morning because:
- Saliva flow naturally decreases during sleep, allowing teeth to settle.
- Gum inflammation worsens at night in those with gum disease.
- Grinding and clenching typically occur during sleep.
As you eat, drink, brush your teeth, and saliva flow increases, the looseness should subside. If it persists throughout the day, have your dentist evaluate your gums and bite.
If one tooth feels loose, will I lose other teeth?
Not always. A tooth may feel loose due to issues specific to just that tooth, like:
- Injury causing damage to a single tooth
- Significant decay under a filling
- A defective crown not fitting properly
But if your teeth feel universally loose rather than just one tooth, it likely indicates generalized gum disease, which can progressively damage multiple teeth. See your dentist to determine whether the problem seems localized or widespread.