Have you ever wondered if a tooth needs blood to survive? The answer is yes and no. While a tooth itself does not need blood, the tissues surrounding the tooth rely on a healthy blood supply to maintain their function and keep the tooth healthy.
The tooth itself is made up of different layers, including the enamel, dentin, and pulp. The enamel and dentin are hard, protective layers that cover the tooth and give it its shape. The pulp, on the other hand, is the soft tissue inside the tooth that contains nerves and blood vessels. While the pulp is essential for the development of the tooth, it is not necessary for the tooth to survive once it has fully formed.
However, the tissues surrounding the tooth, such as the gums and jawbone, require a healthy blood supply to maintain their function and support the tooth. Without proper blood flow, these tissues can become infected or damaged, leading to tooth decay, gum disease, and even tooth loss. So while a tooth may not need blood to survive, the health of the surrounding tissues is crucial for maintaining a healthy and functional smile.
The Importance of Blood Supply in Teeth

Role of Blood in Tooth Health
Blood supply is essential for the health and maintenance of teeth. The blood vessels in teeth provide oxygen and nutrients to the tooth pulp, which is the living tissue inside the tooth. Without an adequate blood supply, the tooth may become weak and susceptible to decay and infection. Blood also carries away waste products and helps to remove harmful bacteria that can cause tooth decay.
Blood Vessels in Teeth
The blood vessels in teeth are part of the dental pulp, which is a soft tissue that contains nerves and blood vessels. The dental pulp is located in the center of the tooth and extends from the crown to the tip of the root. The blood vessels in teeth are responsible for supplying nutrients and oxygen to the dental pulp. The blood vessels in teeth are also responsible for removing waste products and harmful bacteria from the dental pulp.
Table: Blood Vessels in Teeth
| Blood Vessels | Function |
|---|---|
| Arteries | Carry oxygenated blood to the tooth |
| Veins | Carry deoxygenated blood away from the tooth |
| Capillaries | Exchange oxygen and nutrients with the dental pulp |
Bullet Points: Role of Blood in Tooth Health
- Blood supply provides oxygen and nutrients to the tooth pulp.
- Blood removes waste products and harmful bacteria from the dental pulp.
- Without adequate blood supply, the tooth may become weak and susceptible to decay and infection.
Bullet Points: Blood Vessels in Teeth
- The dental pulp contains blood vessels that supply nutrients and oxygen to the tooth.
- The blood vessels in teeth remove waste products and harmful bacteria from the dental pulp.
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood to the tooth, while veins carry deoxygenated blood away from the tooth.
How Blood Reaches the Teeth
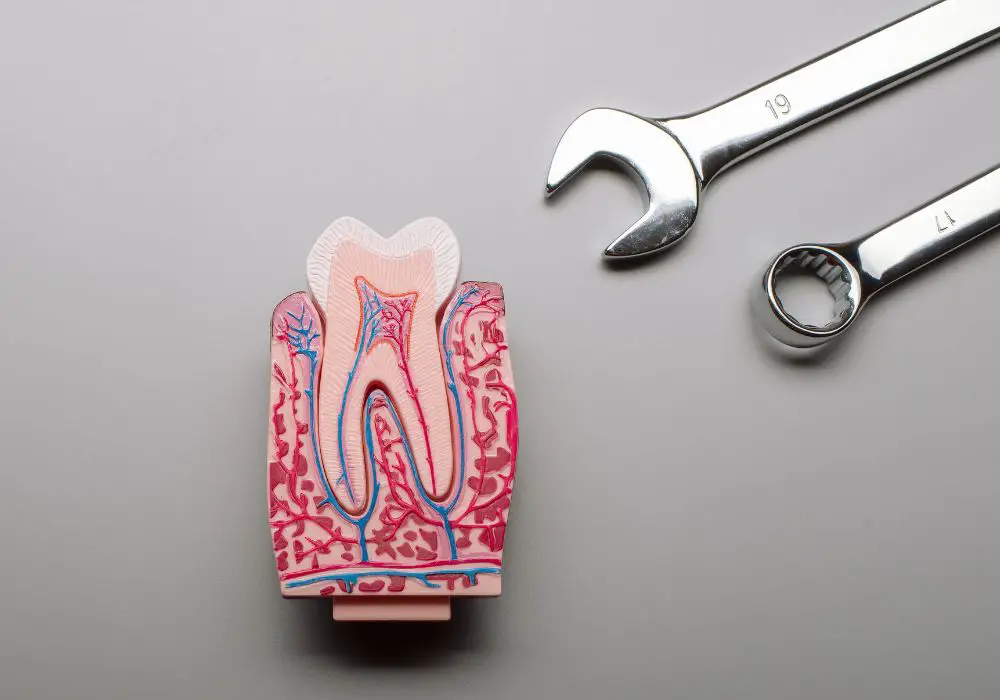
The blood supply to the teeth is essential for their vitality and life. The teeth receive their blood supply through two different pathways: the root canal and the periodontal ligament.
Through the Root Canal
The root canal is a space inside the tooth that contains the dental pulp, which consists of nerves and blood vessels. The blood vessels enter the tooth through the apical foramen, which is located at the tip of the tooth’s root. From there, the blood vessels travel through the root canal and into the pulp chamber, where they supply the dental pulp with nutrients and oxygen.
Via the Periodontal Ligament
The periodontal ligament is a connective tissue that surrounds the tooth and attaches it to the bone. Blood vessels enter the periodontal ligament through the apical foramen and travel along the ligament’s fibers to supply the surrounding tissues with nutrients and oxygen.
The blood supply to the teeth is regulated by the autonomic nervous system, which controls the diameter of the blood vessels. The sympathetic nervous system constricts the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the teeth, while the parasympathetic nervous system dilates the blood vessels, increasing blood flow to the teeth.
In summary, the blood supply to the teeth is crucial for their health and vitality. The teeth receive their blood supply through the root canal and the periodontal ligament, which supply the dental pulp and surrounding tissues with nutrients and oxygen. The autonomic nervous system regulates the blood flow to the teeth, ensuring that they receive the appropriate amount of blood to maintain their health.
Effects of Reduced Blood Flow to Teeth
When blood flow to a tooth is reduced, it can lead to various dental problems. Here are some of the effects of reduced blood flow to teeth:
Tooth Decay and Cavities
When a tooth does not receive enough blood, it can become weakened, making it more susceptible to decay. Tooth decay occurs when bacteria in the mouth produce acids that eat away at the tooth’s enamel. If left untreated, decay can spread to the tooth’s inner layers, including the pulp, which can cause pain and infection.
Cavities are a common result of tooth decay. They are small holes that form in the tooth’s surface and can lead to further decay and infection. Reducing blood flow to a tooth can increase the risk of cavities and other dental problems.
Gum Diseases
Reduced blood flow to the gums can also lead to gum diseases. Gum diseases are caused by bacteria that build up in the mouth and cause inflammation of the gums. When gums are inflamed, they can become red, swollen, and bleed easily.
Gum diseases range from mild gingivitis to more severe periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of gum disease and can be reversed with proper dental care. Periodontitis is a more advanced stage of gum disease and can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
In conclusion, reduced blood flow to teeth can have serious consequences for your dental health. It is important to maintain good oral hygiene and visit your dentist regularly to prevent dental problems.
Restoring Blood Flow to Teeth

If your tooth is experiencing reduced blood flow, it can lead to hypoxia (low oxygen) and tissue death. Fortunately, there are treatments available to restore blood flow to teeth. Here are two common methods:
Root Canal Treatment
Root canal treatment is a procedure that involves removing the infected or inflamed pulp from the tooth’s root canal system. This treatment is necessary when the pulp tissue is damaged, infected, or dead due to a lack of blood flow. During the procedure, the dentist will use specialized tools to remove the damaged pulp, clean the root canal system, and fill it with a biocompatible material. This will help to restore blood flow to the tooth and prevent further infection.
Periodontal Therapy
Periodontal therapy is a treatment that is used to treat gum disease. Gum disease can cause the gums to become inflamed and infected, which can lead to a decreased blood flow to the teeth. Periodontal therapy involves a deep cleaning of the teeth and gums to remove the bacteria and plaque that causes gum disease. This treatment can help to restore blood flow to the teeth and prevent further damage to the gums and teeth.
In addition to these treatments, there are also some things you can do to improve blood flow to your teeth. Here are some tips:
- Maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly
- Eat a healthy diet that is rich in vitamins and minerals
- Avoid smoking and using other tobacco products
- Get regular dental check-ups and cleanings
By following these tips and seeking appropriate treatment, you can help to restore blood flow to your teeth and maintain good oral health.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the function of blood in teeth?
Blood is essential for teeth because it delivers oxygen and nutrients to the tooth’s pulp, which is the innermost part of the tooth. The pulp contains nerves and blood vessels that keep the tooth alive and healthy.
How does blood keep teeth alive?
The blood vessels in the pulp of the tooth provide nourishment and oxygen to the tooth’s cells. This helps the tooth to grow and repair itself. Blood also helps to remove waste products from the tooth’s cells.
What happens when a tooth loses its blood supply?
When a tooth loses its blood supply, it can become infected and die. This can cause pain and swelling. If the tooth is not treated, the infection can spread to other parts of the body.
Can a tooth survive without blood flow?
No, a tooth cannot survive without blood flow. Blood flow is essential to keep the tooth alive and healthy. If the blood flow is cut off, the tooth will die.
What are the consequences of a dead tooth?
A dead tooth can cause pain, swelling, and infection. It can also cause bad breath and discoloration of the tooth. If left untreated, a dead tooth can lead to the loss of the tooth and other health problems.
How can you maintain healthy blood flow in your teeth?
To maintain healthy blood flow in your teeth, you should practice good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day, flossing daily, and visiting your dentist regularly. You should also avoid smoking and limit your intake of sugary foods and drinks.







