Have you ever wondered what happens to your teeth when they get too hot? Maybe you’ve experienced the discomfort of eating or drinking something that’s too hot and felt a sudden sharp pain in your teeth. This sensation is known as tooth sensitivity, and it’s a common problem that affects many people. But what exactly is happening to your teeth when they get too hot?
When your teeth are exposed to extreme temperatures, such as hot or cold foods and drinks, the enamel on the surface of your teeth can expand or contract. This can cause tiny cracks or fissures to form in the enamel, which can expose the underlying dentin layer of your teeth. The dentin layer contains small tubes or canals that lead to the nerve endings in your teeth, which can cause pain or sensitivity when they’re exposed to hot or cold temperatures.
So, what can you do to prevent tooth sensitivity from hot temperatures? There are several things you can try, such as avoiding hot or cold foods and drinks, using a toothpaste designed for sensitive teeth, and practicing good oral hygiene habits. By taking care of your teeth and being mindful of what you eat and drink, you can help prevent tooth sensitivity and keep your teeth healthy and strong.
The Anatomy of Teeth
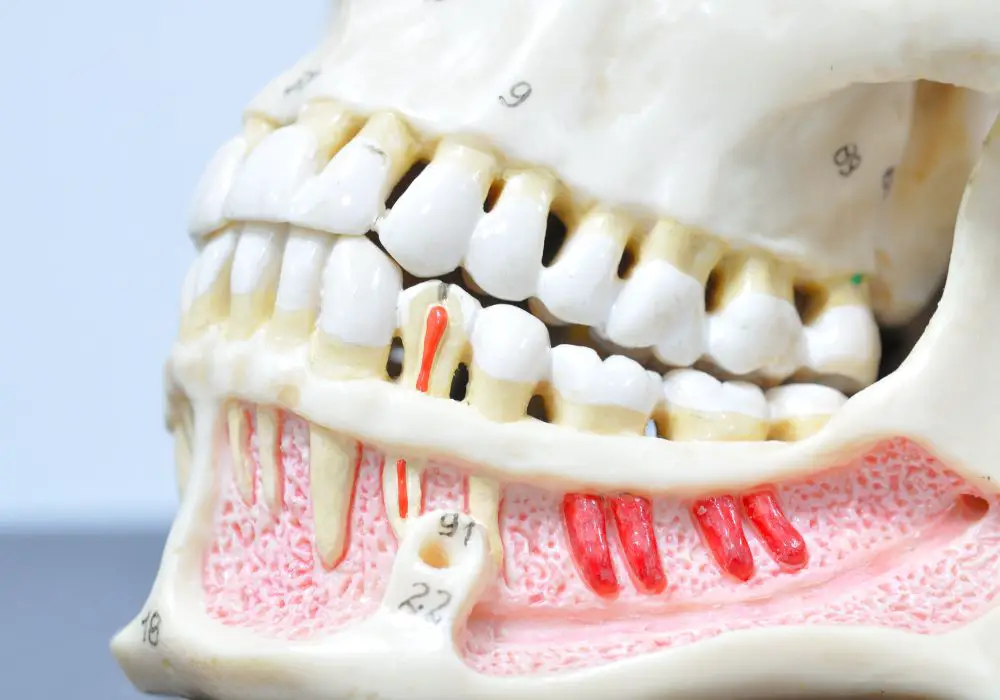
When it comes to understanding what teeth do when they get too hot, it’s important to first understand the anatomy of teeth. Teeth are complex structures that consist of three main layers: the enamel layer, dentin layer, and pulp chamber. Each layer plays a crucial role in the overall function of the tooth.
Enamel Layer
The enamel layer is the outermost layer of the tooth and is the hardest substance in the human body. It is made up of a complex matrix of minerals, including calcium and phosphate, that give it its strength and durability. The primary function of the enamel layer is to protect the underlying layers of the tooth from damage caused by chewing, grinding, and other forms of wear and tear.
Dentin Layer
The dentin layer is the second layer of the tooth and is located directly beneath the enamel layer. It is composed of a dense network of microscopic tubes that contain fluid and nerve endings. The dentin layer is responsible for transmitting sensations such as hot, cold, and pressure to the nerves in the pulp chamber.
Pulp Chamber
The pulp chamber is the innermost layer of the tooth and is located at the center of the tooth. It contains the nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue that make up the dental pulp. The primary function of the pulp chamber is to nourish and support the tooth.
When teeth get too hot, the enamel layer can become damaged, which can lead to discomfort and sensitivity. The dentin layer, which contains nerve endings, can also become irritated, causing pain and discomfort. If the heat is extreme, it can even damage the pulp chamber, leading to more serious problems such as infection and tooth decay.
Overall, understanding the anatomy of teeth is important when it comes to understanding what teeth do when they get too hot. By taking care of your teeth and protecting them from extreme temperatures, you can help ensure that they remain healthy and functional for years to come.
How Heat Affects Teeth
When you take a sip of hot coffee or bite into a slice of pizza that’s fresh out of the oven, you may feel a sudden discomfort in your teeth. This is because heat can affect your teeth in several ways.
Thermal Expansion
When your teeth are exposed to heat, they expand slightly. This is a natural response of the tooth structure to changes in temperature. However, if your teeth are already weakened due to decay, cavities, or cracks, the thermal expansion can cause further damage and discomfort.
Enamel Erosion
Heat can also cause enamel erosion, which is the gradual wearing away of the outer layer of your teeth. This can happen if you consume hot foods and drinks frequently or if you have poor oral hygiene habits. Enamel erosion can lead to tooth sensitivity, discoloration, and even cavities.
Nerve Sensitivity
The nerves in your teeth can become more sensitive to heat due to various factors such as gum disease, tooth decay, or dental procedures. When the nerves are exposed to heat, you may experience a sharp, shooting pain that can last for a few seconds or minutes.
To prevent heat-related damage to your teeth, it’s important to maintain good oral hygiene habits such as brushing and flossing regularly, avoiding sugary and acidic foods and drinks, and visiting your dentist for regular check-ups and cleanings. If you experience tooth sensitivity or pain when consuming hot foods or drinks, talk to your dentist about possible treatments such as fluoride treatments, desensitizing toothpaste, or dental procedures like fillings or root canals.
Preventing Heat Damage to Teeth

If you experience tooth sensitivity to heat, it’s essential to take steps to prevent further damage to your teeth. Here are some ways to prevent heat damage to your teeth:
Proper Oral Hygiene
Maintaining proper oral hygiene is crucial to prevent tooth decay, gum disease, and other dental problems that can lead to tooth sensitivity. Brush your teeth twice a day for two minutes each time, and floss at least once a day to remove food particles and plaque from between your teeth. Use a toothpaste that contains fluoride to strengthen your teeth and protect them from decay.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular dental check-ups are essential to maintain good oral health and prevent dental problems. Your dentist can detect early signs of tooth decay, gum disease, and other dental problems that can lead to tooth sensitivity. Your dentist can also provide you with advice on how to care for your teeth and prevent dental problems.
Avoidance of Excessive Heat
Avoiding excessive heat is crucial to prevent further damage to your teeth. Avoid drinking hot beverages and eating hot foods that can irritate your teeth. If you must drink hot beverages or eat hot foods, try to let them cool down a bit before consuming them. Also, avoid exposing your teeth to excessive heat from hair dryers, steam, and other sources of heat.
In summary, taking care of your teeth by maintaining proper oral hygiene, regular dental check-ups, and avoiding excessive heat can help prevent heat damage to your teeth. By following these simple steps, you can enjoy your favorite hot foods and drinks without experiencing tooth sensitivity.
Heat-Related Dental Conditions
When your teeth are exposed to extreme temperatures, they can experience a variety of heat-related dental conditions. Here are two common ones:
Thermal Cracking
If you eat or drink something that is too hot, your teeth may be at risk of thermal cracking. This is when the enamel on your teeth expands and contracts rapidly, causing tiny cracks to form. Over time, these cracks can become larger and more visible, leading to tooth sensitivity and pain.
To prevent thermal cracking, you should avoid eating or drinking anything that is too hot. If you do consume something hot, try to let it cool down a bit before taking a sip or bite. Additionally, be sure to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing and flossing regularly, as this can help prevent bacteria from entering the cracks in your teeth.
Tooth Discoloration
Another heat-related dental condition is tooth discoloration. When your teeth are exposed to extreme temperatures, the enamel can become damaged and discolored. This can make your teeth look yellow or brown, and can be difficult to reverse.
To prevent tooth discoloration, you should avoid consuming foods and drinks that are high in sugar and acidic content. Additionally, be sure to brush and floss regularly to keep your teeth clean and healthy.
In conclusion, taking care of your teeth is important, especially when it comes to heat-related dental conditions. By avoiding hot foods and drinks, maintaining good oral hygiene, and watching what you eat, you can help prevent these conditions and keep your teeth healthy and strong.
Treatment Options for Heat-Damaged Teeth

If you experience tooth sensitivity or pain after consuming hot food or drinks, your teeth may be damaged by heat. Fortunately, there are several treatment options available to restore your teeth’s health and alleviate your discomfort.
Dental Fillings
If the heat damage is minor and has not affected the inner layers of your teeth, your dentist may recommend a dental filling. Dental fillings are a common treatment for cavities and can also be used to repair minor cracks or chips in your teeth. During the procedure, your dentist will remove the damaged portion of your tooth and fill the cavity with a tooth-colored resin or amalgam.
Root Canal Therapy
If the heat damage has reached the inner layers of your teeth, your dentist may recommend a root canal therapy. This procedure involves removing the damaged pulp tissue from your tooth’s root canal and filling it with a biocompatible material. After the procedure, your dentist may recommend a dental crown to protect your tooth from further damage.
Dental Crowns
If the heat damage is extensive and has weakened your tooth’s structure, your dentist may recommend a dental crown. Dental crowns are custom-made caps that fit over your damaged tooth to restore its shape, size, and strength. Crowns can be made from a variety of materials, including porcelain, ceramic, or metal alloys.
It’s important to seek treatment for heat-damaged teeth as soon as possible to prevent further damage and potential tooth loss. Your dentist can evaluate your teeth’s condition and recommend the best treatment option for your specific needs.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can teeth withstand high temperatures?
Human teeth are remarkable in their ability to withstand extreme heat and thermal shock. However, it is important to note that teeth do have a limit to the amount of heat they can handle before becoming damaged.
What happens to teeth when exposed to extreme heat?
When teeth are exposed to extreme heat, the different structures of the teeth can become damaged. The enamel, which is the hard, outer layer of the tooth, can crack or fracture under extreme heat. The dentin, which is the layer beneath the enamel, can become exposed and sensitive to hot and cold temperatures. The pulp, which is the soft tissue at the center of the tooth, can become inflamed and infected.
Do teeth make a popping sound when they get too hot?
There is a common misconception that teeth will make a popping sound when they get too hot. However, this is not true. Teeth do not make any sound when exposed to extreme heat.
What is the maximum temperature teeth can handle?
The maximum temperature that teeth can handle without becoming damaged varies depending on the individual. However, research has shown that teeth can withstand temperatures of up to 140°F (60°C) without becoming damaged.
How can extreme heat affect dental health?
Exposure to extreme heat can have negative effects on dental health. It can cause damage to the teeth, including cracking and fracturing of the enamel, as well as inflammation and infection of the pulp. It can also lead to sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures.
What are some signs of heat damage to teeth?
Signs of heat damage to teeth include sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures, pain when biting or chewing, and visible cracks or fractures in the enamel. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to see a dentist as soon as possible to prevent further damage to your teeth.