When a tooth dies or becomes non-vital, it means that the pulp tissue inside the tooth has been damaged irreversibly. The most common causes of tooth death include deep decay, repeated dental procedures, trauma, or a crack in the tooth.
Once the pulp tissue dies, the tooth is no longer receiving blood flow or nerves. It becomes brittle and susceptible to infection or abscess. A dead tooth will often change color, becoming darker than surrounding teeth. It may also become painful or sensitive to temperature changes.
So how long can a dead tooth remain in the mouth before it requires treatment? There are a few factors that determine the lifespan of a non-vital tooth.
Factors Affecting Dead Tooth Lifespan
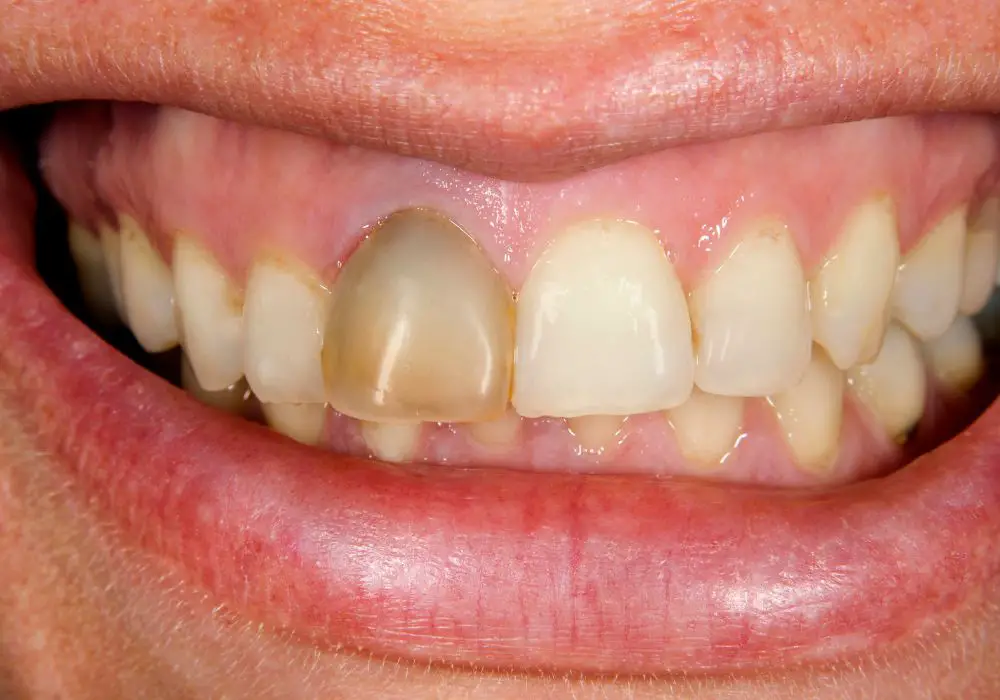
- Severity of infection or abscess – If an infection develops in the dead tooth or surrounding bone, it can spread rapidly and cause severe problems. Infected teeth require immediate treatment.
- Damage to the tooth – Cracks or fractures in the dead tooth can allow new infections to develop. The more damaged a dead tooth is, the faster it will degrade.
- Your oral health – People with conditions like diabetes or suppressed immune systems may be unable to fight infections originating from a dead tooth. For them, seek treatment quickly.
- Presence of symptoms – Pain, swelling, or other symptoms indicate your body responding to an infection related to the dead tooth. Don’t ignore these warning signs.
- Your age – Dead teeth tend to deteriorate faster in younger patients. The pulp chambers are larger and provide more area for infection. Older patients may have more secondary dentin that could delay infection.
How Long Before Treatment is Needed?
So when should a dead tooth be treated? There are a few general timelines to keep in mind:
- With no symptoms – Some dead teeth may be asymptomatic for months or even years. But they still require eventual treatment and will not improve on their own.
- With light symptoms – Slight pain, sensitivity or discoloration means a dead tooth is deteriorating. You should have it treated within weeks to months to prevent worse infection.
- With severe symptoms – Swelling, drainage, or intense tooth pain means infection has taken hold. Emergency dental treatment is needed right away. The tooth must be treated or extracted immediately.
- With abscess – Abscesses at the tip of dead teeth root require urgent treatment. If left alone, the infection can spread to the jaw bone and other areas. Emergency treatment is critical.
- With cracks/fractures – Any cracks or fractures in dead teeth should be evaluated quickly, as they provide pathways for infection into the root and bone. Treatment often cannot be delayed long.
As a general guideline, dead teeth without symptoms should be treated within 6 to 12 months. If you have any symptoms, seek emergency dental care right away. But every patient’s condition is unique, so work with your dentist to determine the ideal timeline for your particular tooth.
Average Lifespan of an Untreated Dead Tooth
On average, most dead teeth that are left untreated will eventually require extraction. Here are some estimates for how long an untreated dead tooth may last before extraction is necessary:
- With no symptoms – 2-5 years
- With mild infection – 6 months – 2 years
- With recurring infection – Less than 6 months
- With abscess – Immediate extraction needed
- With severe decay or fracture – Less than 3 months
These averages can vary based on your unique oral health and the tooth’s condition. Work closely with your dentist to determine the ideal treatment plan for your individual situation.
Signs It’s Time to Treat a Dead Tooth
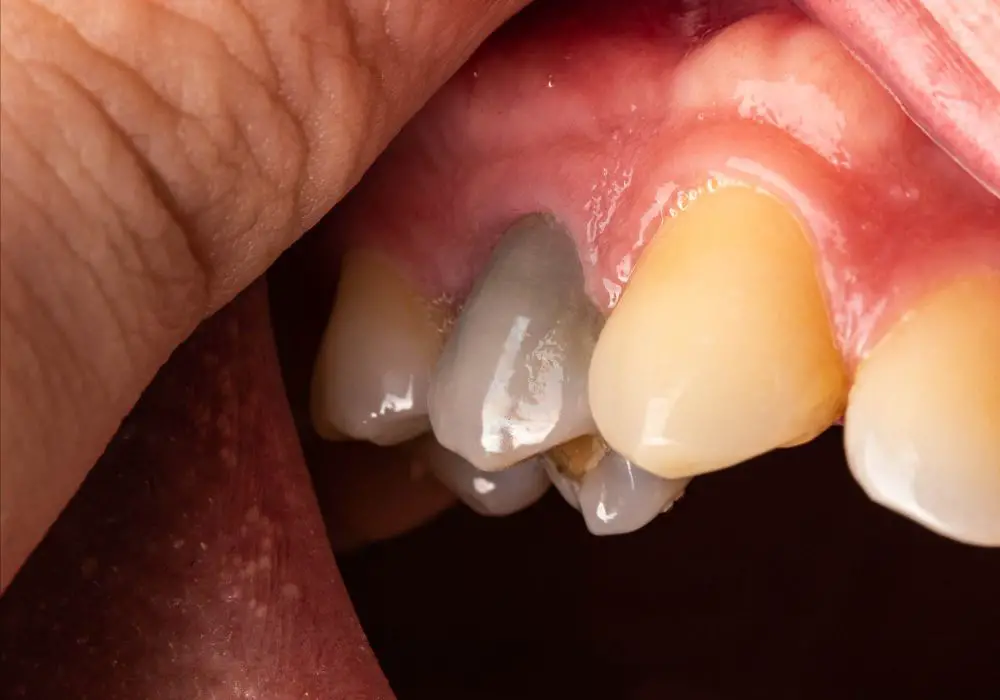
Don’t wait until you have a dental emergency to treat a dead tooth. Be proactive and watch for these signs it’s time for treatment:
- Discoloration or darkening of the tooth
- Pain or sensitivity to hot and cold
- Swelling, foul tastes or foul breath
- Receding gums around the tooth
- Pus around the tooth or gums
- Lost fillings or crowns
- Broken areas, cracks or fractures in the tooth
- Tooth feels loose, moves slightly
- Change in your bite alignment
Schedule an exam with your dentist if you notice any of these issues. The sooner your dead tooth is treated, the more likely it can be saved or treated with a simple root canal. Waiting leads to worse infections and complications.
Consequences of Leaving a Dead Tooth Untreated
Allowing a dead tooth to deteriorate can have very serious health consequences. Potential problems include:
- Tooth loss – Ultimately an infected dead tooth will require extraction if left alone too long. This can affect your bite, function and even facial structure.
- Spreading infection – Infection from the tooth can spread to surrounding gum and jawbone tissue. This can be very painful and necessitate surgical treatment.
- Systemic infection – Severe infections from dead teeth may spread through the bloodstream impacting your whole body. This can become life-threatening.
- Abscesses – Pus-filled abscesses commonly form at the root tips of dead teeth. Apart from being extremely painful, their infection destroys nearby bone.
- Cysts – Cysts can develop from infections of the tooth’s root. Removal requires extensive jawbone surgery.
- Receding gums – Gums may recede as infection spreads, making your teeth look longer and exposing sensitive root surfaces.
Clearly, ignoring a dead tooth’s deterioration can allow relatively minor problems to escalate into more serious issues. Don’t delay treatment. Consult your dentist right away if you suspect you have a non-vital tooth.
Treatment Options for a Dead Tooth
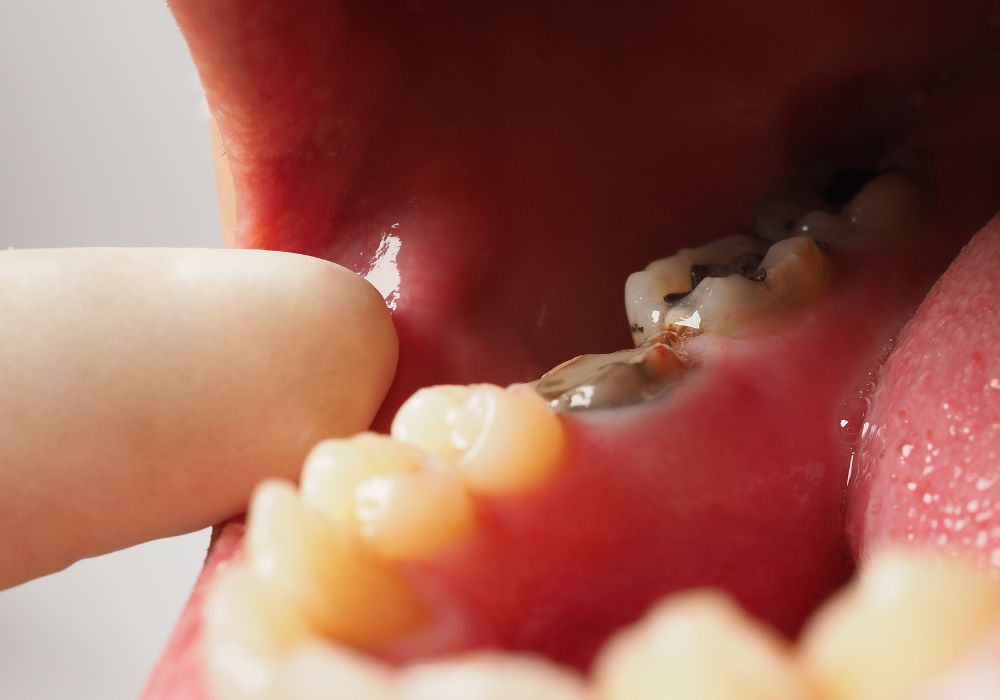
Treating a dead tooth as soon as possible increases your chances for saving it. Here are some common treatment options:
Root Canal Treatment
Also called endodontic treatment, a root canal cleans out dead and infected pulp from inside the tooth and fills and seals the space. This can save the tooth and restore function.
Root Canal Retreatment
If initial root canal treatment fails and infection recurs, retreatment can be attempted to clean and refill the tooth.
Root End Surgery
For challenging root canal cases, endodontic surgery may be required to access and treat the ends of the tooth roots directly.
Tooth Extraction
If a dead tooth cannot be saved by other treatments, safe extraction is required. Your dentist will remove the tooth and infected tissue.
Tooth Replacement
After extraction, options like dental implants, bridges or partial dentures can restore your smile.
Be sure to discuss all possible treatments with your dentist and choose the best option for your situation. With early intervention, root canal treatment can often save a dead tooth.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I tell if I have a dead tooth?
Some signs your tooth may be non-vital or dying include:
- Discoloration – Teeth turn darker compared to surrounding teeth
- Pain – From hot/cold sensitivity or pressure
- Swelling – Around the gums near the tooth
- Decay – Rapidly progressing or unusual decay
- Trauma – Blows or injuries to the tooth
- Large fillings – Teeth with deep or extensive restorations
If you notice any of these issues, see a dentist right away for testing and treatment.
What problems could a dead tooth cause?
A non-vital tooth can lead to:
- Infection – Bacteria multiply in the dead pulp tissue
- Abscess – Pus builds up at the root tip
- Cysts – Fluid-filled sacs develop on roots
- Bone loss – Infection destroys the jawbone
- Gum disease – Gums recede around the tooth
- Systemic infection – Spreads through the bloodstream
That’s why it’s critical to treat dead teeth quickly before they worsen.
How much does it cost to treat a dead tooth?
Costs vary depending on the treatment needed:
- Root canal – $700-$1500 per canal
- Root canal retreatment – $1000-$2000 per canal
- Extraction – $75-$300 per tooth
- Implant – $1500-$3000 per implant
Check with your dental insurance, as they often cover a portion of major treatments.
Can a dead tooth just be left alone?
It’s never advisable to simply leave a dead tooth alone indefinitely. Without treatment, it will continue to deteriorate and cause escalating problems. Exact timelines vary, but most dentists recommend treating within 6-12 months even if no symptoms are present yet. Schedule an exam so your dentist can determine the appropriate treatment timeline for your situation.
How long do root canals last?
With a proper root canal and good oral hygiene, a tooth can often last a lifetime. Studies show root canal treated teeth have a survival rate of over 90% lasting 8-10 years or longer. In some cases, retreatment may be needed if infection recurs. Discuss longevity with your dentist when considering root canal options.
Conclusion
The lifespan of a dead tooth depends on many factors, but on average untreated teeth often require extraction within a few years. While an individual tooth’s timeline may vary, it’s crucial to seek treatment at the first signs of problems to save your tooth and prevent serious complications. Work closely with your dentist to monitor the tooth’s condition and determine the most appropriate treatment approach. With early intervention, root canals and other options can often restore a dead tooth safely and permanently. Don’t wait until you have extreme symptoms or an abscess before addressing a non-vital tooth. Schedule a dental exam if you have any concerns.






