Experiencing a cracked or fractured tooth can be very troubling and in many cases painful. A broken tooth may lead to discomfort when eating or drinking hot and cold foods, pain when biting down, or even infection of the tooth’s pulp which requires root canal treatment. Knowing how long a damaged tooth can safely be left untreated is crucial information to have in order to prevent further deterioration and potential tooth loss. This comprehensive article will provide an in-depth overview of the various types of tooth fractures, what causes them, noticeable symptoms, possible complications from delaying treatment, guidelines for when to seek emergency dental care, treatment options, prevention tips, and what scenarios could be potentially serious.
Types of Tooth Fractures
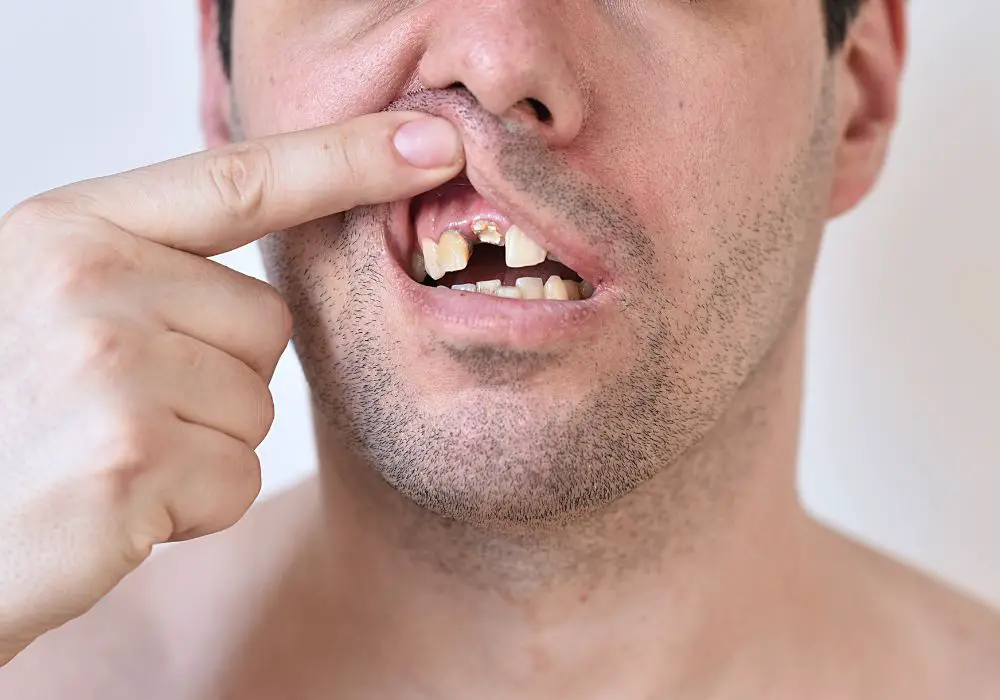
Several different classifications of tooth fractures may occur, depending on the location and extent of the crack or break:
Cracked Tooth
This type of fracture involves a crack that extends from the biting surface of the tooth down towards the root. The crack is confined to the enamel and dentin layers and does not completely split the tooth in two. Cracked teeth may cause mild to severe pain when chewing or biting down. The crack also allows bacteria to seep inside the tooth, increasing risk of pulp inflammation and infection.
Fractured Cusp
A fractured cusp occurs when a small segment of the chewing surface of the tooth breaks off, often due to bite trauma or advanced tooth decay. This does not typically cause acute pain, but the tooth’s biting surface will be weakened and more vulnerable to further cracking.
Split Tooth
A split tooth fracture occurs when the crack propagates through the entire width of the tooth, including the root. This splits the tooth completely in two from top to bottom. Split teeth often require extraction since the fracture is too severe for other restorative treatments.
Vertical Root Fracture
This serious fracture begins in the root of the tooth and extends vertically towards the chewing surface, essentially cracking the root in half lengthwise. Teeth with vertical root fractures also frequently require extraction.
Chipped Tooth
A chipped tooth occurs when a small fragment of tooth enamel breaks off of the tooth’s surface. This does not affect the dentin or pulp and may only cause temporary sensitivity when biting down.
Causes of Cracked and Broken Teeth
A number of factors can contribute to cracked, chipped or fractured teeth:
- Trauma or Injury – A direct impact to the mouth from a fall, sports injury, auto accident, or being struck can easily cause teeth fractures.
- Grinding and Clenching – Putting excessive biting force on teeth from clenching or grinding wears down the enamel over time and makes teeth more susceptible to cracking and fractures.
- Advanced Tooth Decay – Untreated dental caries that is allowed to reach the inner layers of the tooth can weaken tooth structure and more readily lead to breaks.
- Large Dental Fillings – Having extensive dental restorations done with large fillings leaves less remaining natural tooth structure and makes the tooth more prone to cracks and fractures.
- Chewing Hard Items – Constant chewing or biting on hard objects like ice cubes, nuts, hard candy or pens can stress teeth and cause fractures.
- Aging – As we age, teeth gradually lose enamel and moisture, making them more brittle and prone to cracking.
Signs and Symptoms of Broken Teeth
Some common signs and symptoms that may indicate a tooth is cracked, chipped or fractured include:
- Sharp pain when biting down that lingers briefly after releasing the bite
- Hot and cold sensitivity – severe reactions to hot or cold foods and drinks
- Visible crack across top of tooth that can be felt with tongue or fingernail
- Noticeable chip or break that can be seen on tooth surface
- Tooth feels shorter in height or different when biting down
- Tooth moves slightly or feels loose when chewing
- Tooth pain that radiates to ear, sinus or side of face
- Swelling, redness or bleeding from gums around affected tooth
- Extreme sensitivity to changes in temperature
Potential Complications from Delaying Treatment
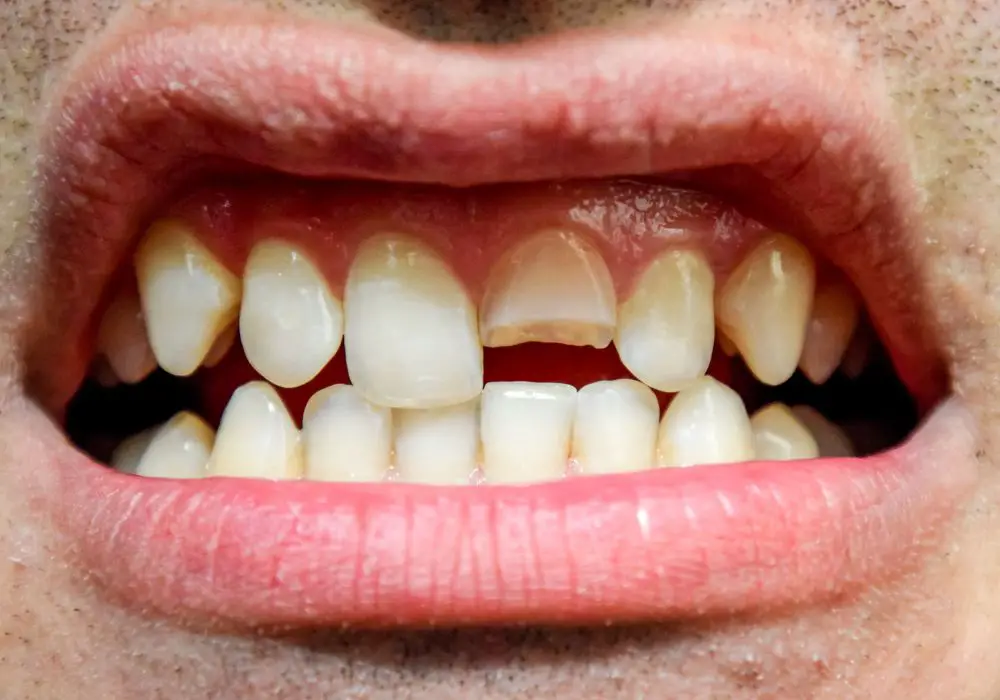
Leaving a cracked or fractured tooth untreated for too long can lead to potentially serious complications:
Infection
Bacteria can invade through the crack into the pulp tissue inside the tooth, causing inflammation of the nerve (pulpitis), dental abscesses, infection of the bone around tooth roots (periodontitis), and even systemic infection spreading through facial planes.
Tooth Loss
If the crack extends below the gum line, it allows periodontal bacteria to proliferate and causes progressive bone loss around the tooth. This process can continue until the tooth becomes very loose and ultimately has to be extracted.
Spreading Infection
A dental infection that originates from an untreated cracked tooth can readily spread to adjacent teeth, causing them to also become infected. The infection can also spread into facial tissues and spaces or down into the jawbone (osteomyelitis).
Excruciating Pain
Leaving a cracked or fractured tooth unrepaired will likely lead to increasing levels of pain ranging from mild discomfort to severe, unrelenting throbbing pain that prevents eating, drinking or sleeping properly.
Sinus involvement
Untreated dental infections from upper back tooth fractures can spread into the maxillary sinuses causing a sinus infection (sinusitis).
When to Seek Emergency Dental Care for a Broken Tooth
It is highly recommended to have a cracked or broken tooth evaluated by a dentist right away for proper diagnosis and early treatment. Here are some general guidelines on when to seek urgent or emergency dental care:
- Moderate to severe toothache pain that disrupts normal activity or sleep
- Any visible cracks or fractures on the tooth surface
- Tooth feels loose, shifts position or moves when chewing
- Swelling, redness or bleeding from gums around the affected tooth
- Trauma or injury involving the mouth, even if no symptoms yet
- Lingering pain when releasing bite pressure
- Extreme hot/cold sensitivity signaling pulp involvement
Seeking prompt assessment and treatment from a dentist provides the best chance of saving the natural tooth and preventing additional problems. The longer treatment is delayed, the lower the likelihood of a favorable outcome.
How Long Can a Broken Tooth Reasonably Be Left Untreated?
The maximum timeframe a cracked or fractured tooth can reasonably be left untreated depends on several factors:
Superficial Cracks in Enamel
Small cracks in the enamel that do not penetrate deep into dentin may only require stabilization with dental bonding or sealants. These can often wait for repair for several weeks to months with minimal risk if not causing pain. However, they should still be treated soon to avoid worsening.
Fractured Cusps
A broken cusp tip that has not yet exposed the nerve chamber can likely hold out for 1-2 weeks before definitive treatment, but is at high risk for pulpal exposure during that time.
Cracked Tooth with Pulp Involvement
Cracks that extend into the pulp space and cause pulpal inflammation or infection necessitate urgent care within 24-48 hours in order to try and save the tooth. The longer treatment is delayed, the lower the chances the tooth can be salvaged.
Split Tooth or Vertical Root Fracture
These severe fractures that completely split the tooth in two require emergency extraction within 24-48 hours to prevent a severe infection. The tooth cannot be saved.
Dental Treatments for Broken Teeth
The type of recommended treatment depends on extent and position of the tooth fracture:
Dental Bonding
Applying dental bonding material can repair small cosmetic chips or help stabilize superficial cracks. This is an affordable, conservative treatment option.
Dental Crowns
If the crack encompasses a large portion of the tooth, a full coverage dental crown is usually required to hold the tooth together and prevent further damage. However, root canal therapy is often needed first.
Root Canal Treatment
If the tooth’s pulp nerve chamber has become infected or inflamed due to a crack or fracture, root canal treatment is warranted to remove the pulp and prevent further infection. A crown is placed afterwards.
Tooth Extraction
If the tooth root is completely cracked in half or has a vertical fracture, extraction is usually the only suitable option. The tooth can later be replaced with a dental implant, bridge, or partial denture.
Veneers
Dental veneers may be used to cover mildly chipped teeth for cosmetic improvement and to help stabilize slightly cracked teeth.
Prevention of Cracked and Broken Teeth
Some tips to help prevent tooth fractures and breaks:
- Get fitted for a custom mouthguard if participating in sports
- Have old large fillings replaced with tooth-colored onlays or crowns
- Wear a nightguard if you grind your teeth
- Avoid chewing on hard items like ice, popcorn kernels, or pens
- Get dental cavities treated early before they enlarge and weaken the tooth
- Maintain excellent oral hygiene to prevent tooth decay
- Regular dental cleanings and exams to detect problems early
Serious Symptoms Requiring Immediate Dental Care
Seek emergency dental care promptly if experiencing:
- Unbearable, throbbing toothache that keeps you awake at night
- Facial swelling around the problematic tooth
- Tooth is loose, pushed upwards, or moves when biting down
- Pus discharge from the gums around the tooth
- Severe reactions to hot and cold – could indicate pulp is exposed
- Tooth feels very different when biting down
These scenarios suggest a serious tooth fracture or infection that requires urgent dental intervention and possibly antibiotics. Leaving treatment for too long can risk losing the tooth altogether. Don’t delay in seeking care.
Conclusion
Cracked and fractured teeth should never be ignored and require timely evaluation and repair for optimal outcomes. While minor cracks may hold out for weeks to months, more severe fractures involving pulp or periodontal damage necessitate treatment within 24-48 hours to save the tooth. Taking quick action gives the best chance of preserving your natural teeth and preventing worsened effects. Report any worrying symptoms like unrelenting pain or loose teeth to your dentist immediately. With early intervention, most cracked and broken teeth can be effectively restored.