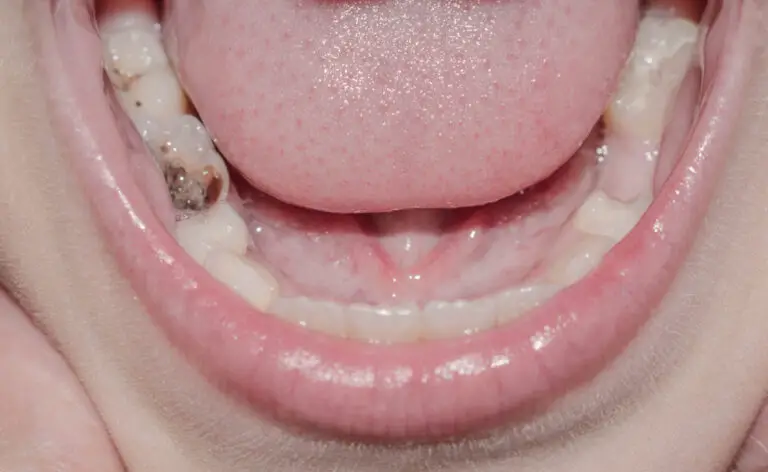
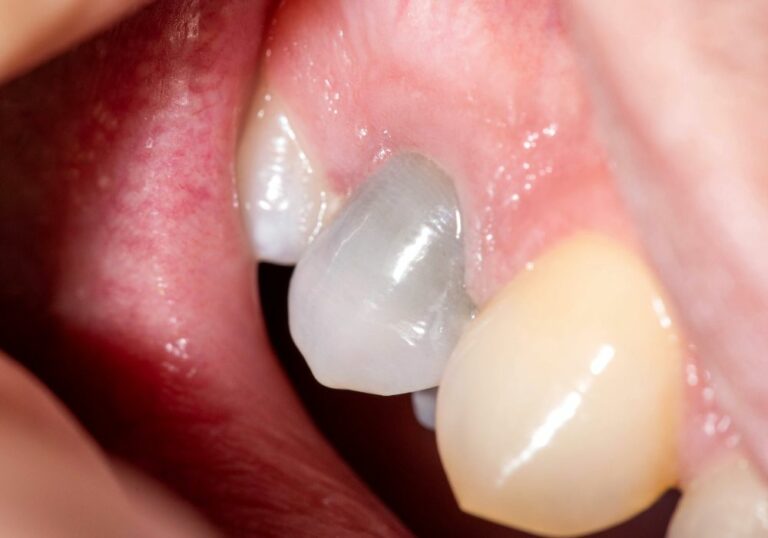
Dental care and maintenance are vital parts of our oral health. Sadly, many people often ignore this aspect of dental health, which makes them susceptible to several oral issues. One such issue is the gum recession.
So, what is gum recession?
As the name suggests, it’s an oral condition that causes the gum tissue that envelopes your teeth to recede or deteriorate. Since gum recession is slow, it usually goes unnoticed. This is bad because receding gums can lead to potential tooth loss.
On that note, this comprehensive guide explores the cause, symptoms, and consequences of receding gums. Moreover, it answers one of the most frequently asked questions online “How far can gums recede before teeth fall out?”.
If you want to learn more about this dental menace, continue reading below.
What is Gum Recession?
Healthy gums usually form a tight seal around the base of teeth, anchoring them firmly in the jawbone. Unfortunately, plaque and tartar tend to sit along the gum line, which can cause the pink gum tissue to weaken and pull back.
When this happens, gaps or pockets can form between the teeth and gum line. These create room for disease-causing bacteria to accommodate and grow.
If left unaddressed, the bacteria can damage the supporting tissues, causing the gum to wear away, exposing the tooth roots. Eventually, the condition causes tooth loss.
The gum recession might seem like a dental issue that came out of nowhere. But surprisingly, gum or gingival recession is a common oral health problem but occurs gradually.
Signs and Symptoms of Gum Recession
- Tooth Sensitivity
- Teeth that look longer
- Rough notch or spot felt at the gum line
- Frequent cases of red, swollen, or bleeding gums after brushing or flossing
What Causes Gums to Recede?
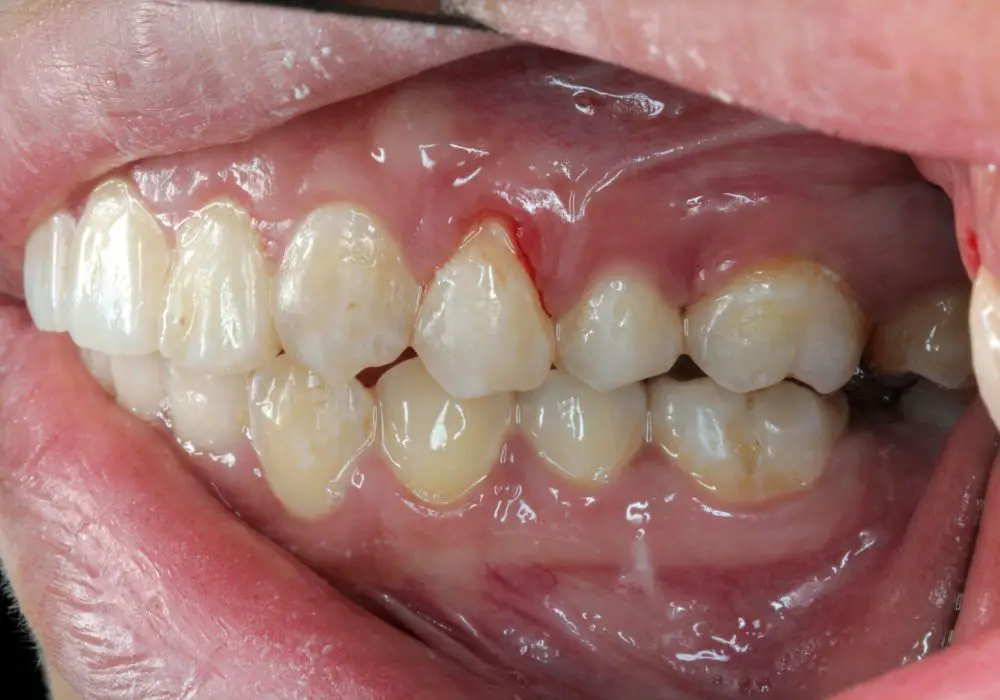
For decades, people associated gum recession with the aging process. However, scientific studies suggest that aging might only increase your risk of the causes of this condition, but it’s not the culprit behind it.
So, what are the primary causes of gingival retraction?
1. Periodontal disease
Periodontal disease occurs when bacteria build up and harden on your teeth and along the gum line, causing an infection. It leads to gradual bone loss and destruction of connecting tissues, which translates to gum recession and tooth exposure.
2. Chronic trauma
Trauma caused by aggressive tooth brushing can slowly cause your teeth’s enamel and gums to wear away. Some abrasive oral hygiene products can also damage your delicate gum margins.
3. Genetics
Some individuals are more predisposed to gingival recession than others. That means, if this condition runs in your family, you will probably deal with it even if you follow the best dental care practices. Your genes also determine the thickness and resilience of your gum tissues.
4. Hormonal changes
Yes, hormones also affect your dental health. Hormonal changes caused by puberty, period, menopause, or pregnancy can contribute to weak gums and bone loss around the teeth. As a result, they can cause gingival recession and other dental issues.
5. Tobacco products
Do you love smoking or use tobacco? Chances are, your teeth have plaque, especially if you don’t brush them regularly. As said earlier, plaque can make your gum weaken and pull out, leading to a recession.
6. Grinding and clenching your teeth
People who grind or clench their teeth are highly susceptible to gum recession. These actions place too much force on the gums, which can irritate and damage them. Because of this, the gums might pull away from your teeth.
7. Insufficient dental care
If you rarely brush, floss, or rinse your mouth with antibacterial mouthwash, the bacteria buildup on your teeth can turn into plaque, then into tartar. When tartar accumulates under the gums, it can pull them away from the teeth and cause the gums to recede.
How Far Can Gums Recede Before Teeth Fall Out?

Healthy gums ensure your teeth stay in their socket. But when they recede, your teeth become exposed, which can lead to instability.
At first, you will not notice the condition. But as time goes on, loss of gum tissue coupled with bacterial infections will damage the ligaments and bones that stabilize the teeth.
At this point, your teeth will become more sensitive. As for the gums, they will swell or bleed anytime you brush your teeth.
If left untreated, the gum recession can reach a critical threshold, where there’s not enough tissue to hold your teeth in place. When this happens, the roots become exposed and unstable. Eventually, they might decay or fall out.
However, the rate of gum recession varies between people due to several factors, like genetics, dental care habits, and lifestyle choices.
Gum Recession: Treatment Options
If you have noticed signs of receding gums and you haven’t visited your dentist lately, it’s best to schedule an appointment soon. When identified early, gum recession can be treated, saving your gums and teeth from further damage.
Nevertheless, the type of receding gums treatment recommended by the dentist will depend on various factors, including:
- Your health history
- Nature of the condition–Mild to Severe
- Underlying causes of gum recession
Here are a few treatments options for receding gums:
Proper Dental Care
Your first line of defense against receding line is re-evaluating your oral care and maintenance practices. These could include:
- Opt for soft-bristle: A toothbrush with hard bristles can cause your enamel and gum line to wear away. This holds, especially if you exert too much force on your teeth when brushing. The best solution here is to invest in a comfortable brush with soft bristles. Opt for an electric brush with a force detector to control the amount of pressure applied to the teeth and gums. Also, change your toothbrushes regularly.
- Change your toothpaste: As said earlier, some abrasive dental care products can contribute to receding gums. So, buy fluoride toothpaste that removes plaque from your teeth while keeping your gums safe.
- Deep cleaning: Mild to moderate cases of gingival retraction might call for deep cleaning. This procedure helps eliminate plaque and tartar buildup on the teeth and gum. Unlike regular cleanings, professional dental cleaning targets the exposed tooth roots to make cementum smoother. This helps to prevent plaque from accumulating in the spaces between the gum and teeth. Your dentist might also recommend some antibiotics to kill residual harmful bacteria and prevent infections.
Surgical Procedures

People dealing with severe cases of gum recession might require surgical interventions. Below, we’ve discussed two surgeries often used to restore gum tissue and protect tooth roots.
- Gum Grafting
A gum tissue graft is an innovative surgical technique that involves removing a piece of tissue from the roof of your mouth and stitching it to the gum tissue around the exposed roots.
But some specialists prefer using graft material sourced from a tissue bank. They might also use tissue-stimulating proteins to activate your body’s ability to grow bone and tissues.
Since this procedure occurs under anesthesia, it’s entirely painless. However, you might experience some discomfort when the surgical site gets poked with the anesthesia needles. The area where the dentist takes the grafting tissue might also feel swollen and sore for a few days.
Fortunately, recovery from this surgery is quick, though your gums might feel tender for several days.
Gum grafting surgery prevents further gum loss and protects previously exposed tooth roots from bacterial attack and decay.
- Pinhole Surgical Treatment
Unlike gum grafting, pinhole surgical treatment, or PST, is less invasive and requires no graft. During the surgery, a dentist relies on specialized tools to make a tiny hole in the area of gum recession.
Using another unique tool, the expert will stretch and push the gum back to its proper position. After that, he (or she) will place collagen strips through the hole and push them under the gums to cover the exposed tooth root surfaces.
PST has little downtime, and you can resume your regular lifestyle a few days after the surgery. The only downside is that you require enough gum tissue for the procedure.
How To Prevent Gum Recession?
While you cannot reverse receding gums, you can follow the tips below to slow or stop the condition.
- Practice good oral hygiene–Brushing and flossing your teeth regularly
- Adopt the correct brushing technique- Place your toothbrush at an angle of 45 degrees and brush your teeth gently for 2 minutes
- Avoiding smoking or chewing tobacco products
- Use antimicrobial mouthwash twice a day
- Wear a mouth guard or splint to prevent gum recession at night, especially if you often grind your teeth.
- Replace ill-fitting dentures
- Schedule regular dental check-ups
Closing Remarks
Gum recession might not seem like a serious dental problem, but it can prove disastrous if left untreated. In fact, gum loss can predispose you to tooth decay, tooth loss, and other oral health issues like bad breath.
Unfortunately, receding gums cannot regenerate. Therefore, consult your dentist immediately if you notice signs of this condition like a rough notch on the gum line or increase teeth sensitivity.
In mild and moderate cases, your dentist might recommend deep cleaning and antibiotic treatments. But those dealing with a severe gum recession might require surgery to stop and restore the gum tissue.
Luckily, you can avoid all these by following good oral hygiene practices, staying away from tobacco products, and going for dental visits.
That’s all for today. And if you found this piece interesting, leave us a comment below!