White spots on teeth are a common dental condition that can have various causes. While they are often harmless, in some cases, white spots may indicate tooth decay or the early stages of cavities. This comprehensive guide examines the possible causes of white spots on teeth and helps you determine if they are a sign of cavities.
What are White Spots on Teeth?
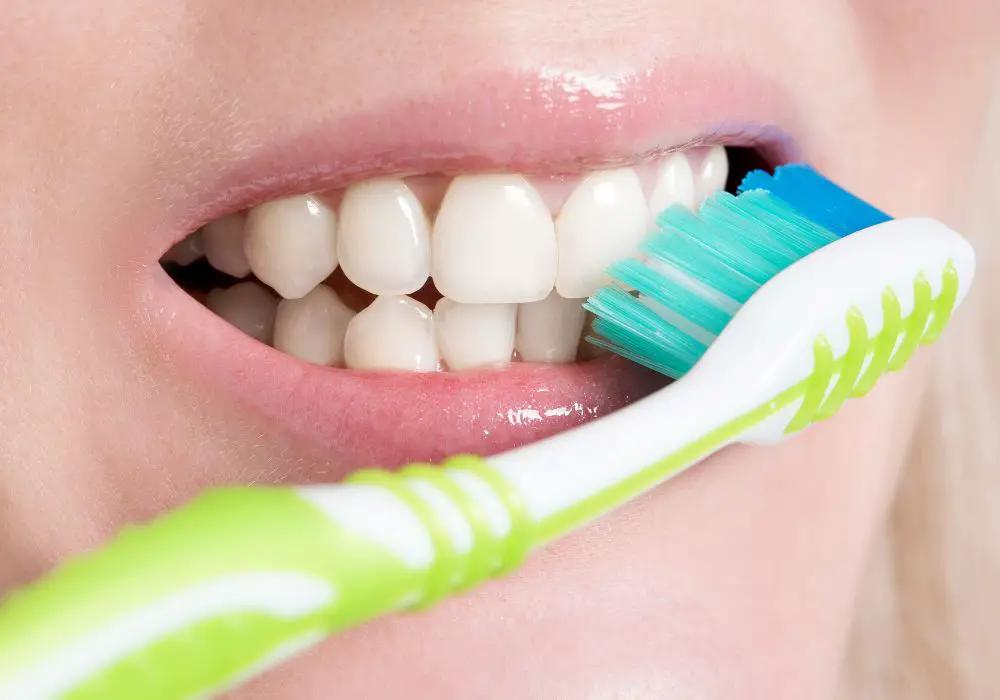

White spots on teeth refer to pale, chalky patches or spots that develop on the enamel. Enamel is the hard, outermost layer of the tooth. It is made up of minerals like calcium, phosphorus, and fluoride that give teeth their white color.
White spots form when minerals are lacking in areas of the enamel. This causes these spots to appear whiter or opaque compared to the surrounding healthy enamel. They have a frosted, chalky look that makes them stand out.
White spots are usually painless and unnoticeable at first. As more minerals are lost over time, the spots may become more pronounced and distinct against the rest of the tooth. They can range in size from tiny pinpoint dots to large patches covering multiple teeth.
The texture of white spots can vary depending on the cause:
- Fluorosis spots tend to have a smooth, shiny appearance.
- Decay spots often have a rougher texture as enamel is actively breaking down.
- Enamel hypoplasia spots have a pitted, irregular texture from defective development.
What Causes White Spots on Teeth?

There are several potential causes of white spots on teeth:
1. Fluorosis
Fluorosis is the most common cause of white spots, accounting for over 50% of cases. It occurs when higher than optimal amounts of fluoride are ingested while teeth are still developing under the gums. Fluoride combines with the enamel proteins and changes how the enamel mineralizes as it hardens.
Both children and adults can develop fluorosis spots if they take in too much fluoride. Sources include:
- Fluoridated drinking water – levels over 2 ppm can cause fluorosis
- Fluoride supplements like drops or tablets
- Excess use of fluoride toothpaste in childhood
- Certain types of bottled waters with fluoride
- Excess fluoride gel treatments
Fluorosis ranges from mild to severe:
- Mild fluorosis shows faint white lines or streaks on teeth.
- Moderate fluorosis results in more noticeable opaque spots and discoloration.
- Severe fluorosis produces extensive dark staining and pitting.
2. Early Stage Tooth Decay
White spots can be the earliest visible sign of tooth decay, before a cavity forms. When acids from bacteria and foods interact with enamel, minerals are dissolved from the tooth surface.
Initially, this mineral loss manifests as white spots as the enamel loses its usual semi-translucent whitish color. The enamel becomes porous and weaker in these demineralized areas.
As decay progresses, the white spot may take on a yellow to dark brown color as the lesion grows. Eventually, if unchecked, the decay will spread inward and form a hole in the enamel layer – a cavity.
3. Enamel Hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a condition where the enamel fails to fully develop in certain areas. It is often caused by childhood illnesses or nutritional deficiencies that disrupt enamel formation. Enamel hypoplasia leaves small, thin spots that are weaker and porous.
Other developmental conditions like amelogenesis imperfecta can also cause similar enamel defects and white spots. The spots in enamel hypoplasia are present from childhood.
4. Orthodontic Braces
The placement of orthodontic braces or aligners can sometimes lead to white spots forming around brackets. The metal bands and adhesive used during treatment create areas that are difficult to clean.
This allows plaque to build up around braces. The bacteria produce acids that attack and demineralize the enamel underneath. This eventually results in white spots around braces if oral hygiene is not meticulous.
5. Dental Trauma
Injury to the teeth can also cause white spots to appear. The impact may chip or crack the enamel leading to mineral loss in those areas. Clenching and grinding of the teeth can likewise lead to white spots due to the constant friction placing stress on the enamel.
6. Tooth Whitening Products
Certain tooth whitening products contain abrasive ingredients that can wear away thin layers of enamel during overuse. This can cause microscopic roughness and pores in the enamel that show through as white spots or areas on the teeth.
Are White Spots an Indication of Cavities?
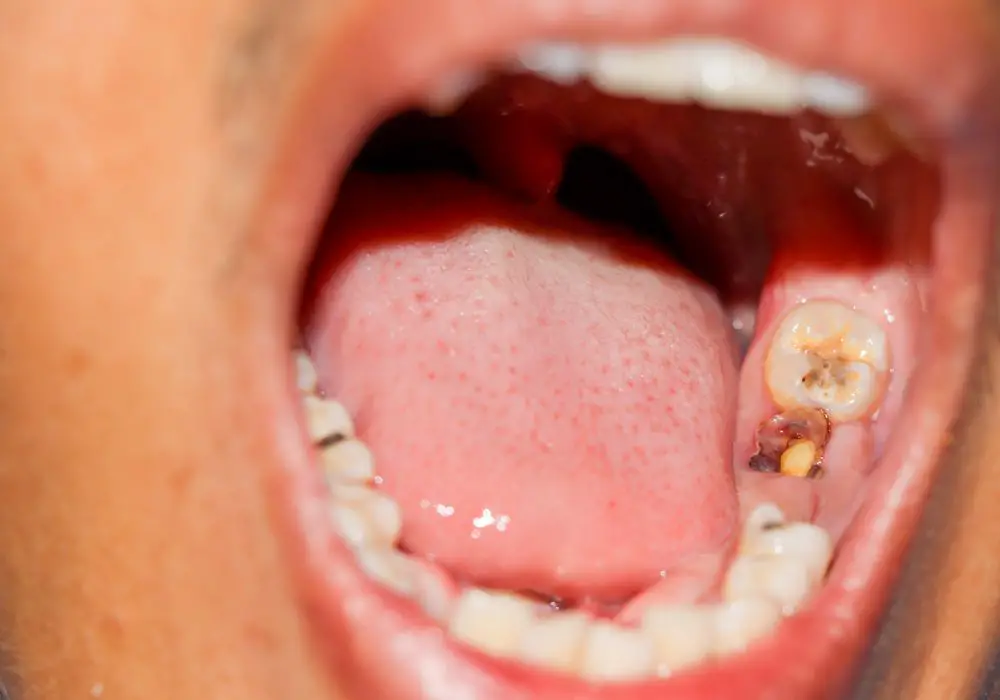
The appearance of new white spots on previously healthy teeth may potentially indicate early stage tooth decay. Enamel demineralization from acid exposure is first visible as white spots before any cavity forms.
However, white spots do not always equate to cavities being present. The cause and nature of the spots must be determined first. Existing developmental or cosmetic white spots are not related to active decay.
White spots due to fluorosis, enamel defects, orthodontics or trauma are generally harmless and only a cosmetic concern. They indicate past issues with enamel formation rather than present decay.
On the other hand, new white spots that form from active tooth demineralization signal that acid erosion and potential cavities are underway.
These active decay spots imply that:
- Acids have started interacting with the enamel
- Demineralization and enamel breakdown have begun
- Cavities are imminent if decay progresses
Therefore, newly formed rough-textured white spots located around the gum line are more likely to indicate the early signs of tooth decay. Careful monitoring and dental examination is advised in these cases to assess for cavities.
How to Determine if White Spots Mean You Have Cavities

Here are some ways to evaluate if your white spots may be signaling tooth decay rather than being benign:
- Spot Origin: New white spots that appeared recently where none existed before. Pre-existing spots since childhood suggest enamel defects.
- Location: White spots located along the gum line or between teeth indicate a higher chance of being decay as these are prime areas for plaque accumulation and acid damage over time.
- Texture & Color: Smooth white spots generally indicate fluorosis or other developmental conditions. Rough, frosted texture and yellowish hues signal demineralization typical of early decay.
- Cavity Testing: Your dentist should evaluate any questionable spots for softness or cavities beneath the intact enamel layer, using visual examination, probing, and bite-wing x-rays. This can help differentiate decay versus harmless spots.
- Risk Assessment: Increased risk factors for cavities like poor diet, dry mouth, or poor oral hygiene raise concerns that white spots may be early decay.
Your dentist can best differentiate if newly formed white spots relate to active decay or not after a clinical exam. They can then guide the appropriate treatment based on the diagnosis.
How to Treat White Spots on Teeth
The ideal treatment for white spots is based on the determined cause:
For fluorosis or enamel defects:
- No treatment is needed since these spots pose no harm to teeth. At best, cosmetic treatment may be considered.
*Try professionally administered products for mild fluorosis spot reduction. Avoid over-the-counter whitening products.
*For moderate to severe cases, enamel microabrasion, dental bonding or veneers can mask appearance.
For active decay white spots:
- Fluoride or remineralizing pastes and gels help reharden and rebuild white spot lesions.
- For cavitated lesions beneath intact enamel, restorations like fillings or inlays may be required to treat decay.
- Regular professional cleanings aid remineralization and monitoring.
For orthodontic white spots:
- Maintain impeccable oral hygiene during orthodontic treatment.
- Use prescription-strength fluoride toothpaste.
- Apply fluoride varnish around braces to remineralize spots after appliance removal.
- Consider microabrasion or bonding if remineralization fails.
For traumatic white spots:
- Topical fluoride, calcium and phosphate treatments to strengthen enamel.
- Try desensitizing toothpastes for sensitive spots.
- Protect teeth from further injury with mouthguards if needed.
For whitening-induced white spots:
- Avoid any further whitening procedures and abrasive pastes.
- Use fluoridated products to remineralize and reduce sensitivity.
Home Care Tips for White Spots

Here are some helpful tips for managing white spots at home:
- Use a fluoridated toothpaste approved by your dentist and limit use on young children.
- Choose non-abrasive toothpaste with baking soda rather than hydrogen peroxide.
- Limit acidic and sugary snacks and beverages which contribute to decay.
- Brush twice daily with a soft-bristled toothbrush and avoid over-brushing.
- Floss daily and use an antibacterial mouthwash to maintain low plaque levels.
- Drink fluoridated water and reduce intake of bottled water high in fluoride.
- Avoid teeth whitening products as they can worsen the appearance of white spots.
- Have any new, suspicious spots or spot progression examined quickly by your dentist.
When to See a Dentist
You should consult your dentist if you notice any of the following about your white spots:
- Sudden development of new white spots
- Existing white spots are becoming larger or more pronounced
- Spots have a rough texture, are soft, or you can poke a hole in them
- White spots are turning yellow, brown or black
- Spots are sensitive, painful, or tingle upon stimulation
- You have other major risk factors for tooth decay
- Spots are causing cosmetic concerns
Seeing your dentist promptly can help diagnose white spots early to determine if they relate to decay or not. They can also guide and deliver the needed treatment based on your diagnosis.
For decay-related white spots, early intervention is key to remineralize enamel and prevent cavities from forming. If cavities exist beneath the enamel, restorative options can repair damage and restore tooth structure before extensive treatment is required.
Key Takeaways: Do White Spots Mean Cavities?
- White spots have various causes – fluorosis, early decay, developmental defects, orthodontics, whitening damage or trauma. They appear as opaque demineralized areas of enamel.
- White spots alone do not indicate cavities – newly formed, rough-textured spots near the gum line have the highest chance of relating to early decay.
- Progression of white spots to brown/black and sensitivity implies advancing decay. Seek dental evaluation immediately in such cases.
- Treatment depends on the diagnosis but may include fluoride, calcium, phosphate therapies, microabrasion, fillings, or bonding.
- Maintain strong oral hygiene and regular dental visits for assessment of white spots to preserve tooth health and prevent cavities.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common causes of white spots on teeth?
The most common causes of white spots on teeth include:
- Fluorosis – From excess fluoride intake while enamel was maturing
- Tooth decay – Early signs of cavities forming
- Enamel defects – Hypoplasia, hypomineralization
- Orthodontic treatment – Demineralization near braces
- Tooth whitening products – Chemical-induced enamel erosion
How can I tell if a white spot is from fluorosis or decay?
Some distinguishing signs:
- Fluorosis spots tend to be bilateral, smooth, glossy, with faint white lines following tooth shape.
- Decay spots often start as frosty, opaque patches near gum line that are rough-textured and turn yellowish.
- Fluorosis is present from childhood; decay spots develop later in life.
- Fluorosis rarely causes sensitivity while decay spots may elicit pain from hot/cold stimuli.
What is the best treatment for white spots on teeth?
It depends on the cause:
- Active decay spots = Prompt dental treatment, fillings if cavitated.
- Fluorosis spots = Whitening, microabrasion, or dental bonding if appearance bothersome.
- Enamel defects = Topical fluoride to strengthen enamel.
- Orthodontic spots = Improved hygiene, fluoride treatments.
- Whitening spots = Cease whitening, fluoride to remineralize.
Can white spots be a sign of teeth needing deep cleaning?
White spots near the gum line can potentially indicate the need for deep cleaning by dental professionals. If plaque builds up it leads to gum inflammation and enamel demineralization along the gum margin. Removing plaque/tartar below the gum line with deep cleaning may help reduce white spot progression.
How can I prevent more white spots from forming on my teeth?
To prevent more white spots:
- Maintain good oral hygiene – brushing, flossing, mouthwash use.
- Limit sugary and acidic foods and drinks.
- Get regular dental cleanings and exams.
- Use fluoride toothpaste/rinse daily.
- Drink fluoridated water.
- Wear mouthguard if you grind teeth.
- Avoid overusing teeth whitening products.