Blue light is commonly used in teeth whitening treatments to enhance and accelerate the whitening process. But why exactly is blue light so effective for whitening teeth? Here is a comprehensive overview of the science behind blue light teeth whitening.
How Does Teeth Whitening Work?
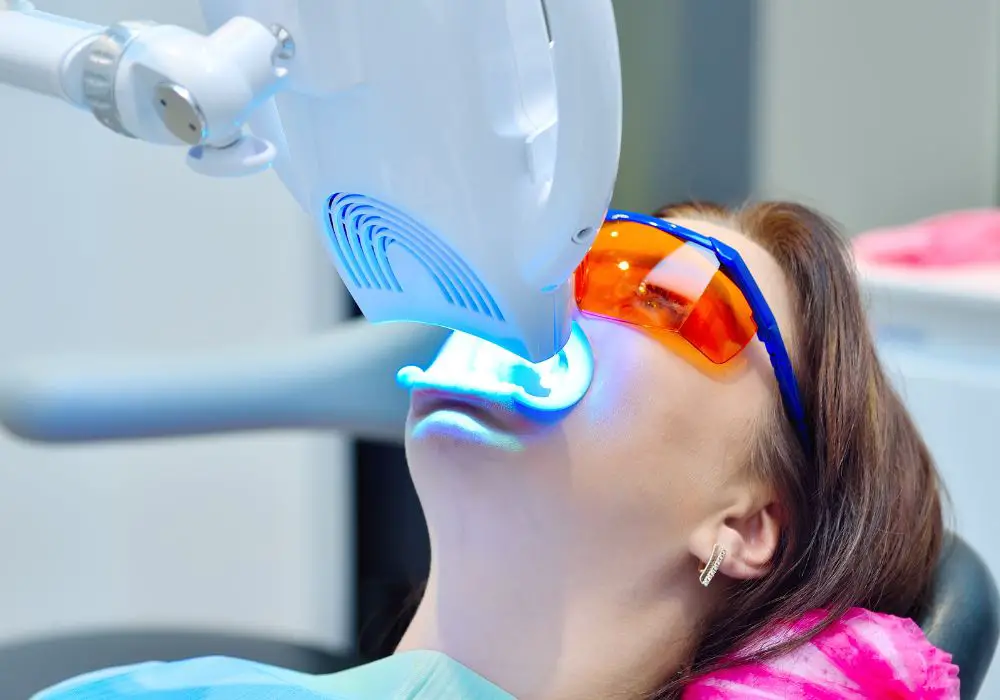
Before understanding why blue light works, it’s helpful to first understand how teeth whitening works in general.
The natural color of teeth is subtly off-white with a very slight yellowish tint. However, over time, teeth can become stained or discolored from food and drink, smoking, medication use, or trauma. These stains can penetrate deep into the microscopic pores and channels in the enamel and dentin layers of the teeth.
The most common teeth whitening products use peroxide-based whitening gels. Peroxide acts as a bleaching agent that can penetrate deep into the tooth structure and break up those stubborn intrinsic stains.
There are two main types of peroxide used in whitening formulations:
- Carbamide peroxide – This whitening agent breaks down into hydrogen peroxide and urea. Carbamide peroxide gels are typically in concentrations between 10-22%.
- Hydrogen peroxide – A stronger bleaching agent than carbamide peroxide. Hydrogen peroxide whitening gels are usually 25-40% concentration.
When these peroxide whitening gels are applied directly to the surface of the teeth, the peroxide breaks down and releases unstable, reactive oxygen molecules. These oxygen radicals are able to penetrate deep into the microscopic enamel rods and dentin tubules within the teeth.
The oxygen molecules then react with the long chained, organic pigment molecules that cause the intrinsic stains. The peroxide effectively breaks apart and decolors these pigment molecules by cleaving the carbon double bonds in their molecular chain. This chemical reaction “bleaches” the stains and makes the teeth visibly whiter.
The effects of the peroxide cause oxidation and gradual decomposition of the deep set stains, making the teeth appear lighter and whiter. However, this whitening process takes time when using the gel alone.
The Role of Light in Activation
Light plays an important role in speeding up and activating the whitening process.
While the peroxide gel on its own can provide moderate whitening over time, the bleaching effect is accelerated and enhanced when the peroxide is activated by light energy.
Specialized whitening gels contain light-sensitive, photoreactive compounds that are designed to strongly react and respond to certain wavelengths of light. When these photosensitive compounds are exposed to specific colors of light, they absorb the light photons and become excited. This triggers the release of a rapid burst of oxygen radicals from the peroxide component in the gel.
Why Blue Light is the Most Effective for Whitening
Extensive research has found that blue light, which lies between 400-500 nm on the visible light spectrum, provides the optimal wavelength for activating whitening gels.
There are several important reasons why blue light is the best for accelerating the whitening reaction:
Maximizes Penetration into Enamel
Due to its relatively short wavelength, blue light is able to penetrate the enamel layer with greater depth and efficiency compared to longer wavelength colors that lie in the green, yellow, orange and red range.
This enhanced penetration into subsurface enamel allows for activation of stains locked deep in the tooth structure. In contrast, the longer wavelengths cannot penetrate as deeply due to scattering and absorbance by the enamel crystallites.
Selectively Activates Photosensitive Compounds
The photosensitive compounds incorporated into whitening gel formulas are designed to specifically react to light in the blue wavelength range.
When exposed to wavelengths of blue light, these photosensitive compounds exhibit heightened reactivity and release a greater concentration of oxygen radicals that activate the bleaching reaction.
Minimizes Heat Damage to Teeth
Longer wavelength lights on the red end of the visible color spectrum, such as some UV lights, produce much more intense heat compared to shorter wavelength light.
Excess heat exposure could potentially damage teeth and irritate the pulp. This thermal damage is minimized with blue light compared to other lights.
Breaks Up Stubborn Stains
While UV light can provide high energy density, it is not as effective at breaking up stubborn intrinsic stains lodged deep in the tooth structure compared to blue light.
Blue light provides the optimal combination of energy density and depth of light penetration. This enables it to better activate the release of oxygen molecules that can diffuse into enamel micropores and dentin fractures to react with stubborn stains.
How Blue Light Whitening Treatments Work
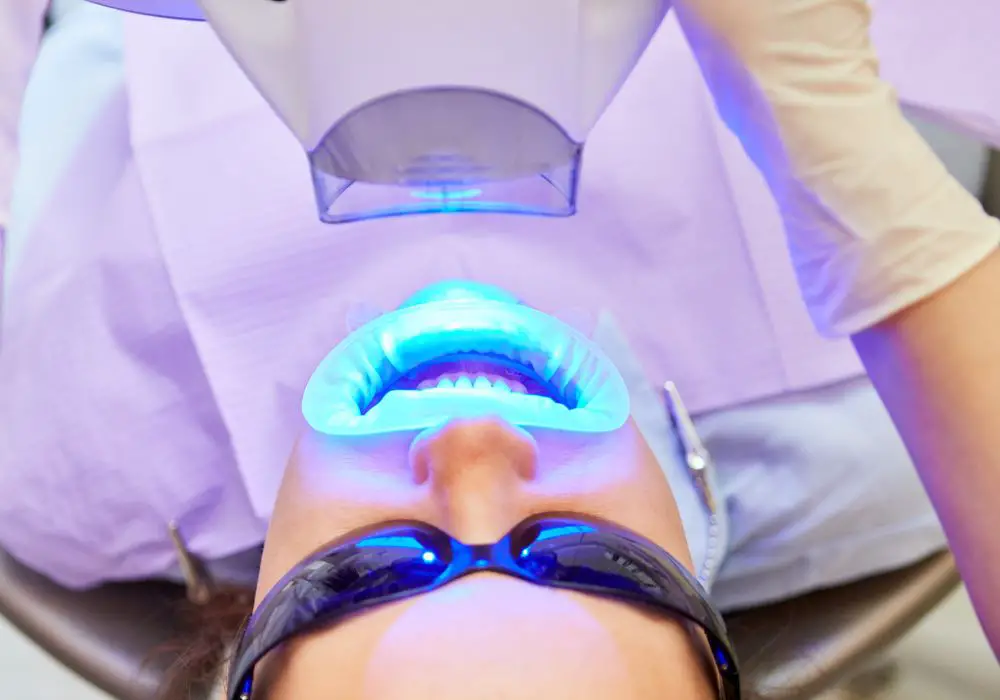
During a professional blue light teeth whitening procedure, the dentist will first isolate the teeth from the gums and lips. Then a concentrated hydrogen peroxide whitening gel, between 25-40%, is applied evenly across the surface of the teeth.
The patient then sits in front of a specialized blue LED light source, which emits light in the optimal 400-500 nm wavelength range. The light is shone on the teeth for around 15-20 minutes.
In at-home whitening strips or custom tray methods, the strips/trays are also embedded with peroxide gel and worn while using a blue LED light source for a longer period.
When the blue light shines on the teeth undergoing treatment, it penetrates through the enamel layer. This energizes the photosensitive compounds in the gel, which rapidly release reactive oxygen molecules from the peroxide compound.
As this light-activated bleaching reaction occurs repeatedly across treatment sessions, the stains become lighter and lighter until the teeth reach the desired whiteness.
The Science of How Blue Light Interacts with Teeth and Gel
The physics and biochemistry behind how blue light interacts with teeth and whitening gel during the whitening process is fascinating but complex. Here is a brief overview:
- Blue light comprises photons carrying energy at wavelengths between 400-500 nm.
- When these photons are absorbed by the photosensitive molecules in gel, their electrons get boosted into an excited, high energy state.
- In this excited state, the photosensitive molecules become highly reactive and trigger the release of oxygen radicals from the peroxide.
- The freed oxygen molecules quickly diffuse into the enamel and dentin matrix.
- The oxygen reacts with large pigmented stain molecules lodged deep in the teeth.
- It does this by cleaving apart the carbon double bonds in the organic molecular chain of the pigment molecules.
- Breaking these bonds decolors and degrades the stain molecules, effectively “bleaching” the stains.
- Repeated cycles of light activation, oxygen release, and reaction gradually decompose the stains over the course of the treatment, making teeth whiter.
- Special compounds in the gel help pull out the destained particles through the enamel, removing stains.
The Blue Light Advantage
Blue light activated tooth whitening has revolutionized teeth whitening because the light energy input exponentially accelerates the bleaching chemical reaction.
Some major advantages of professional blue light whitening:
- Whitening sessions are much shorter in length since the light speeds up the whitening effect.
- The light energy enhances the oxidizing and bleaching effects of the peroxide leading to dramatically whiter teeth, up to six shades lighter.
- The blue light helps destroy bacteria in the mouth during the treatment.
- When used properly, blue light can whiten teeth and gums safely and efficiently.
Numerous clinical studies have proven blue light activated peroxide treatments can whiten teeth up to six shades on the dental shade guide after just a single 15-minute session.
The combination of the blue light photonic energy and advanced peroxide gels has a synergistic effect, producing faster and better whitening results than just using peroxide alone.
Considerations of Blue Light Whitening
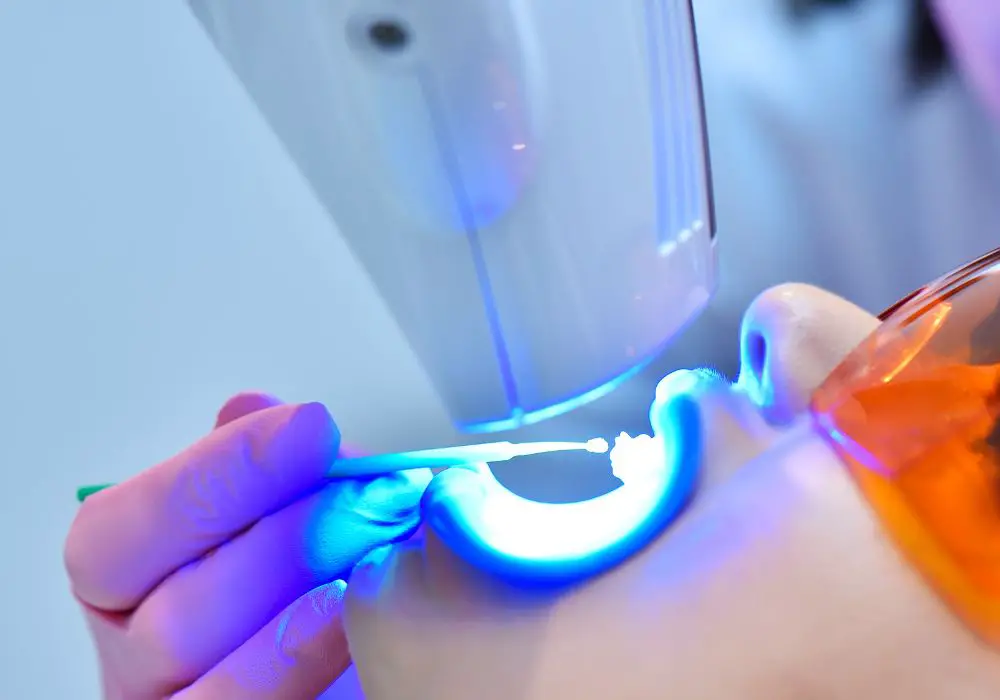
While dental organizations confirm it is widely safe when properly performed by a licensed dentist, here are some considerations around the use of blue light for whitening:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their dentist before undergoing whitening.
- Whitening treatments may cause temporary tooth sensitivity or gum irritation in some people. This usually resolves within 1-2 days.
- Applying the concentrated peroxide gels to the gums can burn and irritate them, so care should be taken to avoid this.
- Whitening is not recommended for children under 16 years old.
- Depending on lifestyle factors, whitening results can last from 1-3 years, but may need to be periodically repeated as some stains can gradually return over time.
- Whitening treatments may be less effective at removing tetracycline antibiotic stains or for people with thin enamel.
With proper precautions, blue light activated professional whitening has proven to be a very safe and highly effective cosmetic treatment for whitening discolored teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions on Blue Light Teeth Whitening:
Does blue light teeth whitening work?
Yes, multiple clinical studies have conclusively shown blue light activated whitening with a hydrogen peroxide gel is able to make teeth up to six shades whiter after just one 15-minute in-office treatment session. The blue light exponentially accelerates and enhances the chemical bleaching reaction.
Is blue light teeth whitening safe?
When performed properly by a licensed dentist, blue light whitening is very safe for teeth and gums. The FDA and dental organizations confirm its safety and efficacy when manufacturer protocols are followed. Minor side effects like sensitivity are usually temporary.
How long do the results of blue light teeth whitening last?
With proper maintenance and avoiding discoloring foods/drinks, professional blue light whitening results can last anywhere from 1-3 years. However, for smokers or coffee/tea/red wine drinkers, some stains may gradually return sooner.
Does dental insurance cover blue light teeth whitening?
Most dental insurance does not cover the cost of professional whitening treatments since it is considered a cosmetic procedure rather than medically necessary. However, some dental plans may provide partial reimbursement for whitening costs. Check with your specific provider.
Is blue light or UV light better for teeth whitening?
Blue light is unequivocally safer and more effective than UV light for activating whitening gels and degrading tooth stains. UV light can potentially damage teeth and is not as capable of stimulating the proprietary photosensitive compounds in whitening gel that react best to blue light.
Conclusion
In summary, blue light provides the optimal light source to activate whitening gels and accelerate the chemical bleaching reaction for professional, rapid teeth whitening treatments. Because of its photochemical interactions with peroxide gels and tooth stains, blue light is uniquely capable of enhancing and speeding up the whitening process far better than other colors of visible or UV light. With blue light technology, dramatic whitening results of up to six shades lighter can be achieved in less time. While not a substitute for dental hygiene, professional blue light whitening gives people the confidence of a whiter, brighter smile.