Having yellow teeth as a teenager can be upsetting. White, healthy-looking teeth are associated with beauty, success, and confidence. Discolored teeth can make teens self-conscious about their smile and reluctant to show their teeth in photos or while talking.
During the teen years, teeth go through major changes. The American Association of Orthodontists reports that all 32 permanent teeth typically finish developing by age 13. The mineralization process that gives teeth their color is mostly complete. This critical window makes the teen years important for preventing permanent stains and damage.
Main causes of yellow teeth in teenagers
There are several key reasons why a teenager may develop yellow teeth:
1. Poor oral hygiene habits
Not properly brushing and flossing allows plaque buildup on teeth. Plaque is a sticky film containing bacteria that forms on teeth. When plaque stays on teeth for extended periods of time, it eventually hardens into tartar that adheres to the teeth. Both plaque and tartar can stain teeth yellow.
Teenagers are notorious for skipping brushing and flossing with their busy schedules. According to studies, over 60% of teens do not brush twice a day or floss once a day as recommended. Irregular oral hygiene and lack of consistency allows staining compounds from food and drinks to accumulate on teeth and discolor the enamel.
2. Smoking cigarettes
Smoking introduces very harsh staining compounds into the mouth like tar and nicotine. These staining substances soak into the grooves of teeth and bind to the enamel. The more frequently and longer someone smokes, the more severe the yellowing effect on their teeth.
While smoking rates have dropped among teenagers in recent years, data shows that still over 3.6 million high school students smoke cigarettes. Even occasional smoking can start to yellow teeth. The enamel takes on a dull, yellowish tint over time with continued exposure to cigarette smoke.
3. Drinking coffee, tea and soda
Coffee, tea, and soda all contain pigments that attach to tooth enamel if consumed frequently. Tea stains teeth due to both its dark color and high tannin content. Coffee causes yellowing due to its deep brown shade. Soda not only contains staining food dye, but the acidity also erodes and yellows the tooth enamel.
These popular beverages are often consumed in large amounts by teens. The 2015-2020 Dietary Guidelines for Americans reported that teens ages 14-18 drink on average 1.2 cups of coffee, 0.6 cups of tea, and 1.0 can of soda per day. Sipping these staining drinks throughout the day allows the pigments to continually coat the teeth. Straws can help reduce contact between staining compounds and the front teeth.
4. Enamel hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is a defect in the mineralization of the teeth. The enamel does not fully form and remains thin and porous. This allows more of the yellow-hued dentin underneath the enamel to show through, creating yellow patches or streaks on the teeth.
Causes of enamel hypoplasia include:
- Poor childhood nutrition with deficiencies in calcium, vitamin D or phosphates
- Childhood dental fluorosis from excessive fluoride intake while teeth were forming
- Developmental disorders like severe jaundice as an infant
5. Tetracycline staining
Taking tetracycline antibiotics extensively between the ages of 2 and 8 can permanently stain teeth yellow-gray. Tetracycline is incorporated into the structure of developing enamel and dentin as the teeth are forming. When exposed to sunlight, the tetracycline turns dark.
Teenagers who took this medication for chronic childhood infections like acne, urinary tract infections or pneumonia are at risk of discolored enamel as young adults. The stain may appear in horizontal bands or be scattered as dark spots.
6. Excess fluoride intake
While fluoride at normal levels helps strengthen enamel, too much fluoride can actually stain and mottle formed enamel. High fluoride content in drinking water, inappropriate use of fluoride supplements, or overuse of prescription fluoride toothpastes and gels can all contribute to mild fluorosis discoloration.
Teenagers who swallow toothpaste instead of spitting while brushing or use more than a pea-sized amount of prescription fluoride gel are at higher risk of white spots or opaque enamel staining.
Ways to prevent yellowing of teeth
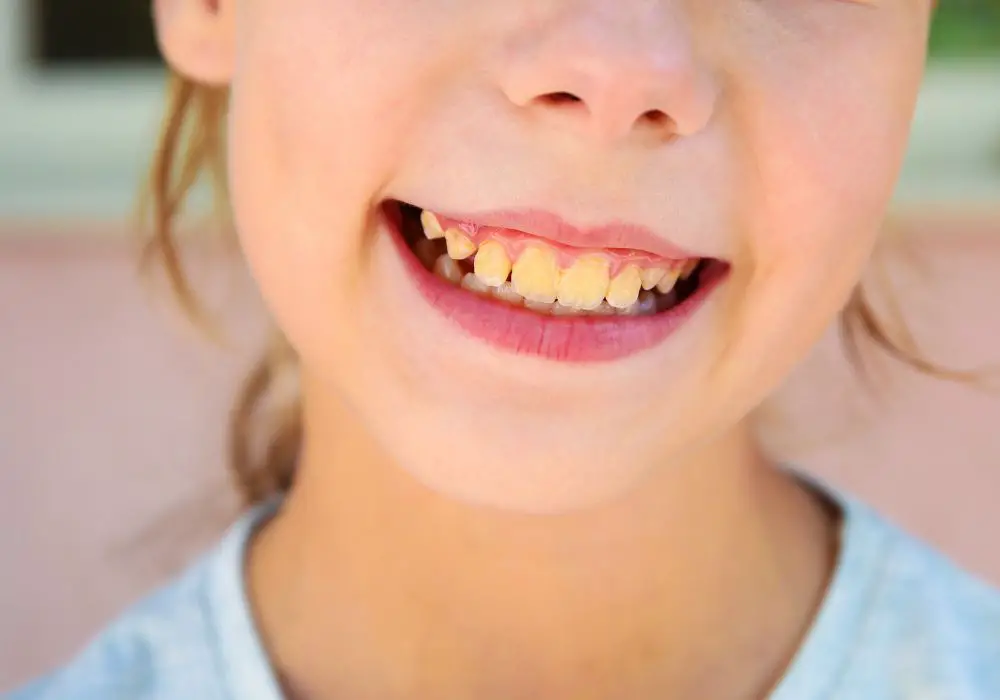

Discoloration of teeth can be prevented through developing good daily oral care habits:
Brush properly
- Brush teeth thoroughly for 2 full minutes twice per day. Many only brush for 30-60 seconds and miss plaque on the inner and outer surfaces.
- Hold the toothbrush at a 45 degree angle to the gums and use gentle circular motions. Apply light pressure -scrubbing too aggressively can damage enamel.
- Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and replace it every 3-4 months when bristles become frayed and worn. Older brushes are less effective at removing plaque.
- Use ADA approved fluoride toothpaste to strengthen enamel. Look for the ADA Seal on the packaging.
Floss every day
- Flossing removes plaque and food particles between teeth that brushing misses. Floss once daily, gently curving the floss around the sides of each tooth.
- Interdental cleaners like irrigation devices and tiny brushes can also clean between teeth.
Limit stain-causing foods and drinks
- Restrict coffee, tea, soda, juices and sports drinks to mealtimes only. Rinse mouth with water after consuming.
- Drink staining beverages quickly through a straw to reduce contact with front teeth.
- Avoid swishing or holding drinks like wine in the mouth. The prolonged contact increases staining.
Stop smoking
- Cigarette and hookah smoking quickly yellow teeth. Stopping smoking improves gum health and prevents worsening of tobacco stains.
- Ask your doctor about nicotine replacement medications or counseling programs to help quit smoking.
Get professional cleanings
- Have teeth professionally cleaned by a dental hygienist every 6 months to scale away tough extrinsic stains.
- Regular cleanings allow early detection of cavities or other problems. Teens with braces require more frequent dental visits.
Whitening treatments for yellowed teeth
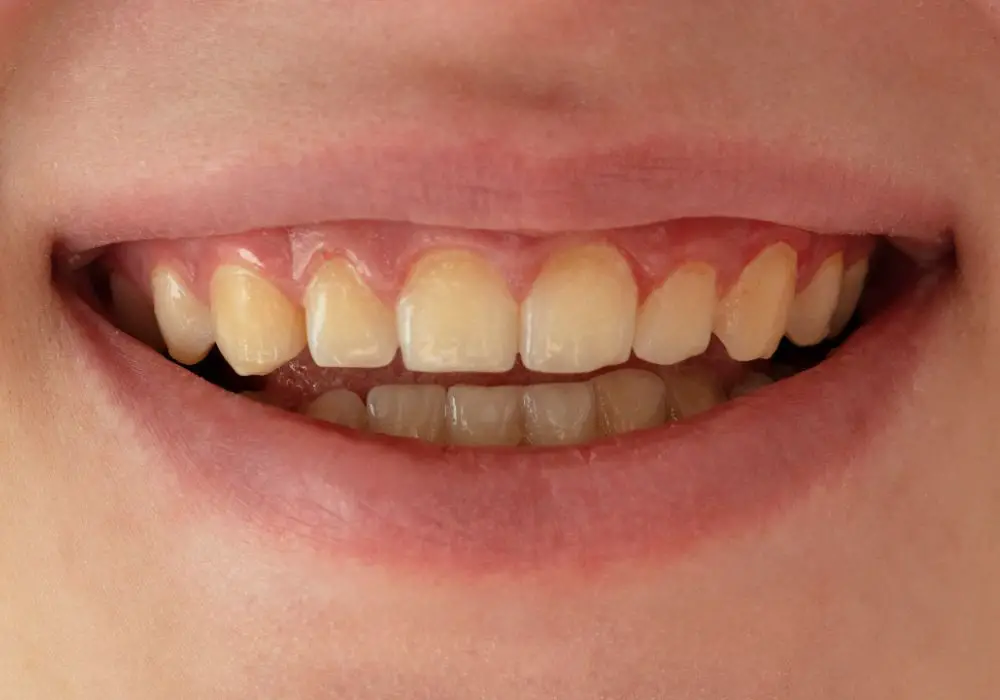
If teeth have already yellowed, these are options to brighten and remove stains:
Whitening toothpastes
- Whitening pastes contain mild abrasives like baking soda or hydrogen peroxide that provide gentle polishing and scrub away surface stains.
- Use whitening toothpaste twice daily in place of regular toothpaste. Look for the American Dental Association (ADA) Seal.
- Results are gradual over 2-4 weeks of continued use. Whitening pastes maintain brightness but won’t significantly lighten deep stains.
Over-the-counter whitening strips and gels
- Whitening strips coated with peroxide gel mold to teeth and brighten over 1-2 week periods with daily use.
- Tray systems come with custom-fit plastic trays prefilled with peroxide whitening gel to wear for 30-60 minutes a day.
- Use products formulated for teenager or sensitive teeth so peroxide percentage is appropriate and safe on enamel.
- Apply OTC gels sparingly and follow directions to avoid gum inflammation.
Professionally supervised whitening
- In-office power whitening performed by a dentist achieves the most dramatic results in 1-2 visits. Higher peroxide concentrations are used with specialized curing lights.
- Custom-fitted trays with professional strength take-home whitening gel are also available through dentists. Wear for 1-2 hours per day.
- Teeth are isolated from gums during professional treatments to avoid burns. Dentists can also remedy any increased sensitivity.
Other whitening methods
- Air polishing with baking soda at the dentist’s office can remove surface stains from grooves and between teeth. No peroxide is used.
- Enamel microabrasion involves a dentist lightly sanding stained enamel with an acidic compound and abrasive paste. It removes thin discolorations.
- If other methods are ineffective, veneers or dental bonding can mask stubborn intrinsic stains for a brighter appearance.
Maintaining a white smile
Once teeth are whitened, it’s important to continue preventive care to avoid re-staining:
- Brush with whitening or tartar control toothpaste twice daily and floss thoroughly once daily.
- Use a fluoride mouthwash to strengthen enamel against new stains.
- Drink staining beverages in moderation and use a straw to bypass teeth. Rinse afterwards.
- Limit juice, tomato sauce, and dark berries which can re-stain whitened teeth.
- Have professional cleanings every 6 months to catch stains early before they worsen.
- Apply OTC whitening strips or gel every 3-6 months as needed to maintain results. Follow product directions closely.
With diligent oral hygiene and moderate use of beverages like coffee and soda, you can keep a bright white smile for years to come. Seek professional help from your dentist if teeth ever become severely discolored again.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are my teeth yellow even though I brush daily?
Brushing alone may not fully remove plaque and surface stains on teeth. Yellow teeth when brushing regularly could indicate:
- Incomplete plaque removal due to brushing too quickly or with improper technique. Take at least 2 minutes to brush.
- Insufficient plaque removal from hard to reach areas. Use floss or interdental cleaners to clear bacteria between teeth.
- Inadequate brush replacement allowing worn bristles to become less effective. Replace brushes every 3-4 months.
- Intrinsic tetracycline staining or fluorosis that requires more than brushing to lighten stains within the enamel.
Can whitening damage your teeth?
When used correctly, whitening is safe for enamel. However, misusing whitening products can cause harm:
- Over-bleaching with peroxide gels over the recommended duration can increase sensitivity and inflammation of the gums.
- Using highly acidic whitening gels without professional supervision can erode enamel.
- Applying whitening products too frequently can wear away enamel over time.
Consult your dentist before DIY whitening and always follow the product instructions carefully. In-office whitening is done under controlled conditions to prevent damage.
Is yellow teeth genetic?
Genetics can play a role in tooth color. Enamel thickness and properties are determined partly by genes passed down in families.
Thinner enamel allows more yellow dentin to show through. Tetracycline staining can also have a genetic component in how the teeth took up and bound the antibiotic during formation.
While you can’t change inherited genetics, you can influence environmental factors that affect tooth color through oral hygiene, diet, and avoiding stain-causing habits.
Can you whiten veneers?
Veneers are thin porcelain covers placed over the front of teeth. Since they are not natural enamel, typical at-home whitening products will not lighten them. However, the dentist can whiten natural teeth around veneers to brighten your overall smile.
In-office professional whitening is sometimes an option for veneers that have gotten darker over time, but the process is only successful on some types of porcelain. Check with your dentist before attempting to whiten veneered teeth.
How can I prevent future yellowing of my teeth after whitening?
To keep your brightened smile, be diligent about your daily oral hygiene and limit stain-causing foods and drinks.
- Brush thoroughly twice a day and floss once daily
- Use whitening or tartar-control toothpaste
- Get professional cleanings every 6 months
- Drink dark beverages through a straw
- Quit smoking and other tobacco habits
You can also do periodic touch-up whitening treatments at home 2-4 times per year as needed to maintain your desired shade.