Have you ever wondered if having 34 teeth is possible? While the normal adult human has 32 teeth, there are rare cases where individuals have extra teeth, a condition known as hyperdontia. This can result in a total of 34 or more teeth in a person’s mouth.
Hyperdontia can occur in any area of the dental arch and can affect any dental organ. The extra teeth can cause a variety of issues, such as crowding, pushing other teeth out of position, and even damaging the roots of other teeth. Cysts may also form around the extra teeth, leading to further complications.
While hyperdontia is considered rare, it is not impossible to have 34 teeth or more. If you suspect you may have extra teeth or are experiencing any dental issues, it is important to consult with a dental professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Understanding Human Dentition
As you may already know, human dentition refers to the arrangement, number, and types of teeth in the mouth. Understanding dentition is crucial to maintaining good oral health. In this section, we will explore the basics of human dentition.
Primary and Permanent Dentition
Humans have two sets of teeth during their lifetime: primary (baby) teeth and permanent (adult) teeth. Primary teeth are the first set of teeth that erupt in the mouth, usually between six months and two years of age. They are eventually replaced by permanent teeth, which begin to erupt around six years of age and continue until early adulthood.
There are typically 20 primary teeth, and they are divided evenly across the maxilla (upper jaw) and mandible (lower jaw). Permanent teeth, on the other hand, consist of 32 teeth, including four wisdom teeth. The teeth are divided into four different classes based on their shape and function: incisors, canines, premolars, and molars.
Types of Teeth
Each type of tooth has a specific function in the mouth. Incisors are the eight front teeth, four on the upper jaw and four on the lower jaw. They are used for biting and cutting food. Canines are the four pointed teeth located next to the incisors. They are used for tearing and ripping food.
Premolars and molars are located in the back of the mouth and are used for grinding and crushing food. Premolars are located between the canines and molars, and there are eight of them in total. Molars are the largest teeth in the mouth and are located at the back of the mouth. There are 12 molars in total, including four wisdom teeth.
Is 34 Teeth Possible?
Based on the information above, you may be wondering if it is possible to have 34 teeth. The answer is yes! While the typical number of teeth in a human mouth is 32, some people may have extra teeth, known as supernumerary teeth. These extra teeth can develop in any part of the mouth and can cause problems such as crowding and misalignment of teeth.
In conclusion, understanding human dentition is essential to maintaining good oral health. Knowing the types and functions of teeth can help you take better care of your teeth and identify any potential problems. And while having 34 teeth may be uncommon, it is indeed possible due to the presence of supernumerary teeth.
The Possibility of 34 Teeth
It is possible for some individuals to have 34 teeth instead of the normal 32. This condition is known as hyperdontia or supernumerary teeth. Hyperdontia is a rare condition, affecting only about 1-4% of the population. The extra teeth can grow anywhere in the dental arch and can affect any dental organ.
The cause of hyperdontia is still unknown, but it is believed to be a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Some studies have identified PAX9 and MsX1 genes being affected alongside some others. Environmental factors such as radiation exposure, infections, and trauma to the mouth during childhood can also increase the likelihood of developing supernumerary teeth.
The extra teeth can be classified into different types based on their location and shape. Some of the common types of supernumerary teeth include:
- Mesiodens: These are extra teeth that grow in the front of the upper jaw, between the two central incisors.
- Distomolars: These are extra molars that grow behind the third molars.
- Paramolars: These are extra molars that grow next to the regular molars.
The presence of supernumerary teeth can cause various dental problems such as crowding, misalignment, and impaction. These problems can lead to difficulties in chewing, speaking, and maintaining good oral hygiene.
If you suspect that you have an extra tooth or teeth, it is important to consult your dentist. Your dentist can perform a thorough examination and take X-rays to determine the location, shape, and size of the extra teeth. Treatment options for hyperdontia depend on the location and size of the extra teeth and may include extraction or orthodontic treatment.
In summary, while having 34 teeth is rare, it is possible due to the condition of hyperdontia. If you suspect that you have an extra tooth or teeth, it is important to consult your dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Genetic Factors Influencing Tooth Count
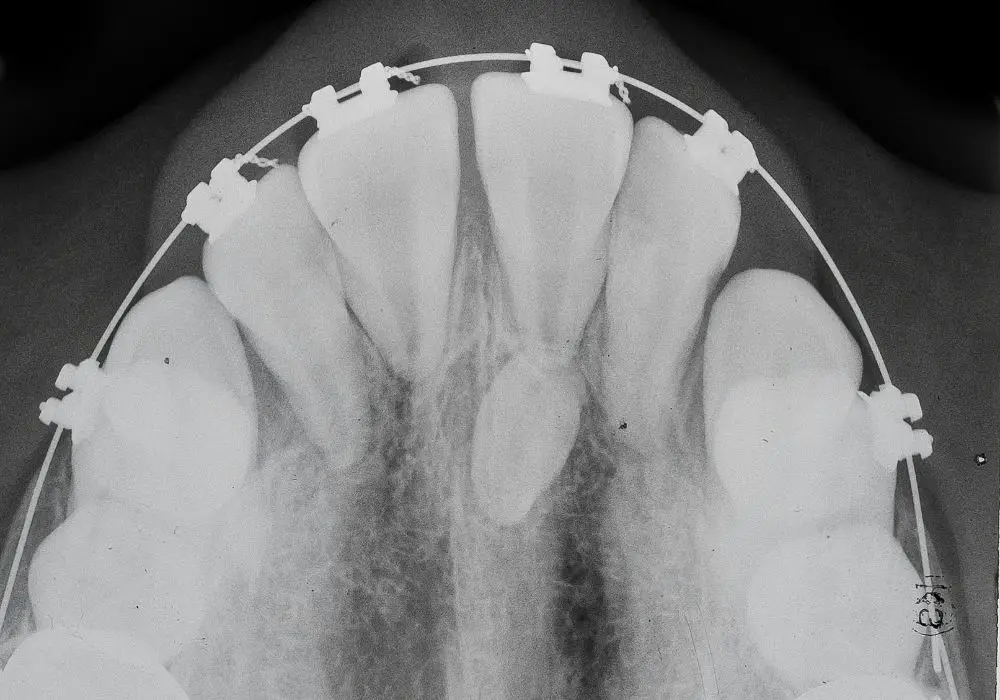
Tooth development is a complex process that involves both genetic and environmental factors. Genetics play a significant role in determining the number of teeth a person has. The normal number of teeth in an adult is 32, but some people can have more or fewer teeth. In this section, we will discuss the genetic factors influencing tooth count.
Tooth Development and Genetics
Tooth development is a highly regulated process that involves the interaction of many genes. The genetic information that controls tooth development is present in the DNA of every cell in the body. The genes that control tooth development are responsible for determining the number, size, shape, and position of teeth.
Genetic Disorders Affecting Tooth Count
Genetic disorders that affect tooth development can result in abnormal tooth count. For example, people with Down syndrome often have fewer teeth than normal. Similarly, people with cleidocranial dysplasia may have extra teeth or missing teeth.
Environmental Factors and Tooth Count
Environmental factors can also affect tooth count. For example, poor nutrition during tooth development can result in fewer teeth. Similarly, exposure to certain drugs or chemicals during tooth development can also affect tooth count.
Conclusion
In conclusion, genetics play a significant role in determining tooth count. Genetic disorders and environmental factors can also affect tooth count. If you have concerns about your tooth count, you should consult with a dentist or genetic counselor.
Dental Anomalies
Dental anomalies refer to abnormalities in the size, shape, number, and structure of teeth. These anomalies can occur due to various factors, including genetic mutations, environmental factors, and developmental disorders.
One of the most common dental anomalies is tooth agenesis, which is the lack of development of one or more teeth. This anomaly can occur in both primary and permanent teeth and is often caused by genetic factors. Tooth agenesis can lead to dental crowding, misalignment, and other orthodontic problems.
Another dental anomaly is supernumerary teeth, which are extra teeth that develop in addition to the regular number of teeth. Supernumerary teeth can cause dental crowding and misalignment and may require extraction.
Tooth shape and size anomalies are also common and can occur due to genetic mutations or environmental factors. These anomalies can lead to dental crowding, misalignment, and other orthodontic problems.
In some cases, dental anomalies can be asymptomatic and may not require treatment. However, in other cases, they can cause significant dental problems and may require orthodontic treatment, such as braces, or surgical intervention, such as tooth extraction.
If you suspect that you have a dental anomaly, it is important to consult with a dental professional who can diagnose and treat the condition. Your dentist or orthodontist can recommend the best course of treatment based on the specific type and severity of the anomaly.
Hyperdontia: Excessive Tooth Condition
Hyperdontia is a dental condition where a person has more teeth than the usual number. The normal number of teeth in adults is 32, but people with hyperdontia can have up to 50 or more teeth in their mouth.
This condition is also known as supernumerary teeth. The extra teeth can grow anywhere in the mouth, but they are most commonly found in the upper jaw. Hyperdontia can affect both primary and permanent teeth.
The causes of hyperdontia are not fully understood, but it can be due to genetic factors or environmental factors. Some medical conditions such as Gardner’s syndrome, cleidocranial dysplasia, and cleft lip and palate can also cause hyperdontia.
The symptoms of hyperdontia can vary depending on the number and location of the extra teeth. Some people may not experience any symptoms, while others may have difficulty eating, speaking, and maintaining proper oral hygiene. In some cases, the extra teeth can cause overcrowding, misalignment, and other dental problems.
Treatment for hyperdontia depends on the severity of the condition and the location of the extra teeth. In some cases, the extra teeth may need to be extracted to prevent dental problems. Orthodontic treatment may also be necessary to correct misalignment and overcrowding.
In conclusion, hyperdontia is a dental condition that can cause excessive tooth growth in the mouth. It can be caused by genetic or environmental factors, and it can lead to various dental problems. If you suspect that you have hyperdontia, it is important to consult a dentist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Implications of Having 34 Teeth
Having 34 teeth is a rare condition known as hyperdontia. While it may seem like having extra teeth would be a good thing, it can actually have some negative implications for your oral health.
Firstly, having extra teeth can cause overcrowding in your mouth, which can lead to crooked or misaligned teeth. This can make it difficult to properly clean your teeth, leading to an increased risk of tooth decay and gum disease.
Additionally, having extra teeth can also cause issues with your bite, making it difficult to properly chew your food and potentially leading to jaw pain or headaches.
If you have hyperdontia, it’s important to work closely with your dentist to develop a treatment plan. This may involve removing some of the extra teeth to alleviate overcrowding and improve your overall oral health.
Overall, while having extra teeth may seem like an interesting quirk, it’s important to be aware of the potential implications and work with your dentist to ensure that you’re taking the necessary steps to maintain good oral health.
Dental Treatment Options for Extra Teeth
If you have been diagnosed with hyperdontia or supernumerary teeth, you may be wondering what treatment options are available to you. The good news is that there are several dental treatments available to help manage this condition.
Extraction
One of the most common treatments for extra teeth is extraction. This involves removing the extra tooth or teeth from your mouth. Extraction is typically recommended if the extra teeth are causing problems such as crowding or misalignment of your other teeth.
Orthodontic Treatment
Orthodontic treatment such as braces or clear aligners may also be recommended to manage extra teeth. These treatments can help to realign your teeth and correct any issues caused by the extra teeth.
Reshaping
In some cases, reshaping the extra tooth or teeth may be an option. This involves filing down the extra tooth or teeth to bring them into alignment with your other teeth. Reshaping is typically only recommended if the extra teeth are small and not causing any significant problems.
Retention
Retention devices such as retainers or space maintainers may also be recommended to manage extra teeth. These devices can help to keep your teeth in their proper positions and prevent any further issues from developing.
It is important to note that the best treatment option for you will depend on your individual situation. Your dentist or orthodontist can help to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your needs.
Case Studies of Individuals with 34 Teeth
If you’re wondering whether it’s possible to have 34 teeth, the answer is yes! While the typical number of permanent teeth in adults is 32, some people can have one or more extra teeth, resulting in a total of 34 teeth.
Here are a few case studies of individuals with 34 teeth:
- Case 1: A 23-year-old male patient had 34 teeth, including four wisdom teeth. The extra teeth were located in the upper arch, and they were all fully erupted. The patient had no complaints of pain or discomfort.
- Case 2: A 32-year-old female patient had 34 teeth, including two extra molars. The extra teeth were located in the lower arch, and they were partially erupted. The patient reported occasional pain and discomfort in the area.
- Case 3: A 45-year-old male patient had 34 teeth, including two extra incisors. The extra teeth were located in the upper arch, and they were fully erupted. The patient had no complaints of pain or discomfort.
While having 34 teeth is not common, it is not necessarily a cause for concern. In some cases, the extra teeth may need to be extracted if they are causing pain or affecting the alignment of the other teeth. However, if the extra teeth are not causing any problems, they can be left in place.
If you suspect that you may have extra teeth, it is important to consult with a dentist or orthodontist for an evaluation. They can determine the best course of action based on your individual situation.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can someone have more than 32 teeth?
Yes, it is possible to have more than 32 teeth. This condition is known as hyperdontia, and it is characterized by the presence of extra teeth in the mouth. The extra teeth can develop anywhere in the mouth, and they can be fully formed or remain as small, undeveloped buds.
Is it normal to have 34 teeth?
No, it is not typical to have 34 teeth. Most adults have 32 teeth, including 8 incisors, 4 canines, 8 premolars, and 12 molars. However, some people may develop extra teeth as a result of hyperdontia or other dental conditions.
What is hyperdontia and is it dangerous?
Hyperdontia is a dental condition characterized by the presence of extra teeth in the mouth. While it is not inherently dangerous, it can cause problems such as overcrowding, misalignment, and difficulty with oral hygiene. In some cases, the extra teeth may need to be removed to prevent these issues.
What are the risks of removing an extra tooth?
Removing an extra tooth is typically a straightforward procedure, but it does carry some risks. These include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding teeth or structures. Your dentist or oral surgeon will discuss these risks with you before the procedure.
What causes a tooth to grow in the upper gums of a child?
A tooth growing in the upper gums of a child is often a result of a condition called mesiodens. This occurs when an extra tooth develops in the midline of the upper jaw, pushing other teeth out of alignment. Mesiodens is more common in children and may require removal to prevent dental problems.
What is the process for extracting a tooth in the roof of the mouth?
Removing a tooth in the roof of the mouth typically requires oral surgery. Your dentist or oral surgeon will numb the area with local anesthesia and make an incision in the gum tissue to access the tooth. The tooth is then carefully removed, and the area is stitched closed to promote healing.