If you’ve recently had a tooth extraction, you may be wondering if it’s possible to get a chest infection from the procedure. While it’s not common, it is possible for a tooth extraction to lead to a chest infection in some cases. This can happen if bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream and travel to the lungs, causing an infection.
Symptoms of a chest infection can include coughing, chest pain, shortness of breath, and fever. If you experience these symptoms after a tooth extraction, it’s important to seek medical attention right away. While a chest infection can be serious, it’s treatable with antibiotics and other medications. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary if the infection is severe.
Understanding Tooth Extraction
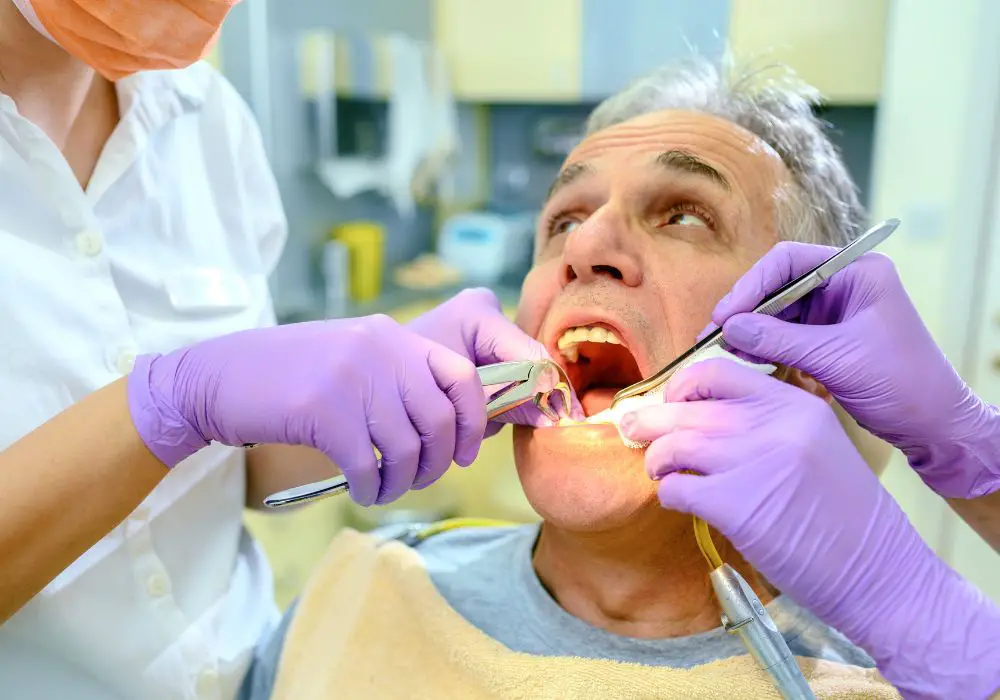
If you have a tooth that is damaged or decayed beyond repair, your dentist may recommend a tooth extraction. This is a common procedure that involves removing a tooth from its socket in the jawbone.
There are two types of tooth extractions: simple and surgical. A simple extraction is performed on a tooth that is visible and not impacted. Your dentist will use forceps to grasp the tooth and gently rock it back and forth until it comes out. A surgical extraction is more complicated and is performed on a tooth that is not visible or is impacted. In this case, your dentist will need to make a small incision in your gum to access the tooth and remove it.
Before the extraction, your dentist will numb the area around the tooth with a local anesthetic. This will prevent you from feeling any pain during the procedure. If you are anxious or nervous, your dentist may also offer you a sedative to help you relax.
After the extraction, your dentist will place a gauze pad over the socket and ask you to bite down to help stop the bleeding. You will need to keep the gauze in place for about 30 to 45 minutes. Your dentist will also provide you with instructions on how to care for your mouth after the extraction, including how to clean the socket and what foods to avoid.
Overall, a tooth extraction is a safe and effective procedure that can help alleviate pain and prevent further dental problems. If you have any questions or concerns about the procedure, be sure to talk to your dentist.
What is a Chest Infection?
A chest infection is an infection that affects your lungs, airways, or both. It can be caused by a virus, bacteria, or fungi. Chest infections can range from mild to severe, and they can be life-threatening if left untreated.
Symptoms of a chest infection may include:
- Coughing up yellow or green mucus
- Feeling short of breath
- Wheezing
- Discomfort in your chest
- Fever
- Headache
- Muscle aches and pains
- Feeling tired or fatigued
Chest infections can be classified into two main types: upper respiratory tract infections (URTIs) and lower respiratory tract infections (LRTIs). URTIs affect the upper respiratory tract, which includes the nose, throat, and sinuses, while LRTIs affect the lower respiratory tract, which includes the lungs and bronchi.
Common types of chest infections include bronchitis, pneumonia, and tuberculosis. Bronchitis is an infection that affects the bronchi, which are the tubes that carry air to your lungs. Pneumonia is an infection that affects the air sacs in your lungs, and it can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. Tuberculosis is a bacterial infection that can affect the lungs and other parts of the body.
If you suspect that you have a chest infection, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible. Your doctor can diagnose your condition and recommend appropriate treatment. Treatment may include antibiotics, antiviral medication, or other medications to help relieve your symptoms.
Link Between Tooth Extraction and Chest Infection
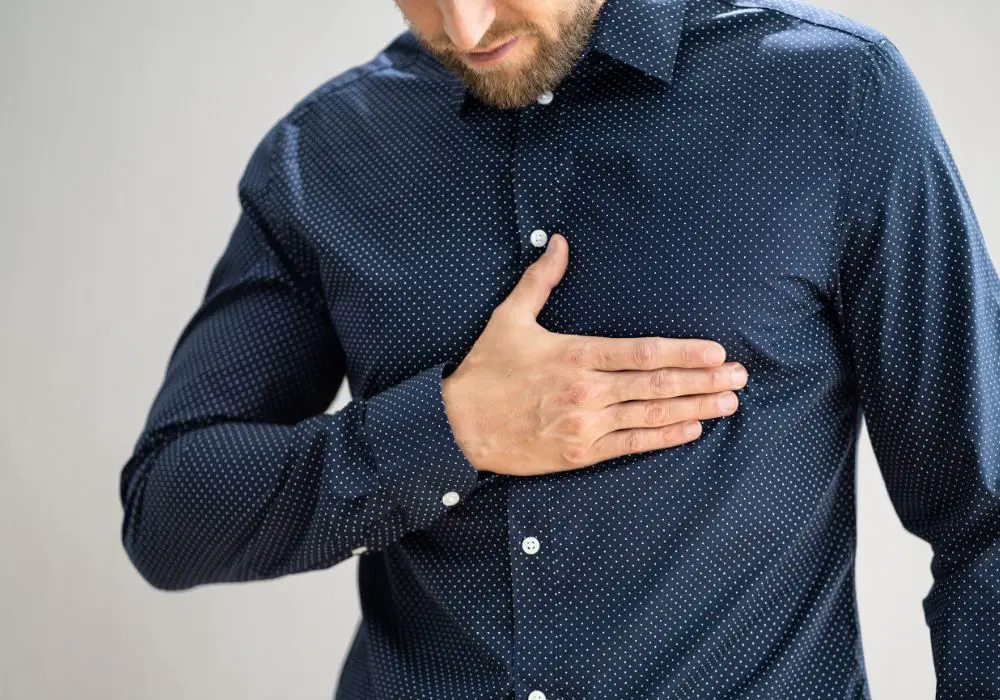

If you recently had a tooth extraction, you might be wondering if it could lead to a chest infection. While it’s not common, there is a potential link between the two. In this section, we’ll explore the possible ways a tooth extraction can lead to a chest infection.
Bacterial Spread
When you have a tooth extracted, there’s a risk of bacteria spreading from the mouth to other parts of the body, including the lungs. This can happen during the procedure itself or in the days following it, as the extraction site heals.
If bacteria enter the bloodstream during the extraction, they can potentially travel to the lungs and cause an infection. Additionally, if the extraction site becomes infected, the bacteria can spread to other parts of the body, including the lungs.
Immune System Response
Another way a tooth extraction can lead to a chest infection is through the immune system response. When you have a tooth extracted, your body responds by sending white blood cells to the area to fight off infection.
However, if your immune system is weak or compromised, it may not be able to fight off the bacteria effectively. This can lead to an infection in the lungs or other parts of the body.
To reduce the risk of developing a chest infection after a tooth extraction, it’s important to follow proper oral hygiene practices and keep the extraction site clean. Additionally, if you notice any symptoms of infection, such as fever or chest pain, seek medical attention right away.
In summary, while it’s not common, there is a potential link between tooth extraction and chest infection. Bacteria can spread from the mouth to the lungs during the extraction or as a result of an infected extraction site. Additionally, a weak immune system can make it harder for the body to fight off infection.
Prevention Measures
To prevent chest infections after a tooth extraction, it is important to take proper care of your oral health before and after the procedure. Here are some important measures to follow:
Pre-Extraction Care
Before the tooth extraction, make sure to inform your dentist if you have any respiratory conditions or chest infections. Your dentist may recommend postponing the extraction until the infection is resolved to prevent the spread of infection.
It is also important to maintain good oral hygiene by brushing your teeth twice a day and flossing regularly. This helps to reduce the risk of infection and inflammation in the mouth.
Post-Extraction Care
After the extraction, your dentist may prescribe antibiotics to prevent infection. Make sure to take the antibiotics as prescribed and complete the full course, even if you start feeling better.
To reduce the risk of chest infection, avoid smoking or using tobacco products for at least 48 hours after the extraction. Smoking can delay the healing process and increase the risk of infection.
You should also avoid strenuous activities, such as heavy lifting or exercise, for at least 24 hours after the extraction. This can help to prevent bleeding and reduce the risk of infection.
In addition, make sure to follow your dentist’s instructions for caring for the extraction site. This may include rinsing your mouth with salt water or using a special mouthwash to help prevent infection and promote healing.
By following these measures, you can help to prevent chest infections after a tooth extraction and promote faster healing.
Risk Factors
When it comes to tooth extraction, there are certain risk factors that can increase your chances of developing a chest infection. Some of these factors are beyond your control, while others can be mitigated with proper preparation and care.
Existing Health Conditions
If you have an existing health condition, such as a weakened immune system or a respiratory illness, you may be more susceptible to developing a chest infection after a tooth extraction. This is because your body may not be able to fight off the bacteria that can enter your bloodstream during the procedure.
Additionally, if you have a history of heart disease or other cardiovascular problems, your risk of developing a chest infection may be higher. This is because the stress of the tooth extraction can put additional strain on your heart and lungs, making it harder for your body to fight off infections.
Age and Lifestyle
Your age and lifestyle can also play a role in your risk of developing a chest infection after a tooth extraction. Older adults may be more susceptible to infections due to a weakened immune system, while smokers and individuals who consume alcohol regularly may also be at higher risk due to the negative effects these substances can have on the body’s ability to fight off infections.
To minimize your risk of developing a chest infection after a tooth extraction, it is important to take steps to strengthen your immune system and prepare your body for the procedure. This may include eating a healthy diet, getting regular exercise, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption. Additionally, following your dentist’s post-operative instructions and taking any prescribed antibiotics can help reduce your risk of developing an infection.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the symptoms of a chest infection after a tooth extraction?
If you experience a chest infection after a tooth extraction, you may have symptoms such as coughing, shortness of breath, chest pain, fever, and fatigue. If you have any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly.
What are the signs of a respiratory infection after a tooth extraction?
Signs of a respiratory infection after a tooth extraction may include coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, chest pain, and fever. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should contact your dentist or doctor as soon as possible.
Can a tooth infection lead to pneumonia?
Yes, a tooth infection can lead to pneumonia if the bacteria from the infection spread to the lungs. This is why it is important to seek prompt treatment for a tooth infection and to practice good oral hygiene to prevent infections from occurring in the first place.
Can a dry socket cause chest pain?
While it is rare, a dry socket can cause chest pain if the pain is severe enough to cause muscle tension and spasms in the chest. However, it is more likely that chest pain after a tooth extraction is due to a respiratory infection or other medical condition.
What are the signs of an infected tooth extraction site?
Signs of an infected tooth extraction site may include pain, swelling, redness, discharge, and a foul odor. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to contact your dentist or doctor right away.
What are the first signs of infection after a tooth extraction?
The first signs of infection after a tooth extraction may include pain, swelling, redness, and a fever. If you experience any of these symptoms, it is important to seek medical attention promptly to prevent the infection from spreading.