Wisdom teeth, also known as third molars, are the last set of teeth to erupt in the mouth. They typically emerge between the ages of 17 and 25, although the timing can vary quite a bit from person to person. Many people wonder just how late wisdom teeth are able to emerge. Can they still come in during the 30s, 40s, or even later in life? Let’s take a closer look at the timing of wisdom tooth eruption and just how late they are able to emerge.
Detailed Stages of Wisdom Tooth Development

Wisdom teeth go through various stages of development before they ultimately erupt through the gums. Here is an in-depth look at the wisdom tooth growth process:
- Initiation stage: The tooth first begins to form from tissue in the dental lamina at around age 8-10. At this point, it exists only as a tooth bud.
- Calcification stage: The cells start to differentiate into tissues that will become the crown and root. Minerals like calcium begin depositing to harden the tissue. This starts around ages 14-15.
- Gum penetration: Around ages 17-21, the wisdom tooth starts moving towards the surface. The crown tips sideways and begins pushing through gum tissue.
- Tissue irritation: Pushing through the tissue can cause inflammation and irritation. Fluid-filled cysts around the crown can also occur.
- Final eruption: The wisdom tooth finishes its journey by fully erupting through the gums, typically by age 21. The tissues heal around it.
This entire process from development to eruption takes around 13-15 years to complete. Delayed development during these stages can push eruption later in life.
What Causes Late Wisdom Tooth Eruption?
There are a number of possible reasons why wisdom teeth may emerge later than expected:
- Partially impacted: Wisdom teeth are partially encased in the jawbone when only partially erupted. This delays full emergence.
- Completely impacted: Fully impacted wisdom teeth are completely encased in bone, often tilted at an angle. This prevents natural eruption.
- Insufficient space: Wisdom teeth need adequate room to erupt. Jaws that are too small or crowded provide insufficient space.
- Dense gum tissue: Thick, rigid gums offer more resistance to emerging teeth. This slows the process.
- Dense jawbone: Harder, denser mature jawbone is more difficult for erupting teeth to penetrate.
- Flipped position: Wisdom teeth occasionally flip into an inverted or sideways orientation, delaying their emergence.
- Supernumerary teeth: Extra nonfunctional teeth can block or alter the path of wisdom tooth eruption.
Potential Complications from Late Eruption
As mentioned previously, some issues that may arise from significantly delayed wisdom tooth eruption include:
- Crowding: Erupting late in a fully mature jaw leaves little space, so wisdom teeth can shift and crowd other teeth.
- Tooth decay: Partially erupted teeth are harder to clean. They develop cavities and decay more readily when emergence is delayed.
- Gum infections: Gum tissue around a partially erupted wisdom tooth is prone to bacteria buildup and infection.
- Cysts: The follicle sac around unerupted wisdom teeth can swell into a cyst and damage surrounding roots.
- Tooth sensitivity: Late emerging wisdom teeth may displace nearby teeth, exposing sensitive roots.
- Jawbone damage: Attempting to penetrate dense mature bone can damage the jawbone during late eruption.
- Sinus issues: Upper wisdom teeth may penetrate the maxillary sinus if eruption is significantly delayed.
Surgical Options for Managing Late Wisdom Teeth
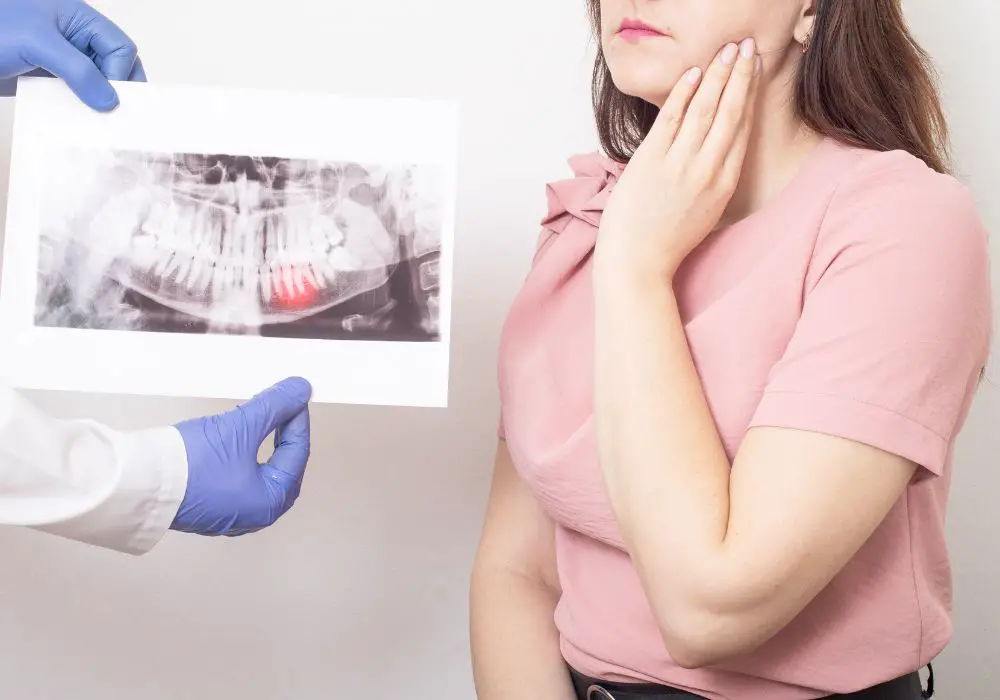
If wisdom teeth are unable to erupt on their own later in life, surgical extraction or exposure may be recommended. Here are some common approaches:
- Simple extraction: Removal of erupted wisdom teeth is relatively straightforward. Deeper impacted teeth may require oral surgeons.
- Coronectomy: The crown is cut away while the root remains in the jawbone to avoid nerve damage.
- Exposure surgery: An incision is made to expose the crown, and tissue is stitched over it to aid eruption.
- Full bony surgery: Bone tissue around the tooth is removed to fully expose it for easier extraction.
- Sectioning: The tooth is sectioned apart in pieces if the root is curved or otherwise difficult to extract.
Dentists will determine the best surgical method based on the specific positioning and development of your late wisdom teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
Here are some common questions and answers about the timing of wisdom tooth eruption:
How can I tell if my wisdom teeth are coming in late?
Look for signs of eruption like teeth pushing against your gums causing pain or swelling in your late teens or beyond. See your dentist for x-rays to look for wisdom teeth forming under your gums if you suspect late development.
Can wisdom teeth erupt as late as age 50?
Yes, it is possible but extremely rare. Only a fraction of a percent of people experience their first wisdom tooth eruption in their 50s.
What problems can wisdom teeth cause if they erupt late?
Potential issues include crowding, decay, infections, cysts, jawbone damage, tooth sensitivity, and sinus problems. The later wisdom teeth emerge, the higher the risks.
Should I get my wisdom teeth removed if they haven’t erupted by age 30?
Not necessarily. Discuss your case with your dentist. If positioned normally and asymptomatic, they may recommend monitoring. Otherwise, surgical extraction may be advised.
How can I make space for wisdom teeth erupting late?
In some cases, orthodontic treatment with braces/appliances can create room for late wisdom teeth. Ask your orthodontist about options.
Key Takeaways
- Wisdom teeth follow a lengthy development process from ages 8-21 on average
- Late eruption beyond the 20s can be caused by impaction, lack of space, dense tissue, and other obstructions
- Complications are more likely with late emergence and may require extraction
- Several surgical techniques exist for removing impacted or problematic wisdom teeth
- See your dentist regularly to monitor wisdom tooth development and address any eruption issues
Although delayed wisdom tooth eruption is uncommon, it occasionally happens. Work with your dentist to manage late wisdom teeth properly.