Have you ever wondered if men have thicker teeth than women? It’s a common belief that men have stronger and more robust bones than women, but what about teeth? Teeth are an essential part of our body, and we rely on them for everything from eating to speaking. So, it’s natural to wonder if there are any differences between men and women’s teeth.
Some people believe that men have thicker teeth than women because of their larger body size and more significant muscle mass. Others think that the difference in teeth thickness is due to hormonal differences between men and women. But is there any truth to these claims? In this article, we will explore the topic of whether men have thicker teeth than women and what science has to say about it. We will look at the research and examine the evidence to see if there is any basis to these claims. So, let’s dive in and find out if there is any truth to the myth of thicker men’s teeth.
Understanding Tooth Anatomy
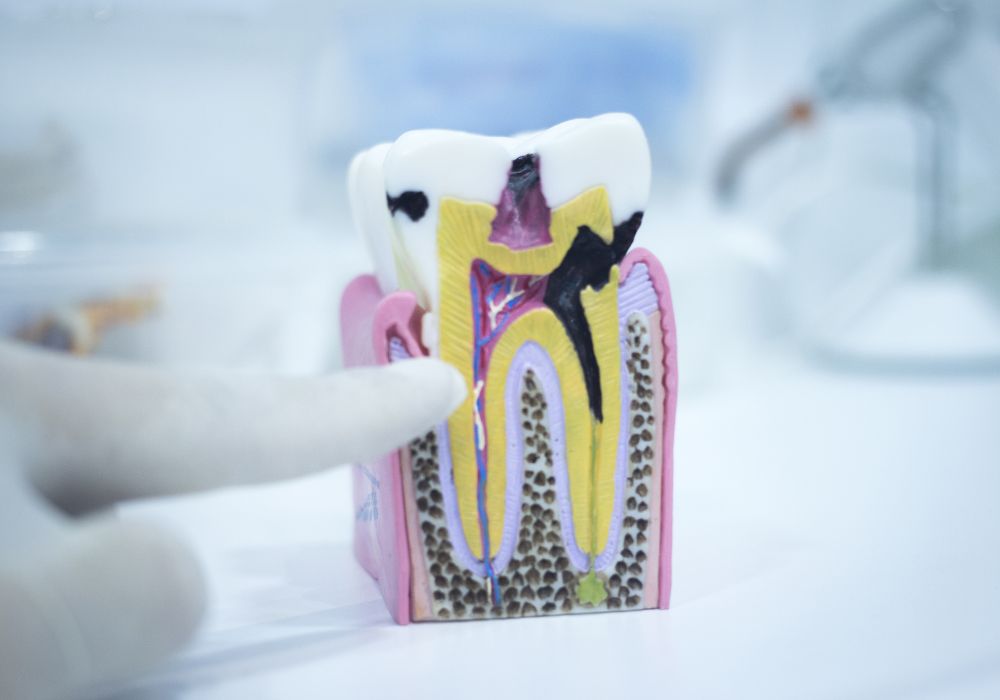
When it comes to understanding tooth anatomy, it’s essential to know the different parts that make up your teeth. Each part plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy teeth and gums. In this section, we will explore the three main parts of the tooth: enamel, dentin, and pulp.
Enamel
Enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth and is the hardest substance in the human body. It covers the crown of the tooth and protects the underlying layers from decay and damage. Enamel is made up of 96% minerals, mainly hydroxyapatite, and is translucent to some degree, allowing the underlying dentin to show through.
Dentin
Dentin is the layer of the tooth that lies beneath the enamel. It is a hard, dense tissue that makes up the bulk of the tooth structure. Dentin is composed of tiny channels called tubules that contain nerve endings, which can transmit sensations of heat, cold, and pressure. Dentin is also responsible for giving the tooth its color.
Pulp
The pulp is the innermost layer of the tooth and contains nerves, blood vessels, and connective tissue. It is located in the center of the tooth and extends from the crown to the tip of the root. The pulp is responsible for providing nutrients to the tooth and is also responsible for transmitting sensations of pain and pressure.
In conclusion, understanding tooth anatomy is crucial in maintaining healthy teeth and gums. Enamel, dentin, and pulp are the three main parts of the tooth, each with its unique function. By taking care of your teeth and visiting your dentist regularly, you can ensure that your teeth remain healthy and strong for years to come.
Gender Differences in Tooth Structure
When it comes to tooth structure, there is no significant difference between men and women’s teeth. Both men and women have the same number of teeth, and their teeth are composed of the same layers of enamel, dentin, and pulp. However, there are some subtle differences in tooth structure that are influenced by gender.
One of the most significant differences is the size of teeth. Men tend to have larger teeth than women, which is attributed to the larger jawbone structure that men have. This difference in tooth size can be observed in both the permanent teeth and the baby teeth.
Another difference is the thickness of the enamel layer. Studies have shown that men have thicker enamel layers than women, which may be due to the higher levels of testosterone in men. This increased thickness of enamel makes men’s teeth more resistant to decay and cavities.
In addition to these differences, men and women may also have different shapes and sizes of teeth. However, these differences are not significant enough to determine gender reliably.
Overall, while there are some subtle differences in tooth structure between men and women, these differences are not significant enough to have a major impact on oral health. Regardless of gender, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene habits, such as regular brushing and flossing, to keep teeth healthy and strong.
Scientific Studies on Tooth Thickness

Tooth thickness is an important factor in dental health and can be influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, and oral hygiene. Scientific studies have been conducted to investigate the relationship between tooth thickness and various factors.
One study published in Nature found that enamel thickness in human teeth has changed over time, possibly due to changes in diet. The study analyzed data from as far back as 2.5 million years ago and found that enamel thickness varied depending on the individual’s diet. This suggests that diet may play a role in determining tooth thickness.
Another study conducted a systematic review of the proximal enamel thickness (PET) of permanent teeth. The study found that mesial and distal enamel thickness was greater for premolars and molars, while it was least for mandibular central incisors. This suggests that tooth location may also play a role in determining tooth thickness.
A third study investigated the relationship between gingival biotype and buccal bone thickness. The study found a positive correlation between gingival biotype and buccal bone thickness for most maxillary teeth, suggesting that gingival biotype may be a useful indicator of tooth thickness.
Overall, scientific studies suggest that tooth thickness is influenced by a variety of factors, including genetics, diet, tooth location, and gingival biotype. Understanding these factors can help individuals better care for their teeth and maintain optimal dental health.
Factors Influencing Tooth Thickness
When it comes to tooth thickness, there are several factors that can influence it. Here are three of the most significant factors:
Genetics
Your genetics play a big role in determining the thickness of your teeth. Some people are simply born with thicker teeth than others. This is because the genes that control tooth thickness can be inherited from your parents. If your parents have thick teeth, there’s a good chance that you will too.
Age
As you age, your teeth naturally become thinner. This is because the enamel on your teeth wears away over time. Enamel is the hard, outer layer of your teeth that protects them from damage. As it wears away, your teeth become more vulnerable to decay and other dental problems. This is why it’s important to take good care of your teeth as you get older.
Diet
Your diet can also have an impact on the thickness of your teeth. If you eat a lot of acidic foods or drinks, it can wear away the enamel on your teeth, making them thinner. On the other hand, if you eat a diet that’s rich in calcium and other minerals, it can help strengthen your teeth and make them thicker.
In conclusion, tooth thickness is influenced by several factors, including genetics, age, and diet. While you can’t change your genetics or stop the aging process, you can take steps to protect your teeth by eating a healthy diet and practicing good oral hygiene.
Misconceptions About Tooth Thickness

When it comes to tooth thickness, there are many misconceptions that people have. Here are a few of the most common ones:
Misconception #1: Men’s teeth are always thicker than women’s teeth.
While it is true that there are some differences in tooth thickness between men and women, it is not always the case that men have thicker teeth. In fact, some studies have shown that there is no significant difference in enamel thickness between men and women.
Misconception #2: Tooth thickness is the same for all teeth.
Each tooth in your mouth is unique, and the thickness of its enamel can vary depending on its location and function. For example, molars tend to have thicker enamel than front teeth because they need to be able to withstand more pressure when chewing.
Misconception #3: Thinning out veneers is always a good idea.
If you have veneers that are thicker than you would like them to be, you may be tempted to have them thinned out. However, this is not always a good idea. Thinning out veneers can affect their final glaze and shine, and it can also cause the bonding to show through.
Misconception #4: Tooth thickness is determined solely by genetics.
While genetics can play a role in tooth thickness, there are other factors that can also affect it. For example, diet, exposure to toxins or radiation, and other environmental factors can all have an impact on the thickness of your tooth enamel.
Misconception #5: Thick teeth are always better than thin teeth.
While thicker teeth may be more resistant to wear and tear, they can also be more prone to cracking and chipping. Additionally, thicker teeth can make it more difficult to perform certain dental procedures, such as root canals or fillings.
In conclusion, there are many misconceptions about tooth thickness, and it is important to understand the facts before making any decisions about your dental health.
Implications of Tooth Thickness on Dental Health
The thickness of teeth can have implications on dental health. Here are some things to consider:
- Enamel thickness: The enamel is the outermost layer of the tooth. It’s the hardest substance in the human body and protects the tooth from decay and damage. Thicker enamel can provide better protection, but it can also make it more difficult to treat cavities or perform dental procedures.
- Bonding and veneers: If you’re considering getting bonding or veneers, it’s important to know that thicker teeth may not be the best candidate for these procedures. Thinning out the teeth can cause problems with the final glaze and shine, and there’s a risk of the bonding showing through.
- Gum disease: Thicker teeth can make it more difficult to clean between teeth and along the gumline. This can increase the risk of gum disease, which can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
- Orthodontics: If you need orthodontic treatment, the thickness of your teeth can impact the amount of space available for movement. Thicker teeth may require more aggressive treatment to create enough space for alignment.
- Tooth loss: Thicker teeth can also make it more difficult to replace missing teeth with dental implants. The implants need to be anchored into the jawbone, and thicker teeth can make it more difficult to achieve a secure fit.
Overall, tooth thickness is just one factor to consider when it comes to dental health. It’s important to maintain good oral hygiene habits and see a dentist regularly for checkups and cleanings, regardless of the thickness of your teeth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the average thickness of dentin in permanent teeth?
The average thickness of dentin in permanent teeth is around 1.5mm. However, this can vary depending on the individual and their dental health.
What is the average thickness of enamel in permanent teeth?
The average thickness of enamel in permanent teeth is around 2mm. This hard, protective layer covers the crown of the tooth and helps to prevent decay and damage.
Is there a difference in the thickness of enamel and dentin in primary teeth between males and females?
There is no significant difference in the thickness of enamel and dentin in primary teeth between males and females.
Do males and females have different types of teeth?
No, males and females have the same types of teeth. However, the size and shape of teeth can vary between individuals.
Do males have stronger teeth than females?
There is no evidence to suggest that males have stronger teeth than females. Dental health is largely determined by individual habits and hygiene practices.
Do men have bigger canine teeth than women?
On average, men tend to have slightly larger canine teeth than women. However, this is not always the case and can vary between individuals.