Do you have white spots on your teeth that make you feel self-conscious when you smile? These spots are called decalcification, and they are caused by the loss of calcium and other minerals from your tooth enamel. Decalcification can occur due to a variety of reasons, including poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugar and acid, and orthodontic treatment. The good news is that decalcification can be reversed with proper care and treatment.
One of the most effective ways to reverse decalcification is to follow a good oral hygiene routine. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste, flossing daily, and using an antibacterial mouthwash. Additionally, you should avoid sugary and acidic foods and drinks, which can erode your tooth enamel and cause further decalcification.
If you have severe decalcification, your dentist may recommend professional treatment options such as fluoride treatments, dental bonding, or dental veneers. Fluoride treatments can help to strengthen your tooth enamel and prevent further mineral loss, while dental bonding and veneers can cover up the white spots and restore the appearance of your teeth. With the right care and treatment, you can reverse decalcification and regain your confidence in your smile.
Understanding Tooth Decalcification
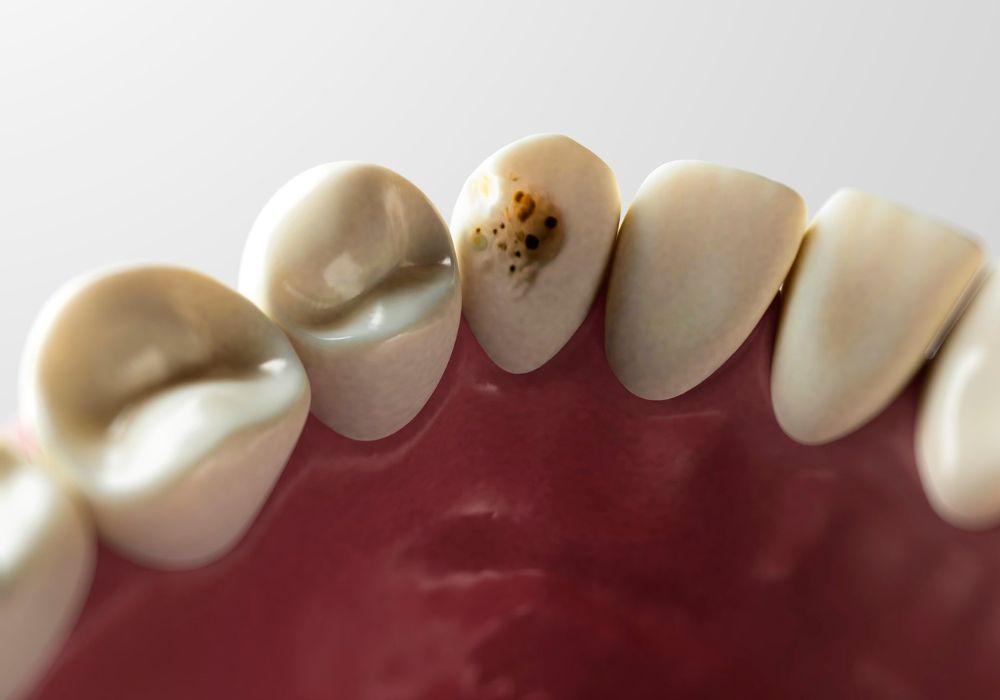
If you have noticed white spots on your teeth, it may be a sign of decalcification. Decalcification is a common dental issue that occurs when the minerals in the tooth enamel are lost, leaving the tooth vulnerable to decay. Understanding the causes and symptoms of decalcification can help you prevent and reverse this condition.
Causes of Decalcification
Decalcification can occur for a variety of reasons, including poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugar and acidic foods, and certain medical conditions. Some common causes of decalcification include:
- Poor oral hygiene: Failing to brush and floss regularly can lead to the buildup of plaque and bacteria, which can erode tooth enamel.
- Acidic foods and drinks: Consuming foods and drinks that are high in acid, such as citrus fruits and soda, can wear away tooth enamel over time.
- Braces and other orthodontic appliances: Braces and other orthodontic appliances can make it difficult to clean teeth properly, leading to decalcification around the brackets and wires.
- Medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as dry mouth and acid reflux, can increase the risk of tooth decalcification.
Symptoms of Decalcification
Decalcification can be difficult to detect in its early stages, but there are some signs to watch out for. These include:
- White spots on teeth: The most common symptom of decalcification is the appearance of white spots on the teeth, which indicate areas where the enamel has been weakened.
- Sensitivity: As the enamel wears away, the tooth becomes more sensitive to hot and cold temperatures.
- Cavities: If left untreated, decalcification can lead to cavities and tooth decay.
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is important to see your dentist as soon as possible. With proper treatment, decalcification can often be reversed, preventing further damage to your teeth.
Can You Reverse Tooth Decalcification?
Tooth decalcification is a condition where the minerals in your tooth enamel are lost, resulting in white spots or chalky areas on your teeth. If left untreated, decalcification can lead to cavities and tooth decay. But can you reverse it?
Fortunately, the answer is yes. With proper care and treatment, you can reverse tooth decalcification and restore your teeth to their natural state. Here are some steps you can take:
Step 1: Improve Your Oral Hygiene
The first step in reversing tooth decalcification is to improve your oral hygiene. This means brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily. You should also consider using an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
Step 2: Adjust Your Diet
Your diet can play a significant role in tooth decalcification. To reverse the condition, you should avoid foods and drinks that are high in sugar and acid, such as soda, candy, and citrus fruits. Instead, focus on consuming a balanced diet that includes plenty of calcium-rich foods, such as milk, cheese, and leafy greens.
Step 3: Visit Your Dentist
Regular dental checkups are essential for preventing and treating tooth decalcification. Your dentist can assess the severity of your condition and recommend appropriate treatment options, such as fluoride treatments, dental sealants, or fillings.
In conclusion, tooth decalcification is a treatable condition. By practicing good oral hygiene, adjusting your diet, and visiting your dentist regularly, you can reverse the condition and restore your teeth to their natural state.
Prevention is Better than Cure
When it comes to decalcification of teeth, prevention is better than cure. Here are some oral hygiene practices and dietary habits that can help prevent decalcification of teeth.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good oral hygiene is crucial for preventing decalcification of teeth. Here are some oral hygiene practices that you should follow:
- Brush your teeth at least twice a day with fluoride toothpaste.
- Floss your teeth at least once a day to remove plaque and food debris from between your teeth.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria and freshen your breath.
- Visit your dentist regularly for checkups and professional cleanings.
Dietary Habits
Your dietary habits can also play a significant role in preventing decalcification of teeth. Here are some dietary habits that you should follow:
- Limit your intake of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, such as soda, candy, and citrus fruits.
- Drink plenty of water to keep your mouth hydrated and to flush away food debris and bacteria.
- Eat a balanced diet that includes plenty of calcium-rich foods, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt.
- Chew sugar-free gum after meals to stimulate saliva production, which can help remineralize your teeth.
By following these oral hygiene practices and dietary habits, you can help prevent decalcification of teeth and maintain good oral health.
Professional Dental Treatments
If you have decalcification of your teeth, your dentist may recommend professional dental treatments to help reverse the damage. Here are two common treatments that may be recommended:
Fluoride Treatment
Fluoride is a mineral that can help strengthen tooth enamel and promote remineralization. During a fluoride treatment, your dentist will apply a high concentration of fluoride to your teeth. The fluoride may be in the form of a gel, foam, or varnish.
After the fluoride is applied, you will need to avoid eating, drinking, or rinsing your mouth for at least 30 minutes. This will give the fluoride time to penetrate your tooth enamel and provide maximum benefit.
Sealants and Fillings
If your decalcification has progressed to the point where you have cavities, your dentist may recommend sealants or fillings. Sealants are a type of protective coating that can be applied to the chewing surfaces of your back teeth to help prevent decay. Fillings, on the other hand, are used to restore teeth that have already been damaged by decay.
During a dental filling procedure, your dentist will remove the decayed portion of your tooth and then fill the cavity with a material such as composite resin or amalgam. The filling material is designed to restore the shape and function of your tooth while also preventing further decay.
Overall, professional dental treatments can be an effective way to reverse decalcification and restore the health of your teeth. However, it’s important to practice good oral hygiene habits and follow your dentist’s recommendations to prevent further damage in the future.
Home Remedies for Tooth Decalcification

If you are experiencing tooth decalcification, there are several home remedies that you can try to help reverse the process. These remedies can also be used to prevent further decalcification from occurring.
1. Brush and Floss Regularly
One of the most effective ways to prevent and reverse tooth decalcification is to maintain good oral hygiene. Brush your teeth at least twice a day and floss once a day to remove plaque and bacteria that can cause decalcification.
2. Use a Fluoride Toothpaste
Fluoride is a mineral that can help strengthen tooth enamel and prevent decalcification. Use a fluoride toothpaste when brushing your teeth to help protect against decalcification.
3. Increase Your Calcium and Vitamin D Intake
Calcium and vitamin D are essential for strong, healthy teeth. Make sure you are getting enough of these nutrients in your diet by eating foods such as dairy products, leafy greens, and fish. You can also take supplements if necessary.
4. Use a Calcium and Phosphate Cream
A calcium and phosphate cream, such as MI Paste, can help remineralize your teeth and reverse decalcification. Apply the cream to your teeth throughout the day, especially after eating and drinking.
5. Limit Acidic Foods and Drinks
Acidic foods and drinks can erode tooth enamel and contribute to decalcification. Limit your intake of acidic foods and drinks such as soda, citrus fruits, and vinegar.
6. Chew Sugar-Free Gum
Chewing sugar-free gum can help stimulate saliva production, which can help neutralize acid in your mouth and prevent decalcification.
By following these home remedies, you can help reverse tooth decalcification and prevent further damage to your teeth. However, it is important to note that severe cases of decalcification may require professional treatment from a dentist.
Potential Risks and Complications
While it is possible to reverse decalcification of teeth, there are potential risks and complications associated with the process. It is important to be aware of these risks before attempting any treatment.
One potential risk is that the treatment may not be effective. Remineralizing toothpaste or mouthwash containing fluoride and calcium may not work for everyone, and some cases of decalcification may be too severe to be reversed.
Another risk is that the treatment may cause further damage to the teeth. If the enamel is already weakened, aggressive brushing or the use of abrasive toothpaste can cause further damage to the teeth.
It is also important to note that some people may be more prone to decalcification than others. Factors such as genetics, diet, and oral hygiene habits can all play a role in the development of decalcification.
If you are considering treatment for decalcification, it is important to consult with a dental professional. They can assess your individual situation and recommend the best course of action.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to reverse decalcification of teeth?
Yes, it is possible to reverse decalcification of teeth. Decalcification is the first stage of tooth decay, and it can be reversed if caught early. With proper dental care and preventive measures, you can remineralize the tooth enamel and prevent further damage.
Are there any treatments for decalcification of teeth?
Dentists may recommend various treatment approaches, including the use of remineralizing toothpaste or mouthwash containing fluoride and calcium. In severe cases, your dentist may suggest a dental filling or bonding to restore the damaged tooth.
What causes decalcification of teeth?
Decalcification of teeth is caused by the loss of minerals from the tooth enamel. This can occur due to poor oral hygiene, a diet high in sugar and acid, or certain medical conditions.
Can decalcification of teeth be prevented?
Yes, decalcification of teeth can be prevented. The key to preventing decalcification is maintaining good oral hygiene, including regular brushing and flossing. You should also limit your intake of sugary and acidic foods and drinks, and visit your dentist regularly for check-ups and cleanings.
How can you remineralize your teeth?
You can remineralize your teeth by using fluoride toothpaste or mouthwash, which helps to strengthen the tooth enamel. You can also increase your intake of calcium and vitamin D, which are essential for healthy teeth and bones.
Is decalcification of teeth a common problem?
Yes, decalcification of teeth is a common problem, especially among children and teenagers. However, it can occur at any age and can lead to more serious dental problems if left untreated. Regular dental check-ups and good oral hygiene are essential for preventing decalcification and maintaining healthy teeth.






