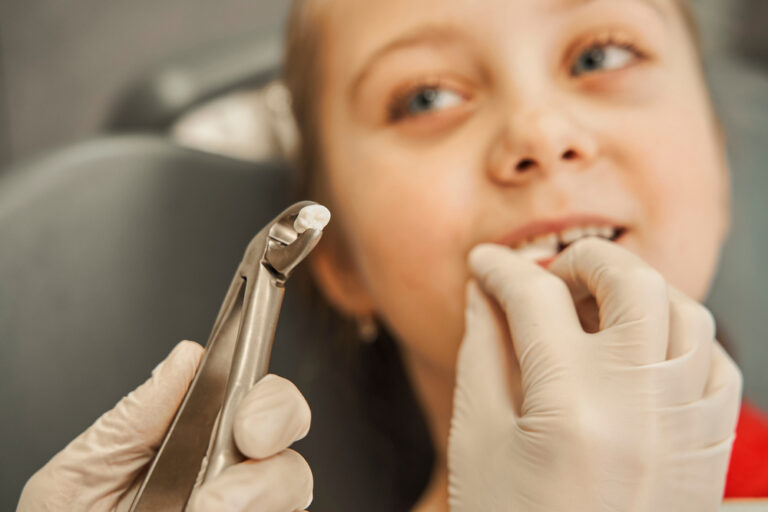
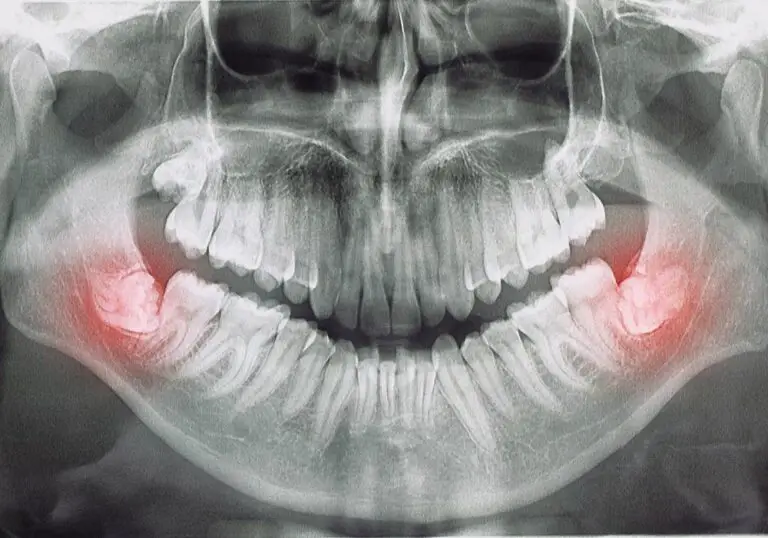
If you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, you may be wondering if your teeth can be saved. The answer is yes, in many cases, it is possible to save your teeth with the right treatment. However, it is important to understand the severity of your condition and the options available to you.
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is caused by an infection in the gums and bone that support your teeth. It can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. The good news is that with proper care, you can slow or even stop the progression of the disease. This may involve a combination of treatments, including deep cleaning, antibiotics, and surgery in some cases.
It is important to work closely with your dentist or periodontist to develop a treatment plan that is right for you. With the right care and maintenance, you can keep your teeth healthy and strong, even if you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease. So, if you are concerned about the health of your teeth, don’t hesitate to seek professional help.
Understanding Periodontal Disease
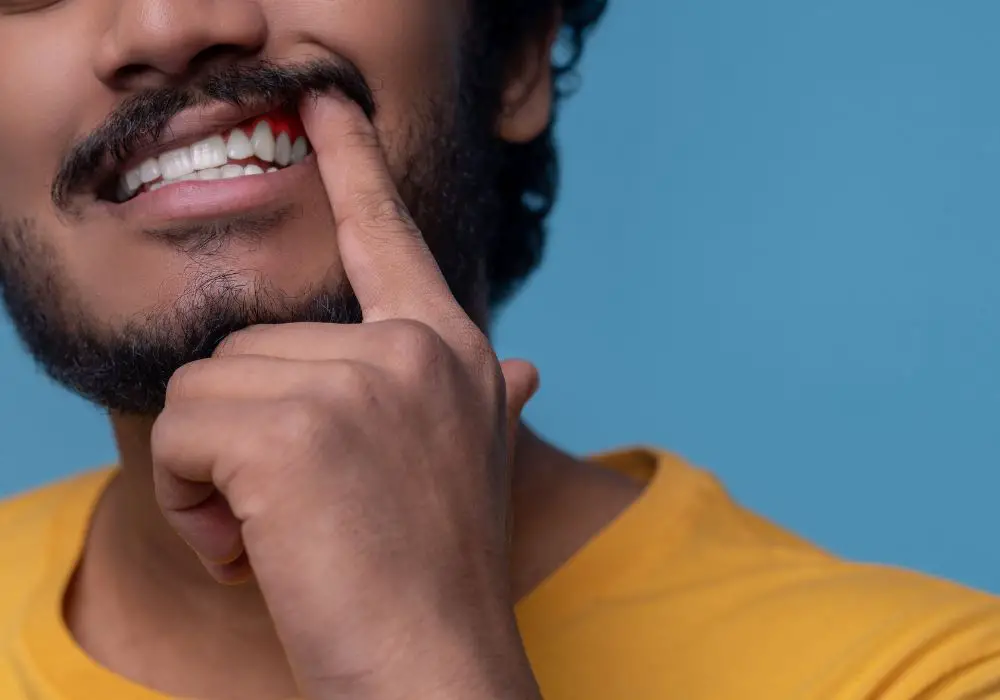

If you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, you may be wondering what it is and how it affects your dental health. Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is an infection of the tissues that support your teeth, including your gums, periodontal ligaments, and alveolar bone. This disease is caused by bacteria that thrive in the plaque and tartar that accumulate on your teeth and gums.
Periodontal disease can range from mild gingivitis, which causes redness and swelling of the gums, to severe periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss and bone damage. Some common symptoms of periodontal disease include bad breath, bleeding gums, loose teeth, and receding gums.
If left untreated, periodontal disease can cause significant damage to your teeth and gums. It is important to seek treatment as soon as possible to prevent the disease from progressing. Your dentist can help you develop a treatment plan that is tailored to your specific needs.
Treatment for periodontal disease may include a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing, antibiotics, or surgery in severe cases. In addition to professional treatment, good oral hygiene practices, such as brushing twice daily and flossing regularly, can help prevent the development of periodontal disease.
It is important to note that periodontal disease is preventable with proper oral hygiene and regular dental checkups. By taking care of your teeth and gums, you can reduce your risk of developing this common dental condition.
Signs and Symptoms of Periodontal Disease
If you have periodontal disease, you may experience the following signs and symptoms:
- Gums that bleed easily when you brush or floss
- Red, swollen, or tender gums
- Receding gums or gums that pull away from your teeth
- Persistent bad breath or a bad taste in your mouth
- Loose teeth or teeth that are separating from each other
- Changes in your bite or the way your teeth fit together
- Pus between your teeth and gums
- A change in the way your partial dentures fit
If you notice any of these signs or symptoms, it’s important to see your dentist or periodontist right away. Early intervention is key to preventing further damage and saving your teeth.
Periodontal disease is caused by bacteria that live in the plaque and tartar on your teeth. When these bacteria are not removed through regular brushing and flossing, they can cause inflammation and infection in your gums. Over time, this can lead to the destruction of the bone and tissue that support your teeth.
While periodontal disease is common, it is also preventable. By practicing good oral hygiene and seeing your dentist or periodontist regularly, you can lower your risk of developing periodontal disease and keep your teeth healthy for years to come.
Preventing Periodontal Disease
Periodontal disease is a serious oral condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated. However, there are steps you can take to prevent periodontal disease from developing in the first place. By following good oral hygiene practices and regularly visiting your dentist, you can reduce your risk of developing periodontal disease.
Oral Hygiene Practices
Good oral hygiene practices are essential for preventing periodontal disease. Here are some tips to help you maintain good oral hygiene:
- Brush your teeth twice a day with a fluoride toothpaste. Be sure to brush for at least two minutes each time.
- Floss your teeth at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
- Use an antiseptic mouthwash to kill bacteria that can cause gum disease.
- Quit smoking or using tobacco products. Smoking can increase your risk of developing periodontal disease.
- Eat a healthy diet that is rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Avoid sugary and starchy foods, which can promote the growth of bacteria in your mouth.
Regular Dental Check-Ups
Regular dental check-ups are also important for preventing periodontal disease. During your check-up, your dentist will examine your teeth and gums for signs of gum disease. They may also perform a deep cleaning to remove plaque and tartar from your teeth.
Here are some tips for scheduling regular dental check-ups:
- Visit your dentist at least twice a year for a routine check-up and cleaning.
- If you have a history of gum disease, your dentist may recommend more frequent check-ups.
- Be sure to tell your dentist if you experience any symptoms of gum disease, such as red or swollen gums, bleeding when you brush or floss, or bad breath.
By following these oral hygiene practices and scheduling regular dental check-ups, you can reduce your risk of developing periodontal disease and keep your teeth healthy for years to come.
Treatment Options for Periodontal Disease
If you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, there are several treatment options available to help you manage the condition. The type of treatment that you receive will depend on the severity of your disease and your overall oral health. In this section, we will explore the two main types of treatment for periodontal disease: non-surgical and surgical.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Non-surgical treatments are typically the first line of defense when it comes to managing periodontal disease. These treatments are designed to remove the plaque and tartar buildup that is contributing to your condition and to help restore your gum health.
One of the most common non-surgical treatments for periodontal disease is scaling and root planing. This procedure involves removing the plaque and tartar buildup from your teeth and smoothing out the roots of your teeth to help prevent further buildup. Your dentist or periodontist may also prescribe antibiotics to help control the bacterial infection that is contributing to your disease.
Other non-surgical treatments for periodontal disease may include:
- Professional dental cleaning
- Antimicrobial mouthwash
- Laser therapy
Surgical Treatments
If your periodontal disease is more advanced, you may require surgical treatment to help manage the condition. Surgical treatments are designed to remove the bacteria and plaque buildup that is contributing to your disease and to help restore your gum health.
One of the most common surgical treatments for periodontal disease is pocket reduction surgery. This procedure involves removing the bacteria and plaque buildup from the pockets that have formed between your teeth and gums. Your dentist or periodontist may also use guided tissue regeneration to help rebuild the bone and tissue that has been lost due to your disease.
Other surgical treatments for periodontal disease may include:
- Gum graft surgery
- Bone graft surgery
- Flap surgery
Remember, the best way to manage periodontal disease is to practice good oral hygiene and to visit your dentist or periodontist regularly. By taking good care of your teeth and gums and seeking treatment as soon as possible, you can help prevent the progression of your disease and keep your teeth for many years to come.
Prognosis of Periodontal Disease
If you have been diagnosed with periodontal disease, you may be wondering about the prognosis of your condition. The prognosis will depend on the severity of the disease and how early it was detected. Here are some factors that can affect the prognosis of periodontal disease:
- Severity of the disease: The severity of periodontal disease is classified into four stages, ranging from mild to severe. The earlier the disease is detected, the better the prognosis. In the early stages, the disease can be treated with non-surgical methods, such as scaling and root planing. In the later stages, surgery may be necessary to save the teeth.
- Response to treatment: Your response to treatment will depend on how well you follow your dentist’s instructions and how well you maintain good oral hygiene. If you are diligent about brushing and flossing regularly and attending regular dental check-ups, you can improve your prognosis.
- Underlying health conditions: Certain health conditions, such as diabetes, can affect the prognosis of periodontal disease. If you have an underlying health condition, it is important to work with your dentist to manage it effectively.
- Smoking: Smoking can worsen periodontal disease and make it more difficult to treat. If you smoke, quitting can improve your prognosis.
Overall, the prognosis of periodontal disease is good if it is detected early and treated promptly. With proper treatment and good oral hygiene, you can prevent further damage to your teeth and gums and maintain a healthy smile.
Maintaining Oral Health After Periodontal Disease
Now that you have received treatment for your periodontal disease, it is important to maintain good oral hygiene to prevent further damage to your teeth and gums. Here are some tips to help you keep your teeth healthy:
Brush and Floss Regularly
Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to brush all surfaces of your teeth, including the front, back, and chewing surfaces. Floss at least once a day to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth.
Use an Antimicrobial Mouthwash
An antimicrobial mouthwash can help control bacterial growth and prevent gum disease. Use it after brushing and flossing to help kill bacteria that cause bad breath, plaque, and gingivitis.
Eat a Healthy Diet
A healthy diet can help prevent gum disease and other oral health problems. Eat a variety of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins. Avoid sugary and starchy foods, which can increase your risk of tooth decay.
Quit Smoking
Smoking can increase your risk of gum disease and other oral health problems. If you smoke, quitting can help improve your oral health and overall health.
Visit Your Dentist Regularly
Regular dental checkups and cleanings can help prevent gum disease and other oral health problems. Your dentist can also check for signs of periodontal disease and recommend treatment if necessary.
By following these tips, you can help maintain good oral health and prevent further damage to your teeth and gums. Remember to brush and floss regularly, use an antimicrobial mouthwash, eat a healthy diet, quit smoking, and visit your dentist regularly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is it possible to save teeth with periodontal disease?
Yes, it is possible to save teeth with periodontal disease. However, it depends on the severity of the disease and how early it is detected. If the disease is caught early, it can be treated with non-surgical methods such as scaling and root planing. If the disease has progressed, surgical treatments such as flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration may be necessary.
What are the stages of periodontal disease?
Periodontal disease has two stages: gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivitis is the early stage of the disease and is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, which is a more advanced stage of the disease. Periodontitis causes the gums to pull away from the teeth, creating pockets that become infected. Over time, the infection can destroy the bone and tissue that support the teeth, leading to tooth loss.
How long can you keep your teeth with periodontal disease?
The length of time that you can keep your teeth with periodontal disease depends on the severity of the disease and how early it is detected. In some cases, people can keep their teeth for their entire lives with proper treatment and maintenance. However, if the disease is left untreated, it can lead to tooth loss.
What happens if periodontal disease goes untreated?
If periodontal disease goes untreated, it can lead to tooth loss and other complications such as bone loss, gum recession, and systemic health problems. The bacteria that cause periodontal disease can enter the bloodstream and travel to other parts of the body, increasing the risk of heart disease, stroke, and other health problems.
What are some treatments for advanced periodontitis?
Some treatments for advanced periodontitis include flap surgery, bone grafting, and guided tissue regeneration. Flap surgery involves lifting the gums to remove tartar and bacteria from deep pockets. Bone grafting involves replacing lost bone with grafts from other parts of the body or synthetic materials. Guided tissue regeneration involves placing a special membrane over the affected area to promote the growth of new bone and tissue.
Can gum disease be cured without a dentist?
No, gum disease cannot be cured without a dentist. While there are things that you can do at home to prevent gum disease, such as brushing and flossing regularly and eating a healthy diet, professional treatment is necessary to cure the disease. A dentist or periodontist can provide the necessary treatments to remove the bacteria and prevent further damage to the gums and teeth.