Have you ever experienced an odd sensation in your mouth, like your teeth are shifting or rocking back and forth? This unsettling feeling of tooth movement likely leaves you wondering what’s going on inside your mouth.
Dentists explain that it is entirely possible to feel your teeth moving. Tooth movement or drift is more common than you may realize and has a variety of potential causes. Understanding the reasons why you may sense your teeth are on the move can help ease your mind when it happens.
What’s Happening Inside Your Mouth?
Before exploring why tooth movement occurs, it helps to visualize what is taking place inside your mouth:
Your teeth are anchored in the jawbone beneath your gums. A tough, elastic tissue called the periodontal ligament surrounds the root of each tooth, attaching it to the bone. This ligament has nerve fibers that allow you to perceive sensations from your teeth.
When forces act on a tooth, it stimulates these nerve endings in the ligament. This triggers your brain to interpret the feeling as tooth movement or looseness.
The severity of sensation depends on how much the force displaces the tooth and strains this ligament. Slight motions cause mild symptoms while larger shifts result in more noticeable discomfort.
Now let’s examine common sources of force that can act on teeth to generate this feeling of motion.
Causes of Tooth Movement
A number of different factors can potentially cause your teeth to shift positions enough to make that motion detectable. Some leading influences include:
1. Orthodontic Tooth Movement
One of the most obvious explanations is intentional tooth movement from orthodontic treatment. Appliances like braces and Invisalign® aligners are designed to gradually push teeth into improved positions over time.
As this force acts on your teeth to reposition them, you will likely sense some distinct sensations:
2. Braces
Traditional metal braces use gentle constant pressure from the orthodontic wires and elastics to guide your teeth into alignment. The placement and tightening of the braces generates pressure that compresses the periodontal ligament, particularly right after an adjustment appointment. As your teeth slowly respond to this force by moving, you will notice:
- General feeling of squeeze or pressure on the teeth
- Sensitivity to hot and cold temperatures
- Soreness and tenderness around braces brackets
- Ache or throbbing, especially when chewing
- Tightness of the jaw muscles
This discomfort is generally worst for the first few days after a braces adjustment, improving as your teeth settle into their new positions. Younger patients also tend to adjust quicker as their teeth are still developing within the jawbone. Keep in mind that some tooth movement and ligament discomfort is expected while straightening your bite.
3. Invisalign Aligners
Invisalign utilizes a series of clear plastic trays called aligners that are switched out approximately every 1-2 weeks during treatment. Each new tray applies light controlled forces to continue moving your teeth incrementally.
When you switch to a new aligner tray, you may notice:
- A feeling of pressure or tightness on the teeth
- Mild to moderate soreness that resolves within a few days
- Sensitivity similar to new braces but less pronounced
The movement may feel more dramatic at the start of a new aligner as your teeth are shifted into slightly different positions. Your teeth will feel stable and stationary between aligner changes. Tracking your progress helps you anticipate these sensations.
4. Retainers After Braces
After your teeth are aligned by braces or Invisalign, retainers are required to hold them in their new positions. If you do not wear your retainer as prescribed, teeth can drift out of alignment. This causes a return of the movement sensations. The less often you wear your retainer, the more looseness and shifting you will start to feel as teeth regress.
Strict retainer wear is essential for at least the first year after orthodontic treatment. This allows the teeth and bone to stabilize so teeth become firmly rooted in position.
5. Natural Tooth Migration
Teeth naturally drift somewhat throughout life due to gradual changes in the mouth. This slow motion is invisible and imperceptible. But certain situations can accelerate tooth migration, making it more apparent:
6. Erupting Teeth
Between ages 6-13, permanent adult teeth begin pushing through the gums to replace baby teeth. The eruption path of these new teeth can displace primary teeth, crowding others together. This jostling about during eruption can make teeth feel looser and more mobile.
Once the adult teeth fully emerge, the prior drifted positions tend to stabilize. If crowding or bite issues remain, orthodontic treatment may be recommended.
7. Loss of Teeth
When a tooth is lost due to decay, gum disease, or trauma, adjacent and opposing teeth can begin to shift and tilt into the newly open space. This migration intensifies the sensation of a loose, rocking tooth.
Promptly replacing missing teeth helps prevent this movement. Restorative options include dental implants, bridges, partials, or retained baby teeth. Without replacement, substantial erosion of remaining teeth and bone structure can occur long-term.
8. Periodontal (Gum) Disease
Inflamed, receding gums provide less support and stability for teeth. This weakened foundation allows teeth to shift more freely, increasing mobility.
Gum disease may also expose more of the tooth root, causing sensitivity and discomfort, especially when chewing. Seeking dental treatment helps resolve inflammation and secure teeth before significant drifting can happen.
9. Bruxism/Clenching
Habitual teeth grinding or clenching puts excessive occlusal pressure on teeth and strain on the temporomandibular joint. This repeated trauma can loosen teeth over time. Since force is often focused in local areas, biting surfaces tend to show the most mobility.
Wearing a custom nightguard relieves this stress and prevents damage during sleep. Options like botox injections and stress reduction may also help minimize bruxism. If loosening occurs, restorations and occlusal adjustments can return stability.
Is All Tooth Movement Cause for Concern?

Not all sensations of tooth movement are problematic. Here are some examples of normal, temporary shifting:
During Active Orthodontic Treatment
The dynamic process of teeth realigning during active orthodontics naturally involves some degree of movement. The forces are intentionally applied to produce desired repositioning.
As long as motion progresses at the expected pace and direction, the squeeze of braces or pressure of new aligners is not cause for alarm. Proper orthodontic mechanics prevent hazardous movement.
After Dental Procedures
It is common for teeth to feel slightly loose for a period after certain dental treatments, like:
- Tooth extractions to alleviate crowding
- Fillings, especially larger restorations
- Root canal therapy due to normal post-op swelling
This brief sensation typically resolves within several weeks as the area heals and stabilizes. Only if excessive looseness persists is further evaluation needed.
Subtle Drifting
Teeth naturally migrate very gradually over a lifetime. Little “tweaks” in position often occur unnoticed and are innocuous, especially in younger patients.
However, patients should still have regular dental exams to monitor for progressive loosening that could lead to bigger problems.
Around Puberty
Hormonal surges during adolescence can contribute to increased mobility. Unless severe or prolonged, this generally stabilizes on its own. But dentists may intervene if concerns arise.
When to See Your Dentist?
Though minor tooth shifting is usually harmless, progressive loosening and drifting is not. Contact your dentist promptly if you experience:
- Unexplained movement that continues worsening
- Visibly increasing gaps developing between teeth
- Teeth feeling extremely loose and insecure
- Significant changes in your bite
- Difficulty chewing or discomfort when eating
- Tooth, jaw, or gum pain made worse by movement
This degree of mobility may signal an underlying dental problem requiring urgent care. To prevent structural damage and potential tooth loss, problems are best managed when detected early.
What Does Shifting Teeth Feel Like?

The actual sensations caused by mobile teeth can vary between patients. But in general, you may notice:
- A feeling of pressure or squeezing
- General sense that teeth are moving or rocking
- Teeth feeling loosely anchored in place
- Tenderness, soreness, or ache around affected teeth
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, and sweet foods
- Pain or tension in jaw muscles
- Discomfort or difficulty chewing
The intensity ranges from mild tightness to severe pain depending on factors like:
- Amount of tooth movement
- Cause and rate of shifting
- Which teeth are affected
- Health of nerves and ligaments
Here are some examples of characteristic sensations with different causes:
New braces or orthodontic adjustment
- General feeling of squeeze or teeth being pushed
- Soreness around brackets intensifying over 3-5 days
- Tight jaw muscles
Gum disease
- Sharper, throbbing pain in gums and under teeth
- Pain when brushing diseased areas
- Sensitive teeth, especially to sweets
Bruxism/Clenching
- Soreness and ache concentrated on edges of front teeth typically in morning
- Jaw tension and tightness in temples
- Grinding noises heard at night
Pay attention to any unfamiliar or increasing sensations you notice in your mouth. Your body is alerting you to possible problems requiring dental evaluation.
Seeing Your Dentist About Tooth Movement
If you feel your teeth conspicuously shifting, promptly consult your dentist. Be prepared to describe:
- Which teeth are involved
- When you first noticed the change
- If it is gradually worsening
- What the movement feels like
- Any associated symptoms (e.g. bite changes, pain while chewing)
Your dentist will perform a clinical exam to check for loose teeth, inspect your bite, and monitor for further movement. They may also recommend x-rays to gain more information about underlying tooth and bone health.
Diagnostic testing can help identify the cause, such as:
- Periapical x-rays to check for decay or gum disease
- Bitewings to look for problems between teeth
- Panoramic film to evaluate tooth root and jawbone support
- CT scan for a 3D view of structural anatomy
What Treatment Options Can Stop Tooth Movement?
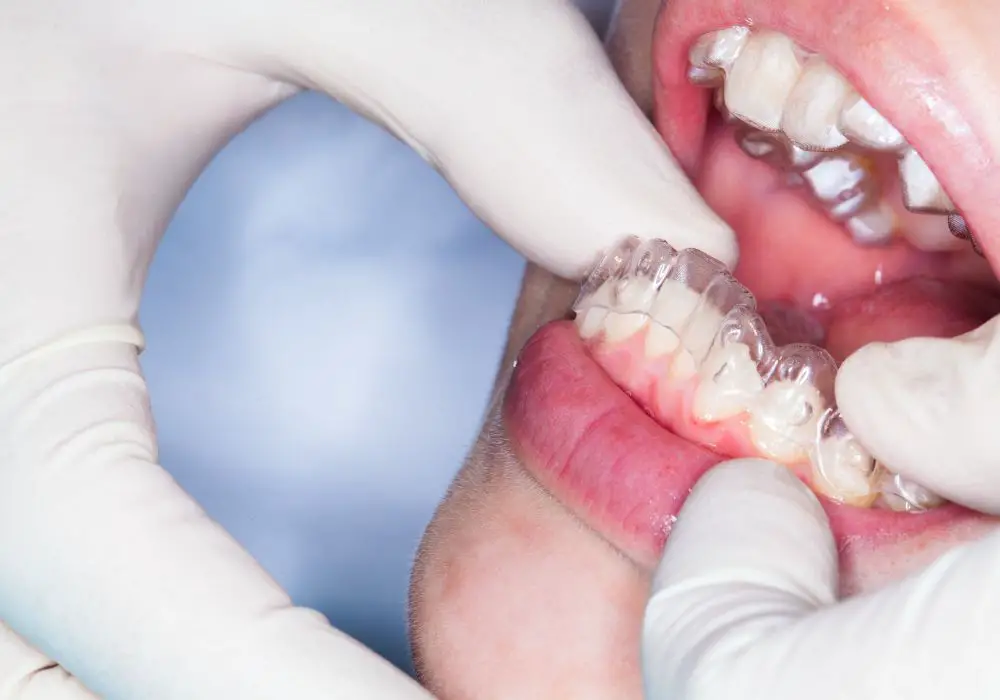
Once a diagnosis is made, your dentist will outline the treatment plan needed to halt progression and stabilize your teeth in place. Depending on the severity, options may include:
1. Minor Movement
- topical Fluoride application to strengthen enamel
- over-the-counter pain relievers
- warm saltwater rinses to soothe discomfort
- dental restoration of any damaged teeth
- nightguard for bruxism
2. Extensive Movement
- Orthodontic treatment to re-align teeth
- Dental restorations like fillings, crowns, bridges, implants
- Treatment of gum disease
- Bite adjustments and occlusal guard
- Muscle relaxants and botox injections for bruxism
- Surgery in severe cases of advanced bone loss
The goals are to relieve pain, restore the integrity of affected teeth, improve structural bone support, and ultimately achieve properly aligned tooth contacts. This should eliminate destabilizing forces on teeth.
Following all recommended dental treatment and oral health practices will help keep your teeth stabilized in place. Be sure to wear any prescribed orthodontic retainers or nightguards as directed.
The Importance of Correcting Tooth Movement
It’s clear that feeling your teeth moving can be unsettling. But stabilizing your teeth is also critical for your oral health. Without intervention, ongoing shifting and mobility can lead to:
- Progressive tooth loss – Excess movement stretches the ligaments to the breaking point, allowing teeth to detach and fall out.
- Loss of supporting bone – Abnormal pressures on mobile teeth can destroy the underlying jawbone faster.
- Functional issues – Misalignment from drift can make it hard to bite and chew properly.
- Facial collapse – Missing teeth and diminished bone cause the lower face to sink in, creating a prematurely aged appearance.
- Temporomandibular joint dysfunction – TMJ and muscle pain arise from imbalance in bite forces.
- Additional drift – The more teeth shift, the more movement tends to occur, compounding problems.
- Damage to adjacent teeth – Tilting teeth knock others out of position also.
- Cosmetic concerns – Gaps, overlaps, and twisting from movement can worsen your smile.
That’s why prompt dental correction of any impaired tooth stability is so vital – it can prevent pain and safeguard both dental and facial structures over the long run.
Key Takeaways
- It is actually possible to perceive teeth shifting or moving due to a variety of dental causes.
- Though unsettling, minor movement sensations may not always need immediate care. But worsening looseness and pain should be evaluated promptly.
- Orthodontics, missing teeth, gum disease, erupting teeth, and bruxism are potential reasons you may feel motion.
- Dentists have various methods to diagnose the cause, halt further movement, and stabilize teeth in proper alignment.
- Restoring stability is crucial to preventing progressive tooth and bone loss, and deterioration of bite function.
Pay attention when your teeth feel on the move. With today’s dental treatments, unstable teeth can be successfully realigned and secured. Consult your dentist to restore comfort and confidence in your smile.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Why might my teeth feel loose even though I wear my retainer every night?
A: Some slight movement may persist as teeth settle. But mention it at your next orthodontic appointment in case adjustments are needed. Strict retainer wear should prevent major loosening.
Q: Can teeth naturally tighten back up on their own if they start to shift?
A: Unfortunately, substantial movement will not spontaneously correct itself without orthodontic intervention. Prompt dental treatment provides the best chance of recovery.
Q: How long after getting braces tightened should teeth be sore?
A: It is common for discomfort to increase over the first 3-5 days as the teeth respond to new forces. If pain persists beyond a week, call your orthodontist.
Q: My dentist recommended a biteguard. Can grinding really move teeth that much?
A: Yes, chronic grinding or clenching applies extreme pressures that can loosen teeth and alter alignment over time. A biteguard is an effective prevention.
Q: Can teeth feel loose during pregnancy? Is it problematic?
A: Hormonal changes and acidity from morning sickness can temporarily increase mobility. Unless it becomes severe, the movement is usually not harmful.
I hope this expanded and more detailed article helps explain why you may sense your teeth moving! Let me know if you would like me to elaborate on or clarify any part of it further.