Having teeth that function properly is crucial for biting, chewing, and eating a variety of foods. As we age, our natural teeth may deteriorate or need to be removed entirely. Thankfully, modern dentistry provides several options for fake teeth that can restore your ability to eat the foods you love. This article explores the different types of fake teeth and evaluates which options allow for the greatest ease and enjoyment of eating.
Dentures
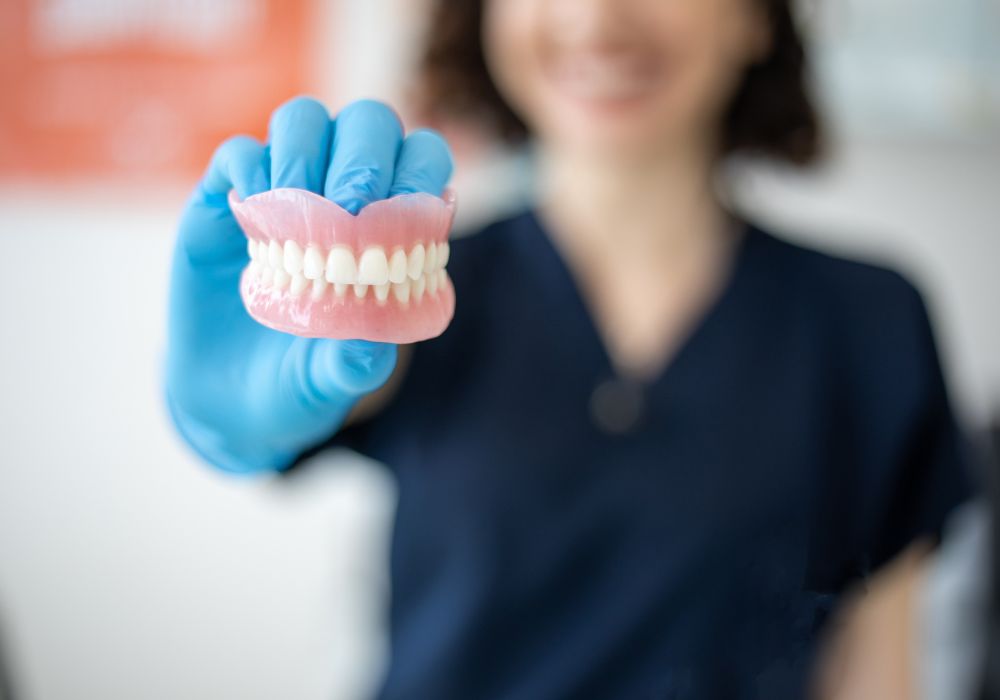
Dentures are removable sets of artificial teeth designed to replace an entire arch of missing teeth, either on the top or bottom of the mouth. They are made of acrylic resin and sit over the gums. Partial dentures replace just a few missing teeth while full dentures replace all teeth in the upper and/or lower jaw.
Can you eat with dentures?
Yes, you absolutely can eat with dentures. However, there are some limitations compared to natural teeth. The amount of biting force dentures can withstand is less than real teeth. As a result, foods that require a lot of chewing or biting pressure may be difficult to manage. Dentures can also shift around in the mouth while chewing and lack sensation, which can make biting and chewing less controlled.
Despite these drawbacks, dentures allow you to consume a variety of foods. Opting for soft, moist foods that don’t require extensive chewing is best. Meats should be tender and cooked thoroughly. Avoid very hard, crunchy, or sticky foods that could dislodge dentures. Adhesives and denture stabilizers can help keep dentures in place while eating. With practice, denture wearers can find an enjoyable diet within the appliance’s capabilities.
Foods you can eat with dentures
- Soft, minced meats (stewed chicken, ground beef, fish)
- Eggs
- Mashed potatoes
- Cooked vegetables
- Soft fruits (bananas, peeled applesauce, berry compotes)
- Cottage cheese
- Oatmeal, cream of wheat
- Yogurt
- Soups
- Pasta
- Loaf breads
Dental Implants
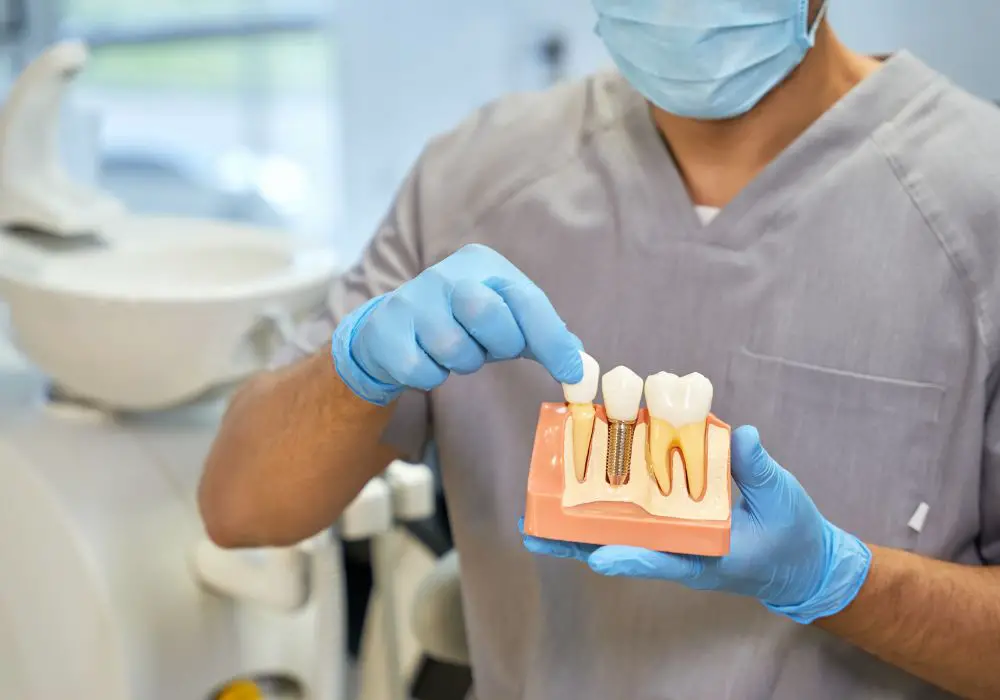
Dental implants are artificial tooth roots surgically inserted into the jawbone. An implant Crown is then attached to the top portion of the implant that protrudes above the gums. Implants fuse to the bone and serve as stable anchors for the replacement teeth attached to them. They can support crowns, bridges, or dentures.
Can you eat with dental implants?
Yes, dental implants allow for full use of teeth for eating. Implants mimic the function of natural tooth roots and provide the same strong foundation for biting and chewing. Unlike dentures, they do not shift in the mouth or require adhesives. The crown or replacement teeth attached to the implants also withstand greater biting forces than dentures without risk of damage.
With implants, you can eat anything you did with your natural teeth without discomfort or restrictions. The sensation and biting control is also superior thanks to their integration with the jawbone and nerves. Dental implants are an excellent solution for active eaters who want to enjoy all foods again without limitations.
Foods you can eat with dental implants
- All meats and poultry
- Fruits and vegetables (raw or cooked)
- Hard breads and bagels
- Sticky foods like caramel or gum
- Hard or crunchy snacks like nuts, popcorn, or hard candy
- Corn on the cob
- Pizza, burgers
- Beans, lentils
- Ice and popsicles
Dental Bridges
Dental bridges consist of an artificial tooth (or teeth) anchored on each side by a dental crown cemented onto natural teeth. The bridge restores the space where teeth are missing. The natural crowns on either end, called abutments, provide support for the bridgework between them.
Can you eat with dental bridges?
Yes, you can eat with dental bridges since they are securely cemented onto natural teeth. Bridges offer similar stability and functionality as natural teeth and dental implants when eating. The materials bridges are made from can withstand biting forces without risk of damage.
With a sturdy bridge in place, you can bite into and chew all types of foods without issues. Bridges offer a fixed solution for missing teeth that retains full use for eating. However, good oral hygiene is important for bridges to keep the abutment teeth and gums around them healthy. Be sure to brush and floss thoroughly around bridgework.
Foods you can eat with dental bridges
- All meats, produce, breads
- Hard or crunchy foods like raw veggies, nuts, seeds
- Sticky foods like peanut butter or gum
- Popcorn, chips
- Corn on the cob
- Apples, carrot sticks
- Pizza, burgers
- Hard candy or ice
Dental Crowns
A dental crown is a prosthetic cap that completely covers an injured or decayed tooth. The crown restores the tooth’s shape, size, and function. Crowns protect damaged teeth from further decay and fracture. Prepping the tooth for a crown does require some removal of outer enamel and inner dentin. But the remaining core is then reinforced by the strong crown material.
Can you eat with dental crowns?
Yes, you can eat all foods with dental crowns in place. Crowns are made of very durable materials that resist cracking or chipping from biting forces. The materials commonly used for crowns include porcelain fused to metal, zirconia, or gold alloys. These create a lasting restoration able to withstand years of wear from biting, chewing, and eating.
Crowns allow you to eat as normal without worrying about damaging the protected tooth. Their strength also prevents teeth around the crowned tooth from shifting or misaligning. As long as the crown is designed and fitted properly, it will provide lasting benefits for eating ability. Proper dental hygiene is still crucial though to prevent decay around the edge of the crown.
Foods you can eat with dental crowns
- All meats, produce, and breads
- Very hot or cold foods
- Hard or crunchy foods like nuts, raw veggies, popcorn
- Sticky candies and chewing gum
- Pizza, burgers, corn on the cob
- Hard candy or ice cubes
Temporary Restorations for Eating
Sometimes a permanent dental restoration can’t be placed right away. This may be due to needing time for healing or manufacturing of the final prosthetic. In these cases, a temporary restoration is used in the interim to protect the prepared tooth and serve for eating. There are three main options:
Temporary Crowns
Temporary acrylic or resin crowns can be placed following crown preparation until delivery of the custom permanent crown. They serve as coverage and protection in the meantime. Temporary crowns allow for light eating while avoiding damage to the prepared tooth underneath. However, they are meant for short-term use only.
Interim Partial Dentures
These are removable acrylic dentures made prior to implants or fixed bridges being completed. They replace missing teeth in the interim for modest eating function, but are not intended for long-term heavy use.
Flippers
A flipper is a single removable acrylic tooth (or several teeth) that fills in a gap from a lost tooth. It is held in by surrounding teeth or dental wire clasps. Flippers allow for eating while awaiting a permanent implant or bridge. But diet may need to be adjusted to softer foods due to their limited biting force.
Factors That Affect Eating Ability with Fake Teeth
The type of prosthetic teeth a person receives can significantly impact their eating capability and experience. But there are several other factors that also play a role in how well fake teeth perform for eating foods safely and comfortably:
Quality of Fit
For any dental prosthetic, the quality of fit in the mouth is imperative. Poorly fitted devices like dentures or bridges raise the risk of discomfort, damage, and deficiencies with eating. Proper molding, shaping, and adjustments to assure a tight, accurate fit helps fake teeth integrate seamlessly into normal eating habits.
Materials Used
The materials prosthetic teeth are fabricated from determine their strength and durability for withstanding biting forces. Dentures tend to be acrylic resin, while bridges and crowns utilize harder metals, porcelain, or zirconia. Implant-supported teeth also have high durability. More resilient materials translate to better eating ability.
Oral Health
Ongoing hygiene and preventive care is key to ensure fake teeth last and function optimally. Brushing and flossing around bridges, crowns, and implants is essential. Dentures must be cleaned and allowed to air out daily. Regular dental cleanings allow for inspection and early correction of any issues.
Diet and Habits
The foods you eat and oral habits impact outcomes with prosthetic teeth. Hard, sticky foods or aggressive chewing may damage more delicate restorations. Dentures in particular require dietary adjustments. Stopping smoking can also improve longevity of fake teeth and oral health.
Bone Loss
For dentures and implants, the amount of bone present affects their stability and performance. Lost bone from missing teeth can undermine dentures. Implants require adequate bone levels to integrate successfully. Procedures like bone grafting may be needed to strengthen the foundation.
Restoration Design
The design and layout of prosthetic teeth influences their eating function. Positioning and shape of replacement teeth in dentures or bridges must properly match natural teeth. Implants need precise placement accounting for anatomy and forces. Good planning prevents problems down the road.
Permanent vs Temporary
There is a significant difference in eating capability with a permanent prosthetic vs a temporary one. Temporary appliances like flippers or interim dentures serve a purpose but are intended for short-term limited use. They cannot match the durability and performance of a permanent solution.
Professional Care and Maintenance
Ongoing adjustments, repairs, relining, and other care from dental providers keeps fake teeth functioning at their best. Poorly maintained devices deteriorate faster. Annual exams allow early detection of problems to prevent eating difficulties.
Eating and Nutrition with Fake Teeth

Fake teeth make it possible to eat a wide variety of nutritious foods again. But some adaptation may be necessary at first. Certain strategies can facilitate optimal nutrition with different kinds of dental prosthetics.
Dentures
For new denture wearers, starting with soft foods and working up to more textured items is best. Use denture adhesive to prevent shifting that could cause choking. Chew slowly and carefully on both sides to distribute forces evenly. Cut harder items like meats and vegetables into small pieces. Opt for cooked vegetables that are easier to chew and digest. Stay hydrated with water and limit sticky, sugary foods.
Over time you can expand food choices as chewing control improves. But continue to avoid excessively hard, crunchy, or chewy fare that could loosen dentures. Be cautious with extremely hot foods that may melt adhesives.
Dental Implants
Implants function like natural teeth and allow free enjoyment of all foods. But certain habits can help implants last. Avoid biting or tearing with your front implants. Cut harder items into pieces and chew equally on both sides back in the mouth. This distributes forces more evenly onto multiple implants.
Focus on crunchy produce and fiberous vegetables to help stimulate gums and bone around implants. Stay hydrated and use fluoride toothpaste for added protection against plaque. See your dentist regularly to ensure implants stay secured and healthy.
Bridges
Food may get stuck under bridges at first. Floss carefully using a floss threader to dislodge debris. Over time you will adjust. Chew mostly on the opposite side of the mouth from bridge placement to protect abutment crowns. Limit sticky candies or chewing ice which could uncement the bridge. Focus on produce, lean proteins, and whole grains for nutrition.
Crowns
No major diet changes are needed with crowns. But favor chewing on the opposite side of the mouth to protect the crowned tooth. This allows it to share biting forces with other teeth. Limit biting hard items like nuts or ice cubes directly with the crowned tooth alone. Sticky foods are fine as long as you floss after to remove any lodged remnants.
Frequently Asked Questions About Eating with Fake Teeth
Do dentures allow you to eat normally?
Dentures facilitate eating to a reasonable degree but chewing and food choices are not the same as with natural teeth. Dentures require more care and control when biting and chewing. Hard, crunchy, or chewy foods in particular should be avoided. With practice, you can find satisfying foods to eat within the limitations. Using adhesives helps.
What foods should you not eat with dentures?
Avoid very hard, crunchy, sticky, or chewy foods that could loosen or damage dentures such as: raw carrots, nuts, seeds, popcorn, caramel, gum, bagels, fruits with skins/pits, ribs, celery, pizza crust, toffees, jerky.
Will implants allow me to eat like I did with my own teeth?
Yes, dental implants restore complete natural function for biting, chewing, and eating all foods. They fuse to the jawbone like tooth roots so you can bite and chew with confidence and full force. Implants bring back ability to enjoy any favorite foods.
How long after getting implants can you eat normally?
Most patients can resume normal eating within 2-6 weeks after getting implants. However, you may need to eat soft foods initially while they fully integrate with the bone over 3-6 months. Your dentist will advise you on diet timelines. Full biting force takes time to build back up.
Should you eat on both sides with dental implants?
Yes, you should try to chew evenly on both sides back in the mouth with implants, instead of favoring just one side. Distributing biting forces equally onto multiple implants helps prevent too much concentrated pressure on any single implant.
Key Takeaways
- Fake teeth like dentures, bridges, crowns, and implants allow for eating ability to varying degrees depending on the prosthetic.
- Dentures provide the most limited eating functionality while implants offer closer to natural teeth. Temporary appliances are for short-term use.
- Material strength, fit, oral health, bone support, and professional maintenance significantly impact eating with fake teeth.
- Adjustment to diet, eating habits, and food preparation can optimize nutrition and enjoyment with different kinds of dental prosthetics.
- Routine dental exams and hygiene are essential for keeping fake teeth functioning properly and allowing you to eat well.