Have you ever wondered where your furry friend’s teeth go when they fall out? As a dog owner, it’s important to know what happens during the teething process, and what to expect when your pup’s baby teeth start to fall out. Understanding this process can help you ensure that your dog’s oral health is in good condition.
Dogs, like humans, have two sets of teeth during their lives. The first set of teeth, known as baby teeth or deciduous teeth, begin to erupt at 3 to 5 weeks of age and usually fall out by 6 months of age. The second set of teeth, known as permanent teeth, develop later and are meant to last a lifetime. During the teething process, your pup’s baby teeth will fall out to make room for the permanent teeth. But where do they go? Some dogs will swallow their teeth while others may lose them while playing with toys. Retained baby teeth can cause issues with malocclusion and discomfort, so it’s important to monitor your pup’s teething process closely.
Understanding Dog Teeth
If you’re a dog owner, you might have wondered what happens to your dog’s teeth when they fall out. Understanding the life cycle of dog teeth and why they lose them can help you take better care of your furry friend’s dental health.
Life Cycle of Dog Teeth
Dogs have two sets of teeth during their lifetime, just like humans. The first set, called deciduous or baby teeth, start to come in when puppies are around three to four weeks old. By six months of age, most of these baby teeth will have fallen out and been replaced by permanent teeth.
Adult dogs have 42 permanent teeth, which include incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. These teeth are essential for biting, chewing, and grinding food. Just like baby teeth, adult teeth can also fall out due to injury, decay, or disease.
Why Do Dogs Lose Teeth?
Dogs lose their baby teeth to make way for their adult teeth. The process of losing baby teeth and growing adult teeth is called teething. It can be a painful and uncomfortable process for puppies, which is why they may chew on objects or become irritable during this time.
Adult dogs can also lose teeth due to dental problems such as gum disease or tooth decay. Other factors that can contribute to tooth loss include injury, trauma, or genetics.
Taking care of your dog’s teeth can help prevent tooth loss and dental problems. Regular brushing, dental check-ups, and providing your dog with chew toys can all help maintain good dental health.
In summary, understanding the life cycle of dog teeth and why they lose them can help you take better care of your furry friend’s dental health. By providing proper dental care, you can help prevent tooth loss and ensure your dog has a healthy and happy smile.
What Happens When Dogs Lose Their Teeth
Losing teeth is a natural part of life for dogs, just like it is for humans. However, unlike humans, dogs do not have the luxury of putting their lost teeth under their pillow for the tooth fairy to collect. So, where do dogs’ teeth go when they fall out?
When dogs lose their teeth, they typically swallow them. This may sound strange, but it is completely normal. In fact, dogs have a strong instinct to swallow anything that is in their mouth, including their own teeth. The good news is that dogs’ digestive systems are designed to handle this. Their stomach acid is strong enough to dissolve bones, so a tiny tooth is no problem.
It is important to note that dogs’ teeth do not fall out all at once like human baby teeth. Instead, their teeth fall out gradually over time as their adult teeth grow in. This process usually starts when they are around 4 months old and continues until they are about 7 months old. During this time, you may notice your puppy chewing on things more than usual. This is because their gums may be sore as their adult teeth come in.
If you notice that your dog is losing teeth outside of this time frame, it could be a sign of a dental problem. For example, if your dog’s teeth are loose or falling out due to injury or disease, it is important to take them to the vet for treatment.
In summary, when dogs lose their teeth, they typically swallow them, and their digestive systems are designed to handle this. If you have any concerns about your dog’s teeth, it is best to consult with your vet.
Where Do The Teeth Go
When your furry friend starts losing their baby teeth, you might wonder where those tiny teeth go. In this section, we will explore the different ways dogs’ teeth are disposed of.
Natural Disposal
Just like with humans, dogs’ baby teeth fall out naturally. The process of losing baby teeth is called “exfoliation.” Dogs usually start losing their baby teeth at around 12 weeks of age, and by the time they are 6 months old, all of their baby teeth should have fallen out.
When dogs lose their baby teeth, they will often swallow them. You might not even notice that your dog has lost a tooth because it is so small. If you are lucky, you might find a tooth on the floor or in your dog’s toys. But most of the time, the teeth are simply swallowed and pass through the digestive system.
Human Intervention
While dogs’ teeth are usually disposed of naturally, some owners choose to keep their dog’s baby teeth as a memento. If you want to keep your dog’s baby teeth, you can ask your veterinarian to save them for you.
If you don’t want to keep your dog’s baby teeth, you can simply dispose of them in the trash. Make sure to wrap them in tissue or paper before throwing them away to avoid accidentally pricking yourself on the sharp edges of the teeth.
It’s important to note that if your dog’s baby teeth don’t fall out naturally or if they are not replaced by permanent teeth, you should consult your veterinarian. Retained baby teeth can cause problems with your dog’s bite and can lead to dental issues in the future.
In conclusion, dogs’ baby teeth are disposed of naturally or through human intervention. Whether you choose to keep your dog’s baby teeth or dispose of them, it’s important to make sure that your dog’s dental health is taken care of.
Effects On The Dog’s Health
When your dog’s teeth fall out, it can have effects on both their physical health and mental well-being.
Physical Health
Missing teeth can lead to a variety of physical health problems for your dog. Without proper dental care, bacteria can build up in their mouth, causing bad breath, gum disease, and tooth decay. This can lead to pain, infection, and even tooth loss.
In addition, missing teeth can make it difficult for your dog to eat their food properly. They may have trouble chewing, which can lead to digestive problems and malnutrition. This can be especially problematic for older dogs, who may already have difficulty eating due to age-related health issues.
Mental Well-Being
Just like humans, dogs can experience emotional distress when they are in pain. Missing teeth can be painful for your dog, and can cause them to feel anxious, irritable, or depressed. This can lead to changes in their behavior, such as decreased appetite, lethargy, or aggression.
In addition, your dog’s appearance may be affected by missing teeth. This can be particularly distressing for dogs who are used to being praised for their looks or who are used to being the center of attention. They may become self-conscious or withdrawn, which can further impact their mental well-being.
Overall, it is important to take care of your dog’s teeth and address any issues as soon as they arise. This can help prevent physical health problems and ensure that your dog remains happy and healthy.
Preventing Tooth Loss In Dogs
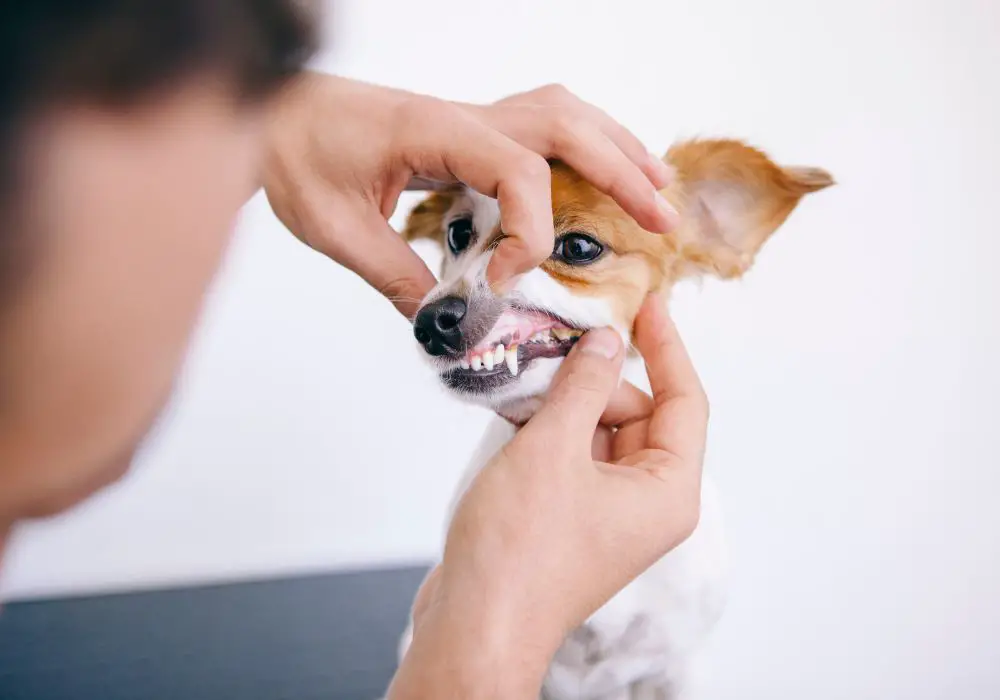

As a dog owner, you want to ensure that your furry friend has healthy teeth and gums throughout their life. Here are some measures you can take to prevent tooth loss in dogs.
Dental Care
Regular dental care is essential to maintain your dog’s oral health. Brushing your dog’s teeth daily is the best way to prevent plaque buildup, which can lead to tooth decay and gum disease. Use a soft-bristled toothbrush and toothpaste that is specifically designed for dogs.
In addition to brushing, you can also provide your dog with dental chews and toys that help clean their teeth and massage their gums. These products can help reduce plaque and tartar buildup and freshen your dog’s breath.
If your dog shows signs of dental problems, such as bad breath, swollen gums, or loose teeth, take them to the vet for a dental exam. Your vet may recommend professional teeth cleaning or other dental treatments to prevent tooth loss.
Dietary Measures
Your dog’s diet can also play a role in their oral health. Feeding your dog a balanced diet that includes high-quality protein and essential nutrients can help keep their teeth and gums healthy.
Avoid feeding your dog table scraps or sugary treats, which can contribute to tooth decay and gum disease. Instead, offer your dog healthy snacks such as carrots, apples, or dental chews that are low in calories and high in nutrients.
If your dog is prone to dental problems, your vet may recommend a special diet that is designed to promote oral health. These diets are formulated with ingredients that help reduce plaque and tartar buildup and maintain healthy teeth and gums.
By following these dental care and dietary measures, you can help prevent tooth loss in your dog and ensure that they have healthy teeth and gums throughout their life.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can I relieve my puppy’s teething discomfort?
Puppies experience discomfort while teething, which can lead to chewing on anything they can find. You can help your puppy by providing them with chew toys designed for teething puppies. Frozen carrots, apples, or sweet potatoes can also provide relief. Cold washcloths or ice cubes wrapped in a towel can also be beneficial.
When do puppies start losing their baby teeth?
Puppies start losing their baby teeth between the ages of 3 and 6 months. The incisors are usually the first to fall out, followed by the premolars and canines. By the time they are 6 months old, most puppies have lost all of their baby teeth.
What does a puppy’s tooth chart look like?
A puppy’s tooth chart shows the order in which their baby teeth come in and fall out. At around 3 weeks old, puppies will have their baby incisors. At 3-4 weeks, they will have their baby canines. At 4-6 weeks, their baby premolars will come in. Finally, between 4-6 months, their baby molars will fall out and be replaced by adult teeth.
What do puppy teeth look like when they fall out?
When puppies lose their teeth, they usually swallow them or drop them on the floor while playing. The teeth are small and sharp, and they look similar to tiny white triangles. If you find a puppy tooth, it will be small and sharp, with a root attached.
Are dogs in pain when they lose their teeth?
Dogs may experience some discomfort when losing their teeth, but it is usually not severe. They may experience some bleeding or swelling in the gums, but this should resolve within a few days. If you notice excessive bleeding or swelling, contact your veterinarian.
Do dogs’ teeth grow back after falling out?
No, dogs’ teeth do not grow back after falling out. Once a tooth falls out, it is gone for good. It is essential to take care of your dog’s teeth to prevent tooth loss and maintain their dental health. Regular dental cleanings and checkups with your veterinarian can help prevent tooth loss and other dental issues.