If you’re a dog owner, you may be wondering if your furry friend’s teeth hurt when they rot. The short answer is yes, dogs can experience pain when their teeth rot. Just like humans, dogs can suffer from dental problems that can cause discomfort and pain.
Rotten teeth in dogs are often caused by periodontal disease, which is a bacterial infection that affects the gums and teeth. If left untreated, it can lead to tooth decay, gum disease, and even tooth loss. As the infection progresses, it can cause pain, discomfort, and difficulty eating. If your dog has bad breath, swollen gums, or loose teeth, it’s important to take them to the vet as soon as possible to prevent further damage and alleviate any pain they may be experiencing.
Understanding Dog’s Teeth
Taking care of your dog’s teeth is essential for their overall health and well-being. Dental problems can cause pain, discomfort, and even lead to serious health issues if left untreated. In this section, we will discuss the anatomy of a dog’s teeth, common dental problems, and how to prevent them.
Anatomy of a Dog’s Teeth
Dogs have two sets of teeth, just like humans. Their first set, known as deciduous teeth or “milk teeth,” falls out as they grow, and their permanent teeth grow in. Adult dogs have 42 teeth, which include incisors, canines, premolars, and molars. Each type of tooth serves a different purpose, from biting and tearing to grinding and chewing.
Common Dental Problems
Dental problems are common in dogs, and they can be painful and uncomfortable. One of the most common dental problems is periodontal disease, which is caused by a buildup of plaque and tartar on the teeth. This can lead to gum inflammation, tooth decay, and even tooth loss. Other dental problems include fractured teeth, abscesses, and oral tumors.
Prevention and Treatment
Preventing dental problems in your dog is essential. Regular dental check-ups, brushing your dog’s teeth, and providing them with dental chews are all effective ways to prevent dental problems. If your dog does have dental problems, treatment options may include professional dental cleaning, extractions, and antibiotics.
In conclusion, understanding your dog’s teeth and how to take care of them is crucial for their overall health and well-being. By regularly checking your dog’s teeth, providing them with proper dental care, and seeking treatment when necessary, you can help prevent dental problems and keep your dog healthy and happy.
Symptoms of Dental Problems in Dogs

If your dog’s teeth are rotting, it can cause them a lot of pain and discomfort. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of dental problems in dogs so that you can take action as soon as possible. Here are some physical signs and behavioral changes to watch out for:
Physical Signs
- Bad breath: One of the most common signs of dental problems in dogs is bad breath. If your dog’s breath smells foul, it could be a sign of rotting teeth.
- Discolored teeth: Another physical sign to look out for is discolored teeth. If your dog’s teeth are yellow or brown, it could be a sign of decay.
- Swollen or bleeding gums: If your dog’s gums are swollen or bleeding, it could be a sign of periodontal disease. This is a serious condition that can lead to tooth loss if left untreated.
- Loose or missing teeth: If your dog’s teeth are loose or missing, it could be a sign of advanced dental disease. This is a painful condition that can make it difficult for your dog to eat and drink.
Behavioral Changes
- Loss of appetite: If your dog is experiencing dental pain, they may lose their appetite. This can lead to weight loss and other health problems.
- Pawing at the mouth: If your dog is pawing at their mouth or rubbing their face against objects, it could be a sign of dental pain.
- Changes in behavior: If your dog is normally friendly and outgoing but suddenly becomes withdrawn or aggressive, it could be a sign of dental pain. Dogs in pain may also be less active than usual.
If you notice any of these symptoms in your dog, it is important to take them to the vet as soon as possible. Your vet can perform a dental exam and recommend treatment options to help alleviate your dog’s pain and prevent further dental problems.
Causes of Tooth Decay in Dogs
If you’re concerned about your dog’s dental health, you may be wondering what causes tooth decay in dogs. There are several factors that can contribute to this problem, including poor oral hygiene, diet, and chewing habits.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Just like with humans, poor oral hygiene is a common cause of tooth decay in dogs. When you don’t brush your dog’s teeth regularly, plaque and tartar can build up on their teeth, leading to tooth decay and gum disease. This can be especially problematic for dogs who are prone to dental issues, such as small breeds and those with crowded teeth.
To prevent tooth decay caused by poor oral hygiene, it’s important to brush your dog’s teeth regularly with a toothbrush and toothpaste designed specifically for dogs. You can also provide them with dental chews and toys to help keep their teeth clean.
Diet and Chewing Habits
Your dog’s diet and chewing habits can also play a role in their dental health. Dogs who eat a lot of sugary or starchy foods are more likely to develop tooth decay, as these foods can stick to their teeth and promote the growth of harmful bacteria.
Chewing on hard objects, such as bones and antlers, can also cause tooth decay if your dog chews too aggressively or if the objects are too hard for their teeth. This can lead to chips, cracks, and other damage that can make it easier for bacteria to invade their teeth and cause decay.
To prevent tooth decay caused by diet and chewing habits, it’s important to feed your dog a balanced diet that’s low in sugar and starch. You should also supervise them when they’re chewing on hard objects and provide them with softer alternatives, such as rubber toys and dental chews.
Effects of Tooth Decay on Dogs
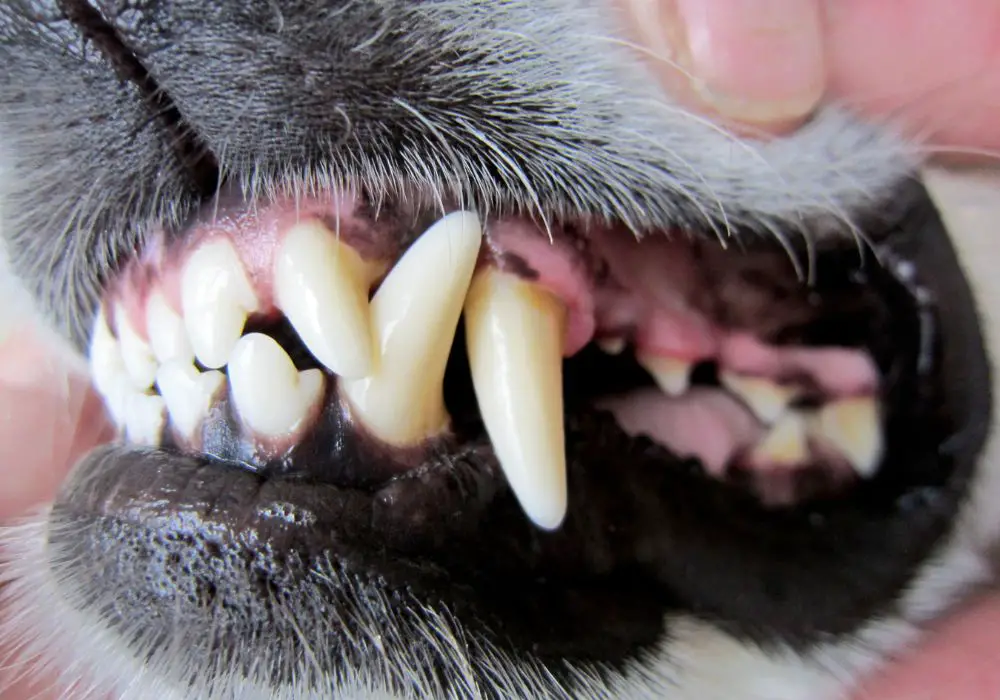
Tooth decay in dogs can cause a range of negative effects on their health and well-being. In this section, we will discuss the pain and discomfort that dogs may experience as well as the potential systemic health issues that can arise from untreated tooth decay.
Pain and Discomfort
As tooth decay progresses, it can cause significant pain and discomfort for your furry friend. Dogs may experience pain when eating, drinking, or even just opening their mouth. They may also drool excessively, paw at their face, or refuse to eat altogether. In severe cases, tooth decay can lead to abscesses, which can cause even more pain and discomfort.
It’s important to note that dogs are often very good at hiding their pain, so it’s essential to be vigilant about their dental health. Regular check-ups with your veterinarian can help identify tooth decay early on, before it becomes a more significant issue.
Systemic Health Issues
Untreated tooth decay in dogs can also lead to systemic health issues. When bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream, they can travel to other parts of the body and cause infections. This can lead to a range of health problems, including:
- Heart disease: Bacteria can travel to the heart and cause inflammation, which can lead to heart disease.
- Kidney disease: Bacteria can also travel to the kidneys and cause infections, which can lead to kidney disease.
- Liver disease: Infections in the liver can also occur when bacteria from the mouth enter the bloodstream.
- Respiratory issues: Bacteria can also travel to the lungs and cause respiratory infections.
In addition to these health issues, untreated tooth decay can also lead to tooth loss, which can make it difficult for your dog to eat and lead to malnutrition.
Overall, it’s essential to take your dog’s dental health seriously and address any signs of tooth decay promptly. Regular dental check-ups, a healthy diet, and good dental hygiene can all help prevent tooth decay and maintain your furry friend’s overall health and well-being.
Prevention and Treatment of Dental Problems
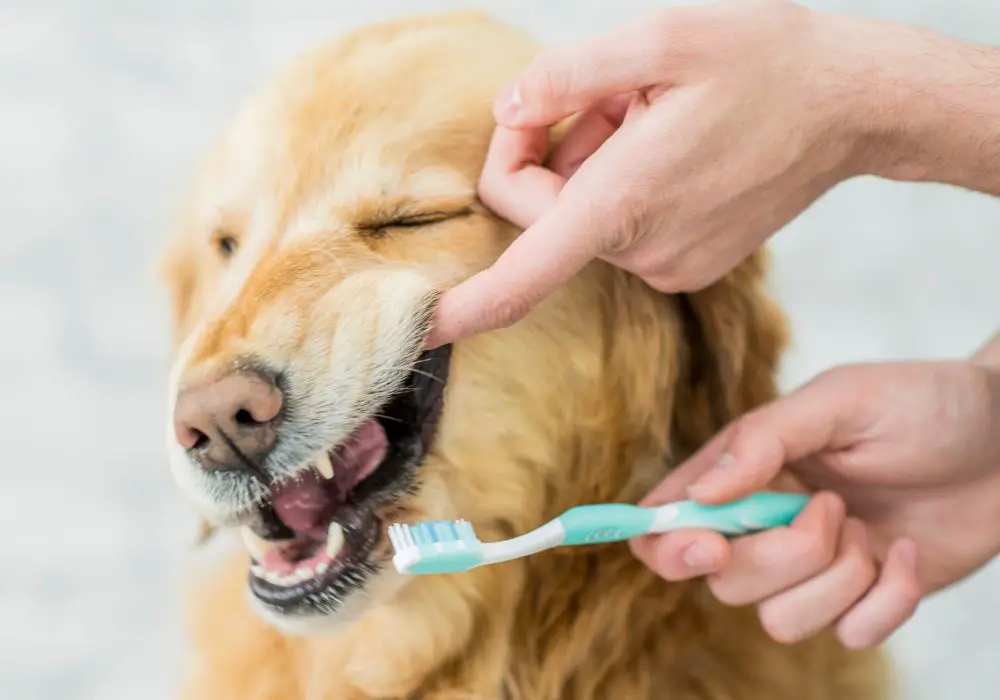
Taking care of your dog’s teeth is essential to prevent dental problems such as rotten teeth. Here are some preventive measures and treatments you can take to ensure your dog’s dental health.
Regular Dental Checkups
It is important to schedule regular dental checkups with your veterinarian to ensure your dog’s teeth are healthy. During the checkup, the vet will examine your dog’s teeth and gums for any signs of dental problems such as tartar buildup, gum disease, or tooth decay. Early detection of dental problems can prevent them from becoming more severe.
At-Home Dental Care
You can also take care of your dog’s teeth at home by brushing them regularly. Use a toothbrush and toothpaste specifically designed for dogs. You can also give your dog dental chews or toys that help clean their teeth and massage their gums. Be sure to provide your dog with a healthy diet that is low in sugar and high in nutrients.
Professional Dental Cleaning and Treatment
If your dog has dental problems, your veterinarian may recommend professional dental cleaning and treatment. This may involve scaling and polishing your dog’s teeth, extracting any rotten teeth, or treating gum disease. Your vet may also prescribe antibiotics to treat any infections.
Remember, prevention is key when it comes to your dog’s dental health. Regular checkups and at-home dental care can prevent dental problems from developing in the first place. If your dog does develop dental problems, seek professional treatment to prevent them from becoming more severe.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the signs of bad teeth in dogs?
Bad teeth in dogs can have a range of signs, including bad breath, yellow or brown discoloration on the teeth, swollen or bleeding gums, difficulty eating or chewing, and loose or missing teeth. If you notice any of these signs, it’s important to take your dog to the vet for a dental exam.
How can I tell if my dog is in pain from tooth decay?
Dogs may not always show obvious signs of pain, but some signs to look out for include decreased appetite, lethargy, pawing at the mouth, drooling, and whining or whimpering. If you suspect your dog is in pain, it’s important to get them checked out by a vet.
What are the symptoms of rotting teeth in dogs?
Symptoms of rotting teeth in dogs can include bad breath, inflamed or bleeding gums, loose or missing teeth, and difficulty eating or chewing. In some cases, dogs may also develop abscesses or infections in the mouth.
What are the stages of tooth decay in dogs?
Tooth decay in dogs typically progresses through several stages, starting with the accumulation of plaque and tartar on the teeth, which can lead to gingivitis and periodontal disease. Over time, the teeth may become loose or fall out, and infections can spread to other parts of the body.
How do I treat my dog’s rotten teeth?
Treatment for rotten teeth in dogs may involve a combination of professional dental cleaning, antibiotics, and extractions of severely damaged teeth. In some cases, surgery may be necessary to address more serious infections or abscesses.
Is tooth decay painful for dogs?
Yes, tooth decay can be painful for dogs, especially as it progresses and affects the nerves and roots of the teeth. It’s important to address dental issues in dogs as soon as possible to prevent pain and discomfort, as well as more serious health problems.