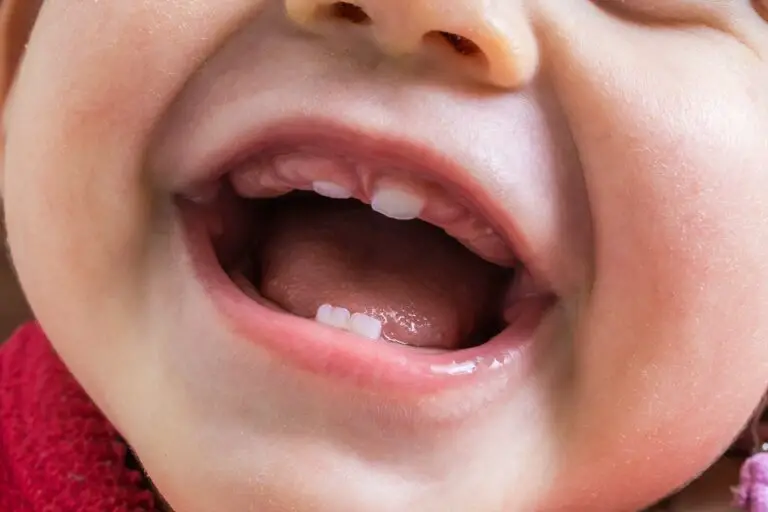
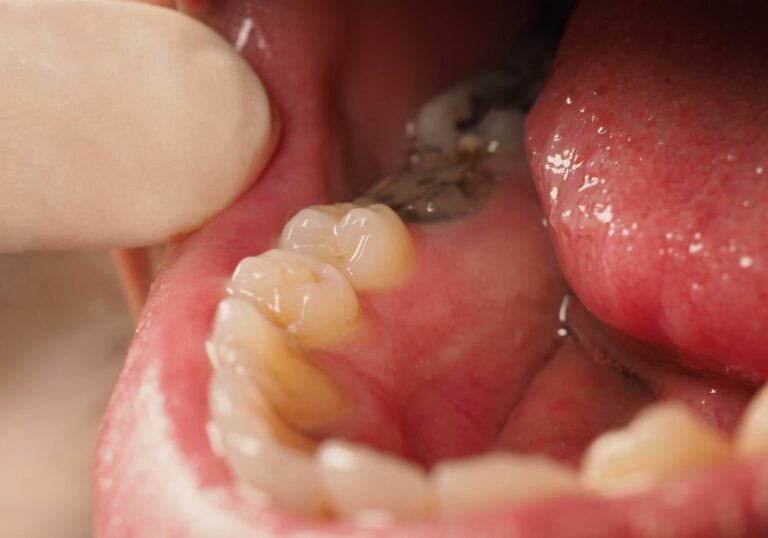
What Causes Gums to Grow Over Teeth?

Gums can overgrow and creep over teeth for several reasons:
Gingivitis
Gingivitis, which is inflammation of the gums, is most commonly caused by plaque buildup. When plaque accumulates along and under the gumline, it irritates the gums and causes them to become puffy, red, and prone to bleeding. In moderate to severe cases, the gums can swell substantially and begin protruding over the teeth. Research shows that about 62% of adults have gingivitis, making it a prevalent precursor to gum overgrowth.
Periodontitis
Periodontitis is a more severe form of gum disease affecting the tissues and jaw bone supporting the teeth. As periodontitis progresses, the gums pull away from the teeth in some areas, while swelling over them in other areas. Periodontitis causes deep gum pockets around the teeth that allow more plaque accumulation and bacterial overgrowth. Over time, chronic inflammation causes both gum recession and substantial overgrowth in different parts of the mouth.
Drug Effects
Certain prescription medications are associated with gum overgrowth as a side effect. Most commonly, drugs like phenytoin for epilepsy, cyclosporine for people with transplants, calcium channel blockers like nifedipine for blood pressure, and some cancer drugs can cause inflated, swollen gums. It appears the drugs modify fibroblasts in gum tissue, which results in overgrown gums in about half of patients taking these medications long-term. The degree of gum swelling varies greatly between individuals.
Hormonal Changes
Hormone fluctuations during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can increase susceptibility to gum tissue swelling and overgrowth in some women. Research indicates estrogen and progesterone levels alter local cytokine regulation and the bacteria balance in the mouth. Gingivitis rates also rise with the influx of hormones. The inflammation and disruption of the periodontium allows gums to swell readily during these hormonal phases. Young girls and women going through hormonal milestones should practice excellent oral hygiene to avoid overgrown gums.
Genetic Factors
Emerging research shows certain genetic variations make some individuals more prone to gum disease and aggressive gum overgrowth. There are complex interactions between gene regulation, oral bacteria, and environmental factors that drive gingival enlargement. While good home care can help control genetic predispositions, some people may experience rapid, substantial gum overgrowth with mild gingival irritation.
Malocclusion
A malocclusion, or misaligned bite where the upper and lower teeth do not fit together properly, can put uneven forces on the teeth. This leads to teeth crowding or spreading in areas, which allows the gum tissue to build up in the spaces created. Malocclusion also makes oral hygiene difficult, increasing plaque accumulation and gum irritation. Orthodontic treatment is often required to correct the bite and subsequent gum overgrowth.
Is it Possible to Reverse Gum Recession?

Mild to moderate gum recession can potentially be reversed if treated early using several techniques:
- Improved oral hygiene – Meticulous brushing and flossing to control plaque is essential to allow gums to heal and reattach to teeth. This limits additional recession.
- Professional cleanings – Dentists and hygienists use scalers and curettes to remove calculus deposits above and below the gumline. This reduces inflammation and pockets for gums to fill back in.
- Gum grafting – A thin layer of tissue is transplanted from the palate or donated tissue to cover exposed roots, protecting them and allowing surrounding gum regrowth. Pinhole grafting is a less invasive option.
- Growth factor protein – Emdogain is a special protein gel derived from enamel that stimulates growth when applied to receded gums. One study showed it regrew an average of 0.9mm of lost tissue.
- Antibiotics or antiseptic washes – These reduce harmful bacteria to resolve gum infection and inflammation as a first step.
However, advanced recession with significant bone loss cannot be reversed fully. Gums can be partially restored but the lost soft and hard tissue cannot be recreated. Preventing additional recession is the goal once substantial damage occurs.
Can Overgrown Gums Covering Teeth Be Reshaped?
Several treatment methods can be used to reshape overgrown gum tissue:
- Professional dental cleanings – Removing plaque above and below the gumline helps reduce inflammation and swelling. Areas of overgrown tissue are smoothed down.
- Medication changes – If drugs are causing the gum overgrowth, discontinuing or changing medications may slowly help shrink inflamed gums. This must be discussed with a doctor.
- Flap surgery – Gums are lifted via an incision and excessive tissue is contoured and repositioned to normal heights. Tartar is removed from tooth roots to reduce pockets.
- Soft tissue grafts – Grafts use thin gum tissue to cover exposed roots and reinforce thin tissue prone to recession after reshaping. This stimulates natural gum contours.
- Bone grafts – Dense mineralized tissue is placed to fill bone defects from periodontitis that contribute to poor gum support and growth.
- Orthodontic treatment – Straightening misaligned teeth allows gums to reshape around the proper tooth positions once excess forces are removed.
- Laser gum reshaping – Lasers precisely remove and contour swollen gum regions with less bleeding and faster healing than traditional surgery.
- Ozone therapy – Applied below the gums, ozone gas can disinfect periodontal pockets and reduce harmful bacteria to shrink inflamed gums.
With moderate to severe overgrowth, a combination of soft tissue grafts, bone grafts, and laser procedures often produce the best cosmetic gum results. Mild cases may respond to conservative treatments alone.
What Happens if Gum Overgrowth is Left Untreated?

Leaving excessive gum tissue to continue growing over the teeth comes with oral health risks:
- Plaque accumulation under the swollen gumlines which causes accelerated tooth decay. The gums provide a sheltered area for bacteria.
- Bone loss around the teeth as chronic inflammation from trapped bacteria dissolves the bony sockets. This can eventually lead to tooth loss.
- Increased risk of painful gum abscesses and infection as the swollen pockets fill with bacteria.
- Difficulty eating or chewing certain foods. Excess gum tissue gets in the way of proper biting and chewing motions.
- Poor aesthetics with a “gummy smile.” Significant overgrowth is often considered unsightly.
- Halitosis or bad breath as bacteria multiply in the enlarged gum pockets.
- Potential association with heart disease, diabetes complications, rheumatoid arthritis, and respiratory disease by prolonging systemic inflammation.
- Greater chance of precancerous lesions developing with long-standing chronic gum inflammation.
Seeking treatment promptly is recommended to avoid these problems and restore proper form and function.
Signs That Indicate Treatment is Needed
See a dentist promptly if the following symptoms develop:
- Swollen, red, or bleeding gums when brushing/flossing
- Gums receding in some areas and puffy in other areas
- Pus or persistent bad odor between gums and teeth
- Teeth feeling loose or shifting positions
- Changes in tooth alignment or bite
- Portions of some tooth crowns being covered by tissue
- Hardened plaque deposits under the gumline
- Persistent gum inflammation or tenderness
- Difficulty eating or discomfort when chewing
At the first signs of gingival inflammation or overgrowth, professional treatment is recommended to prevent recession and extensive overgrowth. Periodic dental exams help detect problems early.
What Treatment Options are Available?
| Treatment | Procedure | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Professional Cleaning | Remove plaque above and below gumlines with scalers/curettes | Non-invasive; treats gingivitis | Temporary results; can’t address significant overgrowth |
| Antibiotics | Prescribe systemic or topical antibiotics to control bacteria | Fights gum infection when combined with cleaning | Ineffective alone; doesn’t address anatomical issues |
| Flap Surgery | Lift gums, contour tissue, clean tooth roots | Reduces deep pockets; reshapes gums; better access | Invasive procedure; cutting of gum tissue required |
| Tissue Grafts | Transplant gum tissue to reinforce thin areas | Stimulates new gum growth; covers exposed roots | Grafts require donor tissue source |
| Bone Grafts | Transplant bone to fill defects under gums | Restores bone lost to disease; stabilizes teeth | Invasive harvesting of bone matter required |
| Orthodontic Treatment | Corrects bite misalignment and crowding | Realigns teeth so gums recontour | Lengthy process; results can relapse |
| Laser Treatment | Precisely remove and reshape swollen gum tissue | Reduced bleeding/discomfort; faster healing | Cannot fully replace conventional surgery |
| Pinhole Technique | Small needle holes allow tissue grafting without incisions | Minimally invasive; no sutures | Limited to minor grafting needs |
Dentists create a tailored treatment plan depending on the amount of inflammation, pocket depth, bone loss, and aesthetic concerns. Options can be used in various combinations for optimal gum reshaping and health.
What is the Typical Recovery Process After Treatment?

Healing times vary based on the treatment methods used:
- Non-surgical cleanings require no recovery period. Patients can resume normal oral hygiene routines immediately.
- Following flap surgery, sutures hold gums in the new position for about 1 week as initial healing occurs. Sutures are removed after this period.
- With soft tissue grafts, the palate donor site heals in 2-3 weeks. Grafted gums require up to 6 weeks for complete healing.
- For laser treatments, gums may have some sensitivity for several days but heal relatively quickly. Multiple sessions are typically scheduled.
- After bone grafts, gums need approximately 6-8 weeks to fully recover. Graft sites tend to be more painful.
- With orthodontics, soreness and adjustment is common after braces are first put on. Teeth with bands can be sensitive to hot and cold.
Proper oral hygiene should be resumed gently after several days. Smoking and alcohol must be avoided during recovery. Follow all post-op instructions carefully to prevent complications.
Are There Effective Home Remedies?
Natural home treatments can temporarily reduce gum swelling and inflammation related to gingivitis but cannot address substantial overgrowth:
- Salt water rinses – Rinsing with warm salt water helps decrease swollen gums and flush out bacteria. It should be done gently following procedures.
- Green tea – Compounds called catechins have natural anti-inflammatory effects that may reduce mild gum swelling when used as a mouthwash.
- Aloe vera – The soothing gel can be applied directly to irritated gums to provide relief. It is antimicrobial and enhances cell healing.
- Oil pulling – Swishing oils like sesame, coconut, or olive oil can help pull toxins from the gums and fight inflammation.
- Proper flossing – Removes debris from between teeth and tightens gums that are starting to swell.
For moderate to severe cases of gum overgrowth, professional treatment is required. Home remedies can support gum health but will not substitute for definitive periodontal procedures.
Are There Any Natural Remedies to Help?
A few natural supplements and herbal remedies may help control gum inflammation:
- Coenzyme Q10 – This antioxidant stimulates collagen production and protects gum tissue when taken orally and rubbed on gums.
- Aloe vera – The plant’s anti-inflammatory properties can reduce swelling when used consistently. It also enhances cell repair.
- Turmeric – Curcumin, the active ingredient in turmeric, offers strong anti-inflammatory benefits. Turmeric paste may aid gum healing.
- Green tea extract – Powerful plant compounds called catechins restrict bacterial growth in the mouth and encourage gum regeneration.
- Cloves – The eugenol compound in cloves provides temporary numbing relief for sore gums when applied topically. It also has antimicrobial effects.
- Myrrh – This herb has natural antiseptic qualities and can be diluted with water and used as an antibacterial mouthwash.
Some herbal toothpaste, mouthwash, and gum products also incorporate these natural ingredients to help control gingival inflammation. While natural remedies can support professional gum treatments, they do not provide definitive treatment for substantial gum overgrowth on their own. Proper oral hygiene and care from dental professionals is still needed.
What Nutritional and Lifestyle Changes Improve Gum Health?
Certain dietary modifications and lifestyle changes can enhance treatment outcomes:
Nutrition
- Eat more antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables – They reduce inflammation and support healing.
- Increase intake of vitamins C, D, B2, B3, B7, and B12 – These strengthen gums and aid tissue regeneration.
- Consume yogurt with active probiotics – Promotes a healthy oral bacteria balance.
- Reduce sugar, refined carbs, and acidic drinks – Limit the nutrients plaque bacteria feed on.
- Drink green tea – The antioxidants fight inflammation and bacteria overgrowth.
- Eat more anti-inflammatory omega-3 fatty acids from fish and nuts – Helps curb swollen gums.
Lifestyle
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol – These aggravate gum problems and impede healing.
- Manage chronic stress – Lower stress hormone levels decrease systemic inflammation.
- Drink plenty of water – Proper hydration maintains saliva flow needed for gum protection.
- Use soft-bristled toothbrush – Prevents gum irritation during brushing.
- Visit dentist regularly – Periodic cleanings and exams ensure problems get treated promptly.
With the right diet and self-care routine, most cases of mild to moderate gum overgrowth can be treated and reversed successfully. More severe cases require coordination with a periodontist as well.