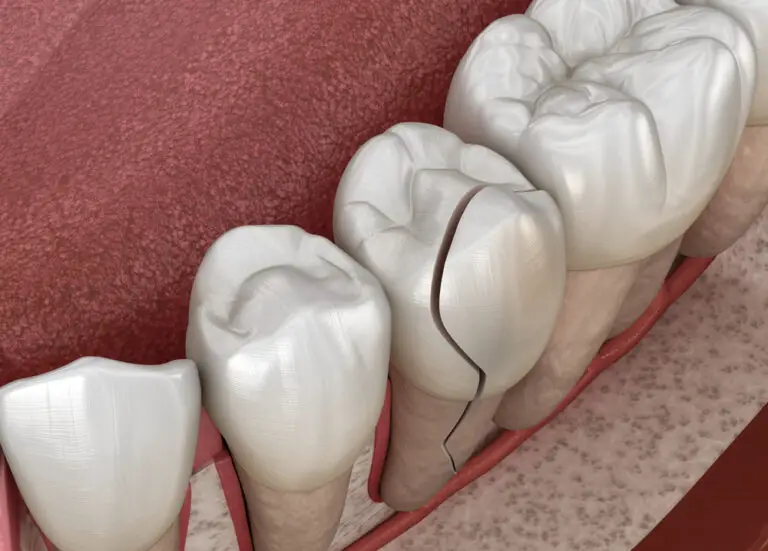
Receding gums, also known as gingival recession, is an oral health condition that affects nearly half of adults over 30. It occurs when the gum tissue surrounding the teeth wears away, exposing more of the tooth surface and roots. As gums recede, it can lead to tooth sensitivity, decay, loose teeth, and eventually tooth loss if left untreated.
The good news is that if caught early, receding gum tissue can often be regenerated and restored through a variety of dental treatments. With proper oral care and gum recession therapy, damaged gums can be repaired and rebuilt back to a healthy state.
What causes gums to recede?
There are several contributing factors that can lead to receding gums:
- Aggressive brushing: Brushing too vigorously with a stiff-bristled toothbrush or improper brushing technique can wear away gum tissue over time. Using a soft brush and gentle motions is essential.
- Poor oral hygiene: Inadequate daily plaque removal allows bacteria to build up along the gumline. This leads to inflammation and infection that damages the gum fibers and bone.
- Smoking and tobacco use: The heat, chemicals, and smoke from smoking constrict blood vessels, limit oxygen delivery, and irritate gum tissues. This impairs healing and worsens recession.
- Genetic factors: Some people are predisposed to thinner gums or irregular gum/tooth architecture that make them more prone to receding gums.
- Hormonal fluctuations: Changes in hormones during puberty, menstruation, pregnancy, and menopause can increase gum sensitivity and inflammation.
- Grinding and clenching: Constant pressure placed on teeth from these behaviors can shift teeth in the bony socket, causing gum detachment.
- Periodontal disease: Chronic gum infections such as gingivitis and advanced periodontitis damage the gum fibers and supporting bone that anchor teeth in place.
- Diabetes: Poor blood sugar control impairs healing and makes gums more susceptible to infections that can cause recession.
- Orthodontic appliances: Excess pressure from braces, aligners, or appliances may inadvertently move teeth out of their normal position, detaching gums.
- Aging: Gums naturally recede and become thinner over time due to weaker gum elasticity and collagen loss. Older individuals often have some degree of recession.
Stages of receding gums
Receding gums progresses through several stages:
Stage 1: Mild recession
At this early stage, the gums have only receded by 1-2 millimeters from the crown down the root surface. There is minimal bone loss or tooth detachment. People may start noticing some tooth sensitivity or root exposure when brushing. Mild inflammation and bleeding when brushing are also common signs during initial recession.
Stage 2: Moderate recession
As gum recession becomes more severe, the gums can recede 4 millimeters or greater, exposing a substantial portion of the root surface. Gum pockets may start to develop between the gumline and teeth.
Moderate to significant bone loss around the teeth is apparent during dental x-rays. Teeth may start to loosen and drift due to the loss of gum and bone support.
Stage 3: Severe recession
In the most advanced stage of gum recession, the gums have receded beyond the jawbone level, exposing the entire root and damaging the periodontium tissues that support the teeth. 6 millimeters or more of the roots may be exposed.
Teeth become extremely sensitive and are often loose or ready to fall out due to such extensive loss of anchoring gum tissue and bone. Decay at the newly exposed root surfaces also accelerates.
Can receding gums grow back?

If caught in the early stages of recession, it may be possible for some natural gum regrowth to occur, covering small areas of exposed roots. However, once recession becomes moderate to severe with substantial tissue loss, the gums cannot regrow back on their own without intervention.
Gum regeneration procedures performed by a dentist or periodontist are required to successfully rebuild receded gum tissue and restore gum coverage to exposed roots.
When gums first start to recede, the gumline is detached from the tooth but the epithelial attachment remains intact. The epithelium is a thin outer cell layer that connects the gums to teeth.
As long as this epithelial attachment remains, it is possible for your gumline to reattach and creep back up over areas of root exposure through proper oral care and light gum stimulation treatments.
However, with more advanced recession, the epithelial attachment becomes damaged or lost. Once this attachment is gone, your gums can no longer grow back up over exposed surfaces on their own power.
Surgical and non-surgical procedures are needed to regenerate new gum tissue and reestablish a seal over exposed roots. Without treatment, the recession will keep progressing.
Treatment options for rebuilding receding gums
Treating receding gums should start early for the best results. Here are the leading treatment options for regenerating lost gum tissue:
1. Gum grafting surgery
Gum grafting is the gold standard treatment for receding gums. During this minor flap procedure, a small piece of gum tissue is removed from the roof of the mouth (palate) or harvested from a tissue bank.
This gum graft is then surgically sutured and secured over the exposed root areas. Over the next 3-6 months, new blood vessels form in the graft allowing it to fully integrate with your existing gumline tissue.
Gum grafts can cover between 2-5 millimeters of lost gum height, effectively masking areas of root exposure for improved aesthetics and protection. Grafts have a 70-90% success rate when done correctly.
2. Pinhole surgical technique
This is a minimally invasive approach performed without any donor grafts or sutures. The gum tissue is gently loosened from its attachment and placed over exposed root surfaces.
Tiny pinhole incisions are made to allow the gums to be stretched and positioned up over areas of recession. There is very minimal recovery time with this technique, and between 1-3 millimeters of root coverage can be achieved.
3. Growth factor treatment
Growth factors derived from blood platelets or other sources can be applied around receding areas to jumpstart gum regeneration. Common options are platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) and enamel matrix derivative (EMD).
They work by stimulating adult stem cells in the area to boost new cell, tissue, blood vessel and collagen growth. This allows gums to fill in defects and reattach over exposed roots. Several monthly treatments are needed for incremental improvements.
4. Dental splinting
Also called dental stabilization, splints connect together neighboring teeth to provide a stable, immobilized environment for loose teeth. This stops additional recession and allows gums a chance to reattach while other regenerative treatments progress.
5. Laser gum therapy
A dental laser is utilized to remove and disinfect diseased, inflamed gum tissues, improve attachment, and stimulate new tissue growth. It can be used to augment grafting procedures or by itself to treat mild recession cases. Several sessions are typically needed. Lasers may provide 1-3 millimeters of root coverage.
| Treatment | Amount of gum regrowth | Recovery time | Success rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gum grafting | 2-5 mm | 4-6 weeks | 70-90% |
| Pinhole technique | 1-3 mm | 1 week | Variable |
| Growth factors | Up to 2 mm | No downtime | Unpredictable |
| Splinting | Stops recession | No downtime | Temporary aid |
| Laser therapy | Up to 3 mm | No downtime | Variable |
The prognosis for receding gums can vary depending on the severity. Mild cases often respond very well to treatment with significant gum regrowth. More advanced recession with substantial tissue loss may only partially recover or stabilize with therapy.
Proper oral care for gum regrowth
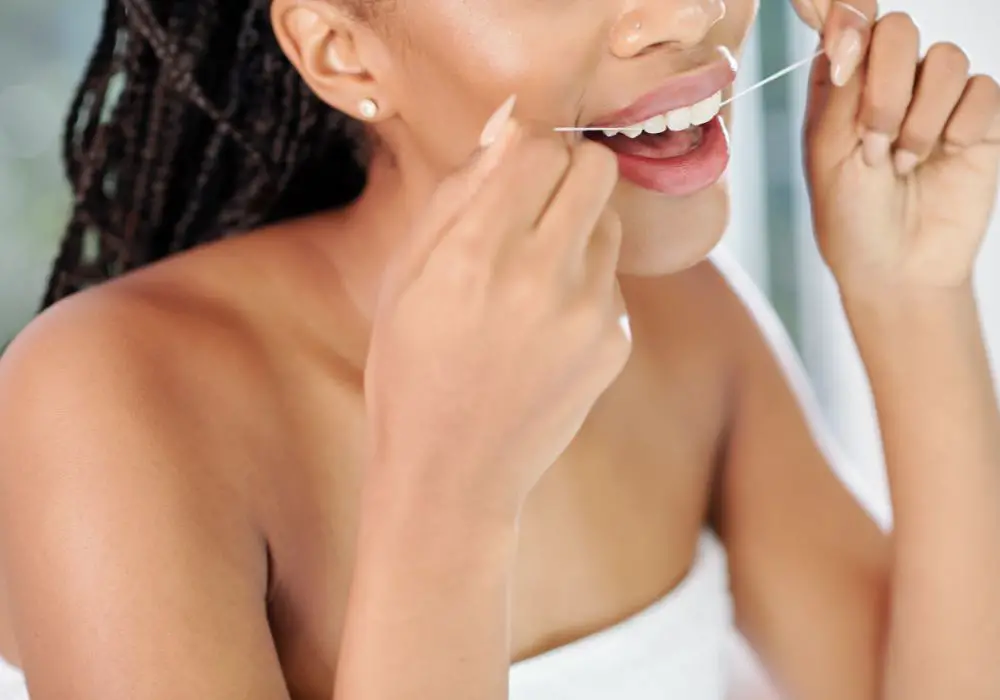

To optimize your chances of gum regrowth after professional treatment, excellent at-home oral hygiene and care is required:
- Gentle, thorough brushing: Use ultrasoft brush and focus on angling bristles along gumline instead of scrubbing hard.
- Daily flossing: Gently floss at the gumline to remove bacterial plaque, being careful not to injure gums.
- Antimicrobial rinses: Use prescription rinses or over-the-counter options daily to reduce pathogenic oral bacteria.
- Quit smoking: Cease all tobacco habits, as smoking greatly slows healing and worsens gum recession.
- Stress reduction: Chronic stress negatively impacts gum inflammation; relax with yoga, meditation, or other methods.
- Healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in whole foods for good immunity and tissue healing.
- Regular cleanings: Visit your dentist every 3-6 months to monitor recession and prevent further gum damage.
With diligent oral hygiene and gum treatments, receding gums can be repaired and induced to grow back over exposed root surfaces. Managing other risk factors is key for optimal treatment success.
Receding gum home remedies
There are some natural home remedies that may help support gum healing and regrowth when combined with professional treatment:
- Aloe vera: The anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera gel can soothe irritated gums and possibly encourage minor tissue regrowth when applied twice daily.
- Green tea: Rinsing with green tea may destroy cavity-causing bacteria in the mouth and provide antioxidant support for healing inflamed gums.
- Coconut oil: Swishing with coconut oil is thought to control inflammation and possibly promote some gum regrowth by fighting bacteria.
- Lemon oil: Diluted lemon essential oil may stimulate gum circulation when gently massaged on the gums, which optimizes conditions for regeneration.
- Cloves: Cloves have mild analgesic and antiseptic effects that may temporarily numb and disinfect irritated gum tissues.
However, severe receding gums require professional treatment rather than only home remedies for substantive regrowth. Natural agents can provide supplementary healing support.
Receding gums: FAQ
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about receding gums:
Can receding gums regrow without surgery?
Mild gum recession may improve up to 1-2 millimeters without surgery using excellent oral hygiene and growth factor treatments. Moderate to severe cases require surgical grafting for significant regrowth of lost gum tissues.
How long does it take for receding gums to regrow after treatment?
With grafting surgery, it takes around 3-6 months for the transplanted gum tissue to fully integrate. Non-surgical options can take 3-9 months to see complete regrowth. Full gum regeneration may take up to 1 year.
Do receding gums ever grow back on their own?
If caught very early when the epithelial attachment remains, gums can potentially regrow 1-2 millimeters on their own. But considerable regrowth will not happen without proactive professional treatment.
What happens if you leave receding gums untreated?
Neglected receding gums will keep worsening over time. This leads to severe sensitivity, accelerated dental decay, loose/lost teeth, bone loss, and a host of other oral health issues.
Can you reverse receding gums naturally?
Proper oral care may help stabilize early recession but cannot reverse moderate-severe gum loss on its own. Dental procedures are required for considerable regrowth of destroyed gum tissues and bone. Natural remedies can support healing.