The causes and risks of tooth decay in dogs
Tooth decay, also known as dental caries, occurs when acids produced by plaque bacteria erode the enamel of a tooth. This causes minerals to be leached out of the enamel, resulting in a hole or “cavity” in the tooth.
Several factors can contribute to tooth decay in dogs:
Diet
- Feeding soft or sticky foods that cling to teeth increases plaque buildup. Hard kibble helps clean teeth.
- Carbohydrates like rice, pasta and bread can promote plaque. Look for low-carb dog foods.
- Sugary treats like milk bones also feed plaque bacteria. Offer dental chews instead.
Breed
- Small breeds with crowded teeth are more prone to dental problems.
- Brachycephalic (short-nosed) breeds tend to accumulate more plaque.
Age
- Plaque buildup occurs over time, so older dogs are more likely to develop decay.
Oral health care
- Lack of preventative dental care like brushing allows plaque to accumulate.
- Missing teeth over time puts more strain on remaining teeth.
Medical conditions
- Conditions that decrease saliva flow increase the risk for decay.
- Liver or kidney disease can also affect oral health.
Medications
- Some medications like antihistamines, diuretics and NSAIDs reduce saliva production.
Tooth decay not only damages the tooth itself, but can lead to serious health risks:
- Dental infections from cavities can enter the bloodstream.
- Tooth root abscesses are very painful.
- Missing teeth impair chewing and can cause nutritional deficits.
- Bacteria from decayed teeth seed infections in organs like the heart, kidneys and liver.
So if you notice any signs of dental disease in your dog like bad breath, yellow/brown tartar, red inflamed gums or loose teeth, seek veterinary care right away. The sooner tooth decay is addressed, the better the outcome.
Professional dental cleaning and extractions
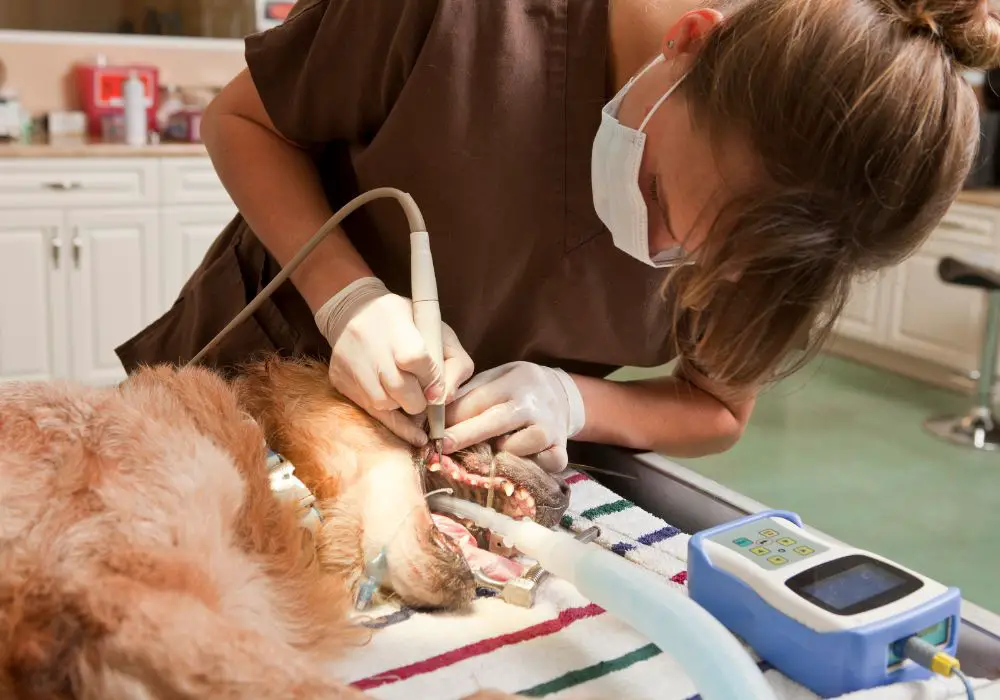
If your dog has advanced dental disease with loose, infected or painfully damaged teeth, a professional dental cleaning and tooth extractions are likely needed.
Your vet will perform pre-anesthetic bloodwork to ensure your dog is healthy enough for anesthesia. They will then:
- Place an IV catheter and intubate your dog to administer gas anesthesia
- Scale all plaque and tartar off the teeth above and below the gumline
- Probe every tooth to check for pockets, root exposure and abscesses
- Take dental x-rays to check for issues below the gumline
- Extract severely damaged or infected teeth as needed
Extractions are done as gently as possible using dental elevators and forceps. The vet sutures the gum where the tooth was removed and prescribes antibiotics and pain medication.
Professional dental cleanings and extractions, though expensive, are extremely important for your dog’s health. They stop dental pain, remove infection sources and allow your dog to comfortably chew again.
Aftercare for extractions
Proper aftercare following extractions helps your dog heal quickly and prevents complications:
Wound care
- Don’t allow rubbing or licking of extraction sites
- Apply cold compresses to minimize swelling
- Follow your vet’s wound care instructions
Activity restriction
- Limit exercise and play to allow gum healing
- Use a leash when going outside to prevent running/jumping
Medications
- Give all prescribed antibiotics and pain meds
- Use an e-collar if your dog won’t stop licking
Diet
- Feed soft foods for 7-10 days to avoid disturbing clots
- Mix food with water to make a “gruel”
- Avoid chews, bones, ice, etc. during initial healing
With proper at-home care following professional dental treatment, your dog’s mouth can return to full health and function. Be sure to follow up with your vet in 2 weeks to check healing.
Ongoing prevention and management

Getting your dog’s advanced dental disease treated is an important first step, but prevention at home is also key to maintaining good oral health long-term.
Brushing
- Brush teeth daily with dog-safe toothpaste
- Use a soft brush or finger brush sized for your dog
- Make it a positive experience with praise and rewards
Dental diets/chews
- Feeding kibble formulated to clean teeth helps scrape away plaque
- Offer specially designed dental chews to freshen breath and clean teeth
Water additives
- Add dental rinses to drinking water to reduce plaque bacteria
- Chlorhexidine and zinc gluconate are proven ingredients
Regular vet dental cleanings
- Even with home care, most dogs need annual cleanings under anesthesia
- Vets can monitor for developing issues and perform needed extractions
With vigilance and proactive steps take at home combined with professional veterinary care, you can effectively manage your dog’s oral health for a happy, healthy smile.
Importance of fixing tooth decay
Here are key reasons why fixing tooth decay in dogs through professional cleanings and extractions leads to improved health and wellbeing:
- Relieves pain – Dogs suffer greatly from untreated dental infections and damaged teeth. Extractions provide lasting pain relief.
- Allows normal eating – Missing or painful teeth make it hard for dogs to pick up and chew food properly. Removing problem teeth enables comfortable eating.
- Eliminates infection source – Bacteria from decay spread to organs via the bloodstream. Extracting infected teeth prevents this.
- Avoids tooth loss – Decay left untreated destroys tooth integrity. Timely treatment prevents unnecessary tooth loss.
- Enables thorough exam – Cleaning allows vets to fully assess all teeth and address issues promptly.
- Restores cheek/tongue function – Severely decayed teeth can rub and injure the cheeks and tongue. Removing these teeth improves function.
- Improves bad breath – Bacteria on rotting teeth cause foul odors. Extracting problem teeth and cleaning the rest ameliorates bad breath.
- Prolongs life – Dogs with untreated dental infections are at risk for kidney, liver and heart damage. Fixing decay improves health and longevity.
Risks of avoiding treatment
Conversely, delaying treatment of tooth decay leads to the following risks:
- Ongoing dental pain and associated behavior changes
- Inability to properly chew and nutritional deficits
- Progression to tooth root abscesses and bone infection
- Spread of bacteria to internal organs through the bloodstream
- Tooth loss and dysfunction
- Premature euthanasia due to suffering from dental disease
So allowing decay to go untreated seriously impacts quality of life and health in dogs. Prompt professional cleaning and extractions is the most compassionate and prudent choice.
Financial assistance options

For owners who cannot readily afford the cost of professional dental treatment, here are some options to look into:
- CareCredit – Offers special financing for veterinary care, including dental procedures. Applications can be completed online or at your vet’s office.
- Scratchpay – Another financing company where you can apply for a line of credit to cover treatment costs and then make fixed monthly payments.
- Non-profit organizations – Groups like the Pet Fund provide financial assistance for owners facing veterinary bills they cannot handle alone.
- Local vet school – Veterinary teaching hospitals sometimes offer dental services at reduced cost, provided you’re willing to have students do the procedures under supervision.
- Insurance claims – If you have pet insurance, dental diseases are often covered once you meet your deductible amount. File a claim to be reimbursed.
- Personal loan – In some cases, people take out small personal loans from their bank to pay for veterinary care. This should be considered carefully, however.
With some research and planning, there are options out there to help manage the investment required to fix tooth decay and restore your dog’s oral health.
FAQ about fixing tooth decay in dogs
Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about treating tooth decay in dogs:
Are extractions absolutely necessary for tooth decay?
In most cases, yes. Decay that reaches the pulp and root of teeth is extremely painful and can’t be reversed or filled the way human cavities can. Extraction is usually the only option for providing lasting relief and preventing complications.
Will my dog be in a lot of pain after extractions?
Your vet will prescribe strong pain medication to keep your dog comfortable after surgery. Some mild discomfort is expected for a few days but your dog should not suffer. Alert your vet if you dog seems to be in severe pain.
How long does it take dogs to recover from losing multiple teeth?
With proper aftercare, your dog should adjust to eating and chewing normally within 1-2 weeks after extractions. The gum tissue takes 4-8 weeks to fully heal. Overall recovery is quick and most dogs feel much better after having painful, infected teeth removed.
What home care is required after dental extractions?
Follow your vet’s home care instructions closely, especially for wound care, activity restriction and medication administration. Also feed soft foods for 7-10 days, prevent vigorous chewing, and allow 2 weeks for recheck appointment to ensure proper healing.
Can missed teeth eventually cause problems for dogs?
Yes, having multiple missing teeth over time can allow remaining teeth to drift or overgrow, cause mouth pain and trauma, and make chewing less efficient. Regular dental exams help monitor this. Artificial crowns can also replace missing teeth in some cases.
Why does tooth decay seem to happen so fast with dogs?
Dogs’ teeth are structured differently than human teeth. The enamel coating them is much thinner and more easily eroded by plaque acids. So once tartar has built up, caries can progress to the pulp and root very quickly in dogs. That’s why early prevention and cleaning is so important for them.
Conclusion
Tooth decay leading to significant destruction is unfortunately quite common in dogs. But professional dental cleanings and extractions can effectively treat existing disease, relieve related pain and complications, and give your dog a healthy mouth again. With vigilance and preventive home care going forward, your dog’s smile and oral health can be maintained for the long run.