Radiographs, also known as X-rays, have been used in dentistry for decades to diagnose dental problems and plan treatments. However, radiographs can also be used to determine a person’s age by examining the teeth. This is particularly useful in forensic dentistry, where age determination is crucial in identifying human remains.
Teeth are one of the least affected parts of the body by the taphonomic process, making them a reliable source for age estimation. Dental age estimation is based on the degree of formation and eruption of teeth, which can be observed on radiographs. The assessment of dental age involves comparing the observed developmental stages of the teeth to established reference data to estimate the person’s age.
There are several methods for dental age estimation using radiographs, including the Demirjian method, the Willems method, and the Kvaal method. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of method depends on the availability of teeth and the specific population being studied. Overall, radiographs provide an accurate and non-invasive method for age estimation in forensic dentistry.
Basics of Dental Development

Dental development is a continuous process that begins during fetal development and continues throughout childhood and adolescence until the teeth reach their final form and position in the mouth. Understanding the basics of dental development is essential for using radiographs to determine age.
Tooth Eruption
Tooth eruption is the process by which teeth emerge from the gums and become visible in the mouth. The timing and sequence of tooth eruption varies among individuals, but the general pattern is consistent. The primary teeth, also known as baby teeth, typically erupt between 6 and 30 months of age. The permanent teeth begin to erupt around age 6 and continue until the late teens or early twenties.
Tooth Maturation
Tooth maturation is the process by which teeth develop and reach their final form and position in the mouth. The degree of tooth maturation can be assessed by examining the degree of calcification of the tooth and the stage of root formation. Tooth maturation is an important factor in determining age using radiographs.
Radiographs can be used to assess tooth development and maturation by examining the degree of calcification of the tooth and the stage of root formation. The degree of calcification of the tooth can be assessed by examining the density of the tooth on the radiograph. The stage of root formation can be assessed by examining the length and shape of the root on the radiograph.
In conclusion, understanding the basics of dental development is essential for using radiographs to determine age. Tooth eruption and tooth maturation are important factors that can be assessed using radiographs. By examining the degree of calcification of the tooth and the stage of root formation, radiographs can be used to estimate the age of an individual with a high degree of accuracy.
Radiographic Techniques in Age Determination
Radiographic techniques can be used to determine the age of an individual by analyzing the development and eruption of teeth. Dental age is an important parameter, especially in forensic dentistry, for estimating the chronological age of an individual. Here are some radiographic techniques used for age determination:
Orthopantomogram (OPG)
Orthopantomogram (OPG) is a panoramic radiograph that captures the entire dentition, including the developing teeth. The OPG is a useful tool for assessing the dental age of an individual as it shows the stage of development of the teeth. The OPG can be used to determine the age of an individual by comparing the stage of development of the teeth with a reference chart.
Periapical Radiographs
Periapical radiographs are used to evaluate the root development of teeth. The stage of root development can be used to determine the age of an individual. The root development of teeth can be compared to a reference chart to determine the age of an individual.
Bitewing Radiographs
Bitewing radiographs can be used to assess the stage of development of the permanent molars. The stage of development of the permanent molars can be used to determine the age of an individual. The stage of development of the permanent molars can be compared to a reference chart to determine the age of an individual.
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT) can be used to evaluate the stage of development of the teeth. CBCT can provide a three-dimensional image of the teeth, which can be used to assess the stage of development of the teeth. The stage of development of the teeth can be compared to a reference chart to determine the age of an individual.
Radiographic techniques are an important tool in age determination. The stage of development of the teeth can be used to determine the age of an individual. Radiographic techniques can provide a non-invasive and accurate method of age determination.
Application of Dental Radiographs in Age Estimation
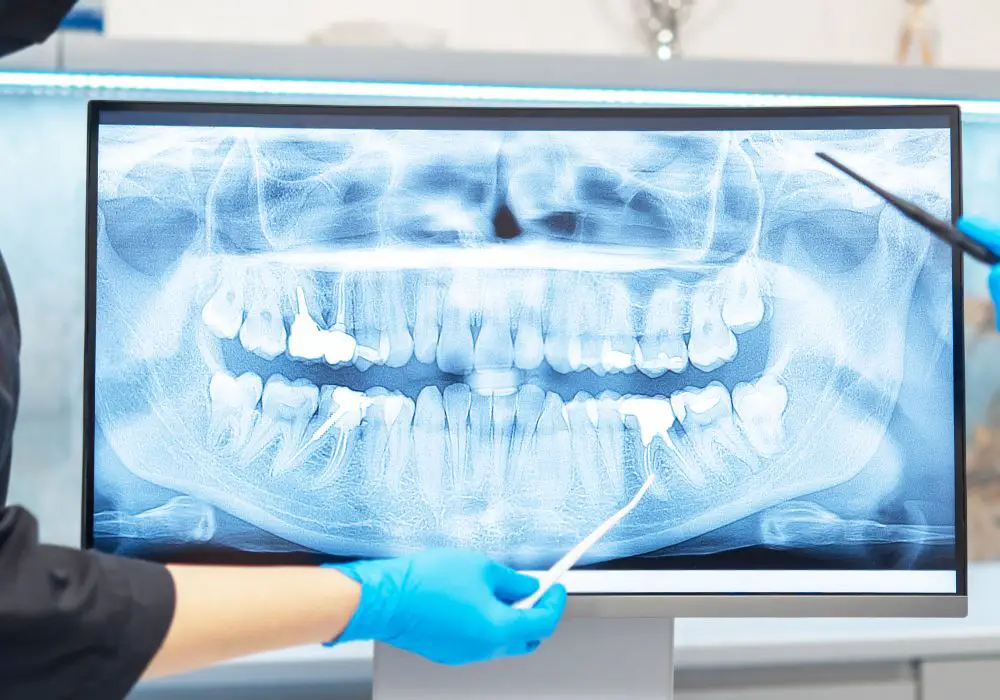
Dental radiographs are commonly used in forensic dentistry to estimate the age of an individual. Radiographs provide a non-invasive and reliable method of age estimation based on the development and eruption of teeth. Dental radiographs can be used to estimate the age of both children and adults. In this section, we will discuss how dental radiographs can be used to estimate age in primary and permanent teeth.
Primary Teeth
Primary teeth are the first set of teeth that erupt in children, and they are usually lost by the age of 12. Dental radiographs can be used to estimate the age of a child based on the development and eruption of their primary teeth. The following table shows the average age of eruption of primary teeth:
| Tooth | Average Age of Eruption |
|---|---|
| A | 6 months |
| B | 8 months |
| C | 10 months |
| D | 14 months |
| E | 18 months |
| F | 2 years |
| G | 2.5 years |
| H | 3 years |
Based on the development and eruption of primary teeth, dental radiographs can be used to estimate the age of a child with an accuracy of +/- 6 months.
Permanent Teeth
Permanent teeth are the second set of teeth that erupt in children, and they are usually fully erupted by the age of 21. Dental radiographs can be used to estimate the age of an individual based on the development and eruption of their permanent teeth. The following table shows the average age of eruption of permanent teeth:
| Tooth | Average Age of Eruption |
|---|---|
| 1 | 6 years |
| 2 | 7 years |
| 3 | 9 years |
| 4 | 10 years |
| 5 | 11 years |
| 6 | 12 years |
| 7 | 13 years |
| 8 | 14 years |
| 9 | 6-7 years |
| 10 | 11-12 years |
| 11 | 12-13 years |
| 12 | 6-7 years |
| 13 | 11-12 years |
| 14 | 12-13 years |
| 15 | 6-7 years |
| 16 | 10-11 years |
| 17 | 12-13 years |
| 18 | 17-25 years |
| 19 | 7-9 years |
| 20 | 10-12 years |
| 21 | 6-7 years |
| 22 | 9-10 years |
| 23 | 11-12 years |
| 24 | 6-7 years |
| 25 | 9-10 years |
| 26 | 10-12 years |
| 27 | 6-7 years |
| 28 | 9-10 years |
| 29 | 11-12 years |
| 30 | 6-7 years |
| 31 | 10-12 years |
| 32 | 17-25 years |
Based on the development and eruption of permanent teeth, dental radiographs can be used to estimate the age of an individual with an accuracy of +/- 2 years.
In conclusion, dental radiographs are an important tool in age estimation, particularly in forensic dentistry. By analyzing the development and eruption of primary and permanent teeth, dental radiographs can provide an accurate estimate of an individual’s age.
Challenges and Limitations of Radiographic Age Determination
Radiographic age determination has several challenges and limitations that must be taken into consideration. Here are some of the most significant ones:
Variation in Tooth Development
Tooth development can vary significantly between individuals. Therefore, it can be challenging to determine the exact age of an individual accurately. The degree of variation depends on factors such as genetics, nutrition, and overall health.
Inaccuracy of Radiographic Techniques
Radiographic techniques used to determine age can be inaccurate, especially if the radiographs are of low quality or taken using outdated equipment. The reliability of the technique can also be affected by the experience and expertise of the radiologist.
Limited Age Range
Radiographic age determination is most reliable within a limited age range, typically between 15 and 25 years. Beyond this range, the accuracy of the method decreases significantly. Therefore, it is not recommended to use radiographic techniques to determine the age of individuals older than 25 years.
Ethical Concerns
Radiographic age determination involves exposing individuals to radiation, which can pose health risks. Therefore, it is essential to consider the ethical implications of using radiographic techniques to determine age, especially in cases involving minors.
Legal Issues
Radiographic age determination is not always admissible in court as evidence. Therefore, it is crucial to consider the legal implications of using radiographic techniques to determine age, especially in cases involving legal disputes.
Overall, radiographic age determination can be a useful tool in determining the age of individuals, but it must be used with caution, taking into consideration the challenges and limitations mentioned above.
Future Directions in Radiographic Age Estimation
Radiographic age estimation has come a long way since its inception. With the advent of new technologies and techniques, the field is poised to make further strides in the future.
One area of research that shows promise is the use of 3D imaging for age estimation. Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) is a technique that can generate high-resolution 3D images of the teeth and jaws. This technology has the potential to provide more accurate age estimates than traditional 2D radiographs.
Another area of research that is gaining attention is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) for age estimation. Deep learning algorithms can analyze large datasets of radiographic images to identify patterns and make predictions. This technology has already shown promise in other areas of medical imaging and could be applied to radiographic age estimation in the future.
In addition to technological advancements, there is also a need for standardized protocols and guidelines for radiographic age estimation. This will help ensure that age estimates are consistent and accurate across different practitioners and settings.
Finally, there is a need for further research to validate and refine existing age estimation techniques. This includes studies to determine the accuracy and reliability of different radiographic features and to identify factors that may affect age estimation accuracy.
Overall, the future of radiographic age estimation looks bright, with new technologies and techniques on the horizon and a growing emphasis on standardization and validation.
Frequently Asked Questions
How can dental radiographs estimate age?
Dental radiographs can estimate age by analyzing the degree of formation of crown and root structures, as well as the sequence and stages of eruption. By comparing the dental age to the chronological age, an estimation of the individual’s age can be made. This method is particularly useful when other methods of age estimation are not possible.
What is the process for comparing antemortem and postmortem radiographs?
The process for comparing antemortem and postmortem radiographs involves a thorough analysis of the dental radiographs to identify unique features and characteristics. These features are then compared between the antemortem and postmortem radiographs to determine if they belong to the same individual. This process requires specialized training and expertise in forensic dentistry.
What can dental radiographs detect?
Dental radiographs can detect a range of oral diseases and conditions, including tooth decay, gum disease, and oral cancer. They can also be used to identify fractures, infections, and abnormalities in the teeth and jaw. In forensic dentistry, dental radiographs can be used to identify individuals and estimate their age at the time of death.
How are teeth used to estimate age of the deceased?
Teeth can be used to estimate the age of the deceased by analyzing the degree of formation of crown and root structures, as well as the sequence and stages of eruption. This method is particularly useful when other methods of age estimation are not possible, such as in cases where there are no soft tissues or bones available for analysis.
What is the difference between chronological age and dental age?
Chronological age refers to the actual age of the individual, while dental age refers to the estimated age based on the degree of formation of crown and root structures, as well as the sequence and stages of eruption. Dental age can be used to estimate the chronological age of an individual, particularly in cases where other methods of age estimation are not possible.
What is the role of forensic radiology in dentistry?
Forensic radiology plays a critical role in dentistry by providing a means to identify individuals and estimate their age at the time of death. Dental radiographs can be used to compare antemortem and postmortem images to determine if they belong to the same individual, and to estimate the age of the deceased. This information can be used in criminal investigations and in the identification of victims of disasters or mass casualties.